This site is the archived OWASP Foundation Wiki and is no longer accepting Account Requests.
To view the new OWASP Foundation website, please visit https://owasp.org
Difference between revisions of "Codereview-Authorization"
(→Vulnerable Patterns for Authorization issues) |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{LinkBar | |
| − | + | | useprev=PrevLink | prev=Codereview-Authentication | lblprev=Authentication | |
| + | | usemain=MainLink | main=OWASP Code Review Guide Table of Contents | lblmain=Table of Contents | ||
| + | | usenext=NextLink | next=Codereview-Session-Management | lblnext=Session Management | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| Line 12: | Line 16: | ||
Authorization is a very bespoke area in application development. It can be implemented via a lookup table in a users' session which is loaded upon successful authentication. It could be a real-time interrogation of a backend LDAP or database system upon each request. | Authorization is a very bespoke area in application development. It can be implemented via a lookup table in a users' session which is loaded upon successful authentication. It could be a real-time interrogation of a backend LDAP or database system upon each request. | ||
| − | ==How to Locate the Potentially Vulnerable Code == | + | ===How to Locate the Potentially Vulnerable Code === |
| − | Business logic errors are key areas in which to look for authorization errors. Areas | + | Business logic errors are key areas in which to look for authorization errors. Areas where authorization checks are performed are worth looking at. Logical conditional cases are areas for examination, such as malformed logic: |
if user.equals("NormalUser"){ | if user.equals("NormalUser"){ | ||
| Line 27: | Line 31: | ||
We have an additional issue here: Information disclosure, as the include file might be called directly and disclose application functionality, as ASP code will not be executed given that Inc extension is not recognized. | We have an additional issue here: Information disclosure, as the include file might be called directly and disclose application functionality, as ASP code will not be executed given that Inc extension is not recognized. | ||
| − | == Vulnerable Patterns for Authorization Issues == | + | === Vulnerable Patterns for Authorization Issues === |
One area of examination is to see if the authorization model simply relies on not displaying certain functions which the user has not authorization to use, security by obscurity in effect. If a crawl can be performed on the application, links may be discovered which are not on the users’ GUI. Simple HTTP Get requests can uncover "Hidden" links. Obviously, a map on the server-side should be used to see if one is authorized to perform a task, and we should not rely on the GUI "hiding" buttons and links. | One area of examination is to see if the authorization model simply relies on not displaying certain functions which the user has not authorization to use, security by obscurity in effect. If a crawl can be performed on the application, links may be discovered which are not on the users’ GUI. Simple HTTP Get requests can uncover "Hidden" links. Obviously, a map on the server-side should be used to see if one is authorized to perform a task, and we should not rely on the GUI "hiding" buttons and links. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 37: | ||
document.form.adminfunction.disabled=true; | document.form.adminfunction.disabled=true; | ||
| − | |||
<form action="./doAdminFunction.asp"> | <form action="./doAdminFunction.asp"> | ||
| Line 42: | Line 45: | ||
'''The Database:''' The account used by the application to access the database. Ensure least privilege is in effect. | '''The Database:''' The account used by the application to access the database. Ensure least privilege is in effect. | ||
| − | == | + | ==ASP.NET: (web.config)== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The <authorization> element controls ASP.NET URL authorization and the accessibility to gain access to specific folders, pages, and resources by users/web clients. Make sure that only authenticated users are authorized to see/visit certain pages. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
<system.web> | <system.web> | ||
<authorization> | <authorization> | ||
| Line 56: | Line 55: | ||
</system.web> | </system.web> | ||
| − | + | The roleManager Element in ASP.NET 2.0 is used to assist in managing roles within the framework. It assists the developer as not as much bespoke code needs to be developed. In web.config, to see if it is enabled check: | |
| − | The roleManager Element in ASP.NET 2.0 is used to assist in managing roles within the framework. It assists the developer as not as much bespoke code needs to be developed. | ||
| − | In web.config, to see if it is enabled check: | ||
<system.web> | <system.web> | ||
| Line 66: | Line 63: | ||
</system.web> | </system.web> | ||
| − | + | ==Apache 1.3== | |
In Apache 1.3 there is a file called httpd. Access control can be implemented from here in the form of the ''Allow'' and ''Deny'' directives. | In Apache 1.3 there is a file called httpd. Access control can be implemented from here in the form of the ''Allow'' and ''Deny'' directives. | ||
