This site is the archived OWASP Foundation Wiki and is no longer accepting Account Requests.
To view the new OWASP Foundation website, please visit https://owasp.org
OWASP Security Integration System
What is the Secure code assurance tool (SCAT)
What SCAT does not do
What SCAT does do
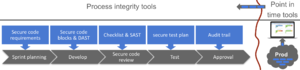
Process integrity tool vs point in time security verification tool
Tools and SDLC
Build, Verify Assure
Low levels of compliance
Compliance and assurance seen as blockers
Duplication of effort and inconsistent implementation
See below how the Secure code assurance tool integrates security into software development phases Sprint planning phaseObjective: Ensures security requirements are understood
Development phaseObjective: Ensure correct implementation of security requirements
Secure code review phaseObjective: Ensure correct implementation of security requirements
Testing phaseObjective: Ensure valid security testing
Approval phaseObjective: Streamline the approval and audit process
Risk managementObjective: Enable risk managers to prioritise, plan and monitor mitigation efforts
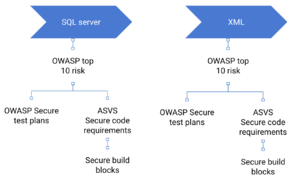
When developing secure software we need to consider both standard secure code and client specific architectural requirements Standard secure code requirements
Client specific architectural requirements
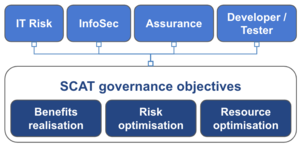
SCAT has the following governance objectives implemented by the following “first line of defense” functions Benefits realisation: Enabling development teams to deliver at speedRisk optimisation: Minimise the negative and maximise the positive consequencesResource optimisation: Predictable, repeatable and consistent level of security across all teams
Promoting compliance to security requirements
Minimising the impact of audit and assurance
Informing risk based decision making
Integrating security into the software development process
LicensingThis program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the link GNU Affero General Public License 3.0 as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version. Project Resources[Installation Package] [Source Code] Project LeaderClassifications
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||