|
Instructions are in RED text and should be removed from your document by deleting the text with the span tags. This document is intended to serve as an example of what is required of an OWASP project wiki page. The text in red serves as instructions, while the text in black serves as an example. Text in black is expected to be replaced entirely with information specific to your OWASP project.
Project About
PROJECT INFO
What does this OWASP project offer you?
|
RELEASE(S) INFO
What releases are available for this project?
|
| what
|
is this project?
|
| Name: Software Integration System
|
| Purpose: N/A
|
| License: N/A
|
| who
|
is working on this project?
|
| Project Leader(s):
|
| how
|
can you learn more?
|
| Project Pamphlet: Not Yet Created
|
| Project Presentation:
|
| Mailing list: N/A
|
| Project Roadmap: Not Yet Created
|
| Key Contacts
|
|
- Contact Michael Bergman @ to contribute to this project
- Contact Michael Bergman @ to review or sponsor this project
|
|
|
OWASP Tool Project Template
This section should include an overview of what the project is, why the project was started, and what security issue is being addressed by the project deliverable.
Introduction
Secure software development has a number of stakeholders.
- IT risk: I need to know where my highest risks are, so I can focus on mitigating these
- Information security: I need to generate a list f security requirements to protect against vulnerabilities
- Compliance and Assurance: I need to ensure the code meets security requirements and we have evidence proving that
- Business: I need to get the functionality to the market before our competitors
- Development teams: I need to do all of the above and within a two week sprint cycle :-)
How these stakeholder requirements be met
For every development cycle
- IT risk: Needs to understand the functional requirement and identify the risks associated with implementing it
- Information security: Needs to understand the technology behind the functional requirement and its associated risks. Then generate a list of security requirements to protect the technology against exploitation
- Development teams: Need to implement the technology, test it and record evidence proving the security requirements are met and
- Approvers: Need to review testing evidence against the organisations risk tolerance levels. Then accept the risk associate with the functional requirement by approving the release
- Compliance and Assurance: Need to review the testing evidence collected by the development teams and verify its consistency, traceability and quality
Why is it so hard to meet these stakeholder requirements?
- Vast body of knowledge: Development, security, risk, compliance and assurance teams need to combine their GDPR, ISO, risk tolerances level, OWASP ASVS, security testing, JAVA and .Net knowledge, filter it, and apply it to every critical functional requirement
- Complex environments: Securing rapidly evolving development languages, technologies and deployment environments requires constant effort and strains already scares resources
- Further compounding the problem is the fact that most other organisational processes have a first line of defence making sure all controls are understood and integrated into the process
- Software development process: Unless your organisation is gifted with budget and resources the software development process does not have a first line of defence
The lack of a dedicated fist line of defence and their control integration function all to often results in a a 50 page security policy being dumped on the developers desk with the comment "Implement this please"
What will the role of a first line of defence be in the software development process:
- Understand GDPR, ISO, risk tolerance level, OWASP ASVS, security testing, JAVA and .Net and most importantly know which pf these apply to which functional requirement
- Generates security requirements before coding begins
- Guiding developers towards correctly implementing security requirements
- Check for compliance to security requirements
- Guiding testers towards correctly verifying security requirements are met
- Centrally store testing evidence to speeding up the approval process so not to block releases
- Help to ensure that risk tolerance levels are maintained
Secure coding tool attempts to fill the shoes of the first line of defence
Please note
Before we go into any more detail, It's important to note that the secure coding tool is part of a system of components to secure software development.
Other components of the system include governance, human support and vulnerability management.
I've detailed these components in a different article that will be published in the Nov/Dec issue of the ISC2 magazine, I will add a link here after publication.
Description
This is where you need to add your more robust project description. A project description should outline the purpose of the project, how it is used, and the value it provides to application security. Ideally, project descriptions should be written in such a way that there is no question what value the project provides to the software security community. This section will be seen and used in various places within the Projects Portal. Poorly written project descriptions therefore detract from a project’s visibility, so project leaders should ensure that the description is meaningful.
What does the Secure coding tool do?
The secure coding tool, goes beyond theory and procedure and attempts to implement a planned control integration effort.