| − | ''allow from address'' is the usage where address is the IP address or domain name to apply access to. | + | ''allow from address'' is the usage where address is the IP address or domain name to apply access to. Note this granularity is host level granularity. |
| − | Note this granularity is host level granularity. | ||
deny from 124.20.0.249 denies access to that IP. | deny from 124.20.0.249 denies access to that IP. | ||
| Line 76: | Line 72: | ||
Order ensures that the 'order'of access is observed. | Order ensures that the 'order'of access is observed. | ||
| − | Order Deny,Allow | + | Order Deny,Allow<br> |
| − | Deny from all | + | Deny from all <br> |
| − | Allow from owasp.org | + | Allow from owasp.org <br> |
Above, all is denied apart from owasp.org | Above, all is denied apart from owasp.org | ||
| Line 84: | Line 80: | ||
To move the authorization to the user level in apache we can use the ''Satisfy'' directive. | To move the authorization to the user level in apache we can use the ''Satisfy'' directive. | ||
| − | ==Good Example== | + | ===Good Example=== |
| − | Check | + | Check authorization upon every user request. |
| − | |||
String action = request.getParameter("action") | String action = request.getParameter("action") | ||
| − | if (action | + | if (action.equals("doStuff")){ |
boolean permit = session.authTable.isAuthorised(action); // check table if authoirsed to do action | boolean permit = session.authTable.isAuthorised(action); // check table if authoirsed to do action | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 99: | Line 94: | ||
} | } | ||
| − | + | '''Authorization being performed upon all requests from external entities''' | |
| + | |||
[[Image:Authorisation.jpg]] | [[Image:Authorisation.jpg]] | ||
| − | ==Bad Example== | + | ===Bad Example=== |
| + | |||
| + | Building the GUI based on the user’s authorization. "If he can’t see the control he won’t be able to use it" | ||
| − | + | Common enough error. If a user has the URL, the functionality can still be called. This is due to no authorization check being performed upon every HTTP request. | |
| − | |||
==Related Vulnerabilities== | ==Related Vulnerabilities== | ||
*[[Reviewing Code for OS Injection]] | *[[Reviewing Code for OS Injection]] | ||
| − | + | Operating System injection can be used to totally ignore authorisation constraints. Access to the underlying host is a key objective of system breach. The application is simply a conduit for access to data. | |
*[[Reviewing Code for SQL Injection]] | *[[Reviewing Code for SQL Injection]] | ||
| − | + | SQL injection can be used to circumvent authorisation. Again, systems are breached to obtain underlying data, they are not breached for the applications themselves. SQL injection is in essence accessing the data via an "out of band" channel not intended by the application. | |
*[[Reviewing Code for Data Validation]] | *[[Reviewing Code for Data Validation]] | ||
| − | + | The root of all evil - Need we say more :) | |
*[[Reviewing The Secure Code Environment]] | *[[Reviewing The Secure Code Environment]] | ||
| − | + | Insecure class files, folders in deployment may be used to attack an application outside the actual application itself. | |
*[[Reviewing Code for Session Integrity issues]] | *[[Reviewing Code for Session Integrity issues]] | ||
| − | + | Impersonation can obviously be used to gain unauthorised privilege. | |
*[[Reviewing Code for Race Conditions]] | *[[Reviewing Code for Race Conditions]] | ||
| − | + | In a multi user, multi-threaded environment thread safety is important as one may obtain another individuals session in error. | |
| + | |||
| + | {{LinkBar | ||
| + | | useprev=PrevLink | prev=Codereview-Authentication | lblprev=Authentication | ||
| + | | usemain=MainLink | main=OWASP Code Review Guide Table of Contents | lblmain=Table of Contents | ||
| + | | usenext=NextLink | next=Codereview-Session-Management | lblnext=Session Management | ||
| + | }} | ||
[[Category:OWASP Code Review Project]] | [[Category:OWASP Code Review Project]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Access Control]] |
Latest revision as of 22:32, 26 February 2016
Introduction
Authorization issues cover a wide array of layers in a web application; from the functional authorization of a user to gain access to a particular function of the application at the application layer, to the Database access authorization and least privilege issues at the persistence layer. So what to look for when performing a code review? From an attack perspective, the most common issues are a result of curiosity and also exploitation of vulnerabilities such as SQL injection.
Example: A Database account used by an application with system/admin access upon which the application was vulnerable to SQL injection would result in a higher degree of impact rather than the same vulnerable application with a least privilege database account.
Authorization is key in multiuser environments where user data should be segregated. Different clients/users should not see other clients' data (Horizontal authorization). Authorization can also be used to restrict functionality to a subset of users. "Super users" would have extra admin functionality that a "regular user" would not have access to (Vertical authorization).
