|
|
| Line 8: |
Line 8: |
| | <li>[https://www.owasp.org/index.php?title=OWASP_Security_Integration_System#What_is_the_Secure_code_assurance_tool What is the Secure code assurance tool]</li> | | <li>[https://www.owasp.org/index.php?title=OWASP_Security_Integration_System#What_is_the_Secure_code_assurance_tool What is the Secure code assurance tool]</li> |
| | <li>[https://www.owasp.org/index.php?title=OWASP_Security_Integration_System#Description Description of the Secure code assurance tool (SCAT) and how it builds, verifies and assures secure software]</li> | | <li>[https://www.owasp.org/index.php?title=OWASP_Security_Integration_System#Description Description of the Secure code assurance tool (SCAT) and how it builds, verifies and assures secure software]</li> |
| − | <li>[https://www.owasp.org/index.php?title=OWASP_Security_Integration_System#See_how_developers_use_SCAT See how the SCAT single purpose screens integrate security into each of the SDLC phases]</li> | + | <li>[https://www.owasp.org/index.php?title=OWASP_Security_Integration_System#See_how_developers_use_SCAT See how development teams use SCAT]</li> |
| | <li>[https://www.owasp.org/index.php?title=OWASP_Security_Integration_System#Preparation_phase How to import client specific risks, security requirements and tests]</li> | | <li>[https://www.owasp.org/index.php?title=OWASP_Security_Integration_System#Preparation_phase How to import client specific risks, security requirements and tests]</li> |
| | </ol> | | </ol> |
Table of content
- What is the Secure code assurance tool
- Description of the Secure code assurance tool (SCAT) and how it builds, verifies and assures secure software
- See how development teams use SCAT
- How to import client specific risks, security requirements and tests
What is the Secure code assurance tool
What does SCAT not do
- SCAT is not a point in time security verification tool for detecting vulnerabilities after development
What does SCAT do
- SCAT is a process integrity tool implementing a consistent, authorized and auditable software development process
- SCAT’s primary objective is proving security controls operate efficiently over a period of time and preventing vulnerabilities from reaching or recurring in production
- SCAT uses free OWASP SAST and DAST tools (point in time security verification tool)
- These are deployed in local docker containers as on demand verification tools, that development teams can run on localhost for immediate pre-checkin verification
Description
- SCAT is used by inhouse and third party development teams to build, verify and assure secure software
- Build: SCAT uses code level guidance to clearly instructs developers on how to correctly implement security requirements
- Verify: SCAT uses a combination of ZAP basic scans and security test plans to verify correct implementation of security requirements
- Assure: SCAT centrally stores and publishes evidence of secure development and testing as an audit trail. Providing traceability through requirements and proving a secure development process
- SCAT is a simple 5 screen MVC, C# web application with a small footprint that can be deployed without further complicating development environment
- SCAT is part of three domains to consider when securing software development. I've detailed the other domains in an article that will be published in the Nov/Dec issue of the ISC2 magazine, I will add a link here after publication.
See how developers use SCAT
See below how the Secure code assurance tool integrates security into software development phases
- Sprint planning phase
Objective: Enabling developers to generate security requirements before development begins
- Developers use the Identify risks screen to
- Select the critical function to developing/changing
- Identify the technologies used
- Automatically generate the security requirements and tests
See how to use the tools and its internal mapping to generate security requirements
- Product owners use the Secure code requirements screen to
- Create an audit trail to store evidence of secure development
- Create Jira tickets for requirements and tests to manage work
- Development phase
Objective: Consistent and correct implementation of security requirements across all teams
- Secure code review phase
Objective: Consistent and correct implementation of security requirements
- Testing phase
Objective: Guide the secure testing process
- Approval phase
Objective: Streamline the approval and audit process
- Risk management
Objective: Enable risk managers to prioritise, plan and monitor mitigation efforts
- Risk managers use the Application risk exposure screen to
- View each application critical function and the associated risks
- Identify where mitigation effort is required by viewing which risks require security requirements
- Identify where development effort is required by viewing which security requirements need secure code blocks
- Identify where extra testing effort is required by viewing which risks require security test plans
See how the Application landscape overview screen informs risk based decision making
Preparation phase
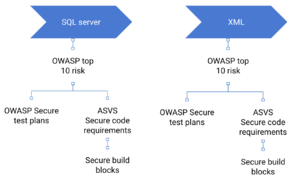
When developing secure software we need to consider both standard secure code and client specific architectural requirements
Standard secure code requirements
- SCAT comes out the box with a standard OWASP secure code requirements map. This mapping need to be modified to the specific organisation requirements
- Information security and development team use the Internal mapping screen to
- Map the security requirements to OWASP risks
- Map organisation approved secure code blocks to security requirements
- Map security test plans to OWASP risks
See how to setup the SCAT's internal mapping
Client specific architectural requirements
- To generate these requirements we perform a risk assessment on client application landscape and identify
- Critical applications and functions
- Risk associated with each critical application function
- Architectural security requirements to secure each critical application functions
- Client specific secure code blocks to implement security requirements
- Secure test plans to verify risk has been mitigated
- Tool administrators use the Internal mapping screen to
- Create json files of the organisation specific risks, security requirements, secure code blocks and tests
- Import these into the SCAT
See how to import organisations specific risks, security requirements, secure code blocks and tests
How does the SCAT implement first line of defence
Promoting compliance to security requirements
- Understand the security requirement: The tool maintains the following internal mapping allowing organisations to translate complex security requirements into code level and testing guidance
- Risks mapped to technologies and secure code requirements
- Secure code requirements (OWASP ASVS) mapped to secure code building block
- Secure test plans (OWASP testing guide) mapped to risks
- The second mapping is lifted from OWASP secure knowledge framework and duplicated in the SCAT. I hope to link with the SKF and remove the duplicate functionality from the SCAT tool
- Verify understanding: The tool also makes use of OWASP ZAP basic scan to scan localhost for vulnerabilities, confirming the correct implementation of security requirements
Minimising the impact of audit and assurance
- In the testing and approval phase SCAT allows testers to stores testing evidence against the critical application function and its associated risk. Providing traceability through requirements and centrally storing and publishing test evidence
Informing risk based decision making
- For each application critical function, SCAT shows
- The risks that impact that application critical function
- Security requirements and secure code block to protect against the risk
- Test evidence proving risk has been mitigated to within tolerance
- Allowing risk teams see levels of exposure, easily compare it to tolerance levels. And prioritise and coordinate mitigation activities across teams and the whole application landscape
Integrating security into the software development process
- SCAT wraps security theory, best practices and requirements into set of single purpose security screens. Then plots each of those screens to a specific software development phase
- Plotting security screens to specific software development phases provides development teams with concise information when and how they need it
Licensing
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the link GNU Affero General Public License 3.0 as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
Project Resources
[Installation Package]
[Source Code]
Project Leader
Michael Bergman
Classifications
|