The Secure coding tool is written in MVC \ MySQL and consists of 5 screens each serving a specific stakeholder
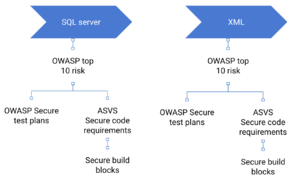
- Information security stakeholder: Filters the security requirements according to the functional requirement: Streamlining security requirements generation
- Dev team stakeholder: Provides secure code blocks to implement the security requirement: Providing code level guidance for developers towards correctly implementing security requirements
- Dev team stakeholder: Provides security test plans to testing the security requirements: Guiding testers towards correctly verifying security requirements are met
- Compliance and assurance stakeholder: Provides a central store for testing results: Promoting traceability through requirements and serving as a quick reference screen for assurance to view control assurance evidence, speeding up the approval process and minimising its impact on responsiveness to market
- IT risk stakeholder: Provides IT risk with an overview of each applications exposure to OWASP TOP 10 risks: Informing risk based decision making and prioritising
How does the secure coding tool do it?
The secure coding tool, goes beyond theory and procedure and attempts to implement a planned control integration effort.
The Secure coding tool is written in MVC \ MySQL and consists of 5 screens each serving a specific stakeholder
- Information security stakeholder: Filters the security requirements according to the functional requirement: Streamlining security requirements generation
- Dev team stakeholder: Provides secure code blocks to implement the security requirement: Providing code level guidance for developers towards correctly implementing security requirements
- Dev team stakeholder: Provides security test plans to testing the security requirements: Guiding testers towards correctly verifying security requirements are met
- Compliance and assurance stakeholder: Provides a central store for testing results: Promoting traceability through requirements and serving as a quick reference screen for assurance to view control assurance evidence, speeding up the approval process and minimising its impact on responsiveness to market
- IT risk stakeholder: Provides IT risk with an overview of each applications exposure to OWASP TOP 10 risks: Informing risk based decision making and prioritising
For a more detailed look at the inner workings of the tool and a brief instructional video please take a look at my linkedIn article
Secure coding tool
Implementation instructions
Not a silver bullet ready to go
- Filter the list of OWASP risks
- Filter the list of OWASP ASVS requirements
- Add additional architectural security requirements
- Filter the list of OWASP security tests
Licensing
A project must be licensed under a community friendly or open source license. For more information on OWASP recommended licenses, please see OWASP Licenses. While OWASP does not promote any particular license over another, the vast majority of projects have chosen a Creative Commons license variant for documentation projects, or a GNU General Public License variant for tools and code projects. This example assumes that you want to use the AGPL 3.0 license.
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the link GNU Affero General Public License 3.0 as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version. OWASP XXX and any contributions are Copyright © by {the Project Leader(s) or OWASP} {Year(s)}.
Roadmap
As of November, 2013, the highest priorities for the next 6 months are:
- Complete the first draft of the Tool Project Template
- Get other people to review the Tool Project Template and provide feedback
- Incorporate feedback into changes in the Tool Project Template
- Finalize the Tool Project template and have it reviewed to be promoted from an Incubator Project to a Lab Project
Subsequent Releases will add
- Internationalization Support
- Additional Unit Tests
- Automated Regression tests
Getting Involved
Involvement in the development and promotion of Tool Project Template is actively encouraged!
You do not have to be a security expert or a programmer to contribute.
Some of the ways you can help are as follows:
|
Project Resources
This is where you can link to the key locations for project files, including setup programs, the source code repository, online documentation, a Wiki Home Page, threaded discussions about the project, and Issue Tracking system, etc.
Installation Package
Source Code
What's New (Revision History)
Documentation
Wiki Home Page
Issue Tracker
Slide Presentation
Video
Project Leader
A project leader is the individual who decides to lead the project throughout its lifecycle. The project leader is responsible for communicating the project’s progress to the OWASP Foundation, and he/she is ultimately responsible for the project’s deliverables. The project leader must provide OWASP with his/her real name and contact e-mail address for his/her project application to be accepted, as OWASP prides itself on the openness of its products, operations, and members.
Michael Bergman
Related Projects
This is where you can link to other OWASP Projects that are similar to yours.
Classifications
|