Authorization is a very bespoke area in application development. It can be implemented via a lookup table in a users' session which is loaded upon successful authentication. It could be a real-time interrogation of a backend LDAP or database system upon each request.
How to Locate the Potentially Vulnerable Code
Business logic errors are key areas in which to look for authorization errors. Areas where authorization checks are performed are worth looking at. Logical conditional cases are areas for examination, such as malformed logic:
if user.equals("NormalUser"){
grantUser(Normal_Permissions);
}else{ //user must be admin/super
grantUser("Super_Persmissions);
}
For classic ASP pages, authorization is usually performed using include files that contain the access control validation and restrictions. So you usually will look for something like
<!--#include file="ValidateUser.inc"-->
We have an additional issue here: Information disclosure, as the include file might be called directly and disclose application functionality, as ASP code will not be executed given that Inc extension is not recognized.
Vulnerable Patterns for Authorization Issues
One area of examination is to see if the authorization model simply relies on not displaying certain functions which the user has not authorization to use, security by obscurity in effect. If a crawl can be performed on the application, links may be discovered which are not on the users’ GUI. Simple HTTP Get requests can uncover "Hidden" links. Obviously, a map on the server-side should be used to see if one is authorized to perform a task, and we should not rely on the GUI "hiding" buttons and links.
Disabling buttons on the client side, due to the authorization level of user, shall not prevent the user from executing the action relating to the button.
document.form.adminfunction.disabled=true; <form action="./doAdminFunction.asp">
By simply saving the page locally, and editing the disabled=true to disabled=false and adding the absolute form action, one can proceed to activate the disabled button.
HotSpots
The Database: The account used by the application to access the database. Ensure least privilege is in effect.
ASP.NET: (web.config)
The <authorization> element controls ASP.NET URL authorization and the accessibility to gain access to specific folders, pages, and resources by users/web clients. Make sure that only authenticated users are authorized to see/visit certain pages.
<system.web> <authorization> <deny users="?"/> <-- Anonymous users are denied access. Users must be authenticated. </authorization> </system.web>
The roleManager Element in ASP.NET 2.0 is used to assist in managing roles within the framework. It assists the developer as not as much bespoke code needs to be developed. In web.config, to see if it is enabled check:
<system.web> .......... <roleManager enabled="true|false" <providers>...</providers> </roleManager> .......... </system.web>
Apache 1.3
In Apache 1.3 there is a file called httpd. Access control can be implemented from here in the form of the Allow and Deny directives. allow from address is the usage where address is the IP address or domain name to apply access to. Note this granularity is host level granularity.
deny from 124.20.0.249 denies access to that IP.
Order ensures that the 'order'of access is observed.
Order Deny,Allow
Deny from all
Allow from owasp.org
Above, all is denied apart from owasp.org
To move the authorization to the user level in apache we can use the Satisfy directive.
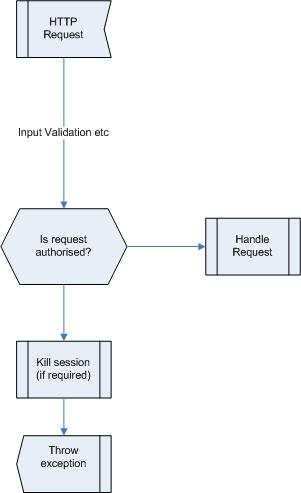
Good Example
Check authorization upon every user request.
String action = request.getParameter("action")
if (action.equals("doStuff")){
boolean permit = session.authTable.isAuthorised(action); // check table if authoirsed to do action
}
if (permit){
doStuff();
}else{
throw new (InvalidRequestException("Unauthorised request"); // inform user of no authorisation
session.invalidate(); // Kill session
}
Authorization being performed upon all requests from external entities
Bad Example
Building the GUI based on the user’s authorization. "If he can’t see the control he won’t be able to use it"
Common enough error. If a user has the URL, the functionality can still be called. This is due to no authorization check being performed upon every HTTP request.
Related Vulnerabilities
Operating System injection can be used to totally ignore authorisation constraints. Access to the underlying host is a key objective of system breach. The application is simply a conduit for access to data.
SQL injection can be used to circumvent authorisation. Again, systems are breached to obtain underlying data, they are not breached for the applications themselves. SQL injection is in essence accessing the data via an "out of band" channel not intended by the application.
The root of all evil - Need we say more :)
Insecure class files, folders in deployment may be used to attack an application outside the actual application itself.
Impersonation can obviously be used to gain unauthorised privilege.
In a multi user, multi-threaded environment thread safety is important as one may obtain another individuals session in error.