This site is the archived OWASP Foundation Wiki and is no longer accepting Account Requests.
To view the new OWASP Foundation website, please visit https://owasp.org
OWASP Dependency Track Project
OWASP Dependency-TrackOWASP Dependency-Track is an intelligent Software Composition Analysis (SCA) application that allows organizations to automatically ingest and identify vulnerable third-party components. IntroductionOver the last several years, organizations have faced a growing trend on the number of vulnerabilities reported due to the use of vulnerable third-party components. The risk involved in using third-party components is described in a paper by Jeff Williams and Arshan Dabirsiaghi titled, "The Unfortunate Reality of Insecure Libraries". This upward trend propelled the use of third-party components into a new category in the OWASP Top Ten, specifically, A9: Using Components with Known Vulnerabilities. OWASP Dependency-Track is designed to enable organizations to easily identify use of vulnerable components across an entire portfolio of applications. OWASP Dependency-Track can monitor vulnerable component usage for applications that are in production (via static components), and can be leveraged in continuous security environments to enable real-time feedback and increased visibility to DevOps teams. DescriptionDependency-Track has two main goals:
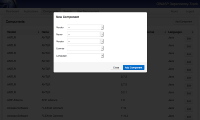
Dependency-Track incorporates a web-based asset management system specifically designed to track applications and the components that each application relies on. Many organizations have legal or new product introduction requirements that require software engineering teams to provide documentation on the use of third-party components. Dependency-Track fulfills this requirement. Using the Dependency-Track database as the sole source of evidence, the system will check the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) to determine if the components contain known vulnerabilities. Dependency-Track embeds OWASP Dependency-Check, a tool used to automatically identify components and determine if they contain known vulnerabilities. Dependency-Track varies from Dependency-Check in how evidence is obtained. While Dependency-Check relies on files on a filesystem or build environment to scan, Dependency-Track relies on user supplied metadata about each component. These two techniques are complimentary and fulfill different requirements. Often times, an organization may rely upon both systems for a comprehensive solution. LicensingOWASP Dependency-Track is licensed under the Apache 2.0 license.
|
Quick DownloadDependency-Track is available as a Docker container and a deployable WAR. News and Events
Features
PresentationIntroducing OWASP Dependency-Track (on SlideShare) OWASP Dependency-Track (on YouTube) DocumentationDependency-Track Project Wiki on GitHub Project LeaderRelated ProjectsClassifications
|
- What are the system requirements?
- Dependency-Track requires Java 7 or higher and can run on any Servlet container such as Tomcat or Jetty.
- What type of database is used?
- Dependency-Track embeds the H2 database engine. A standalone database server may optionally be used.
- How often is the NVD data updated?
- The NVD update is handled by Dependency-Check. Upon starting the servlet container for the first time, the entire contents of the NVD data feed is downloaded. Once downloaded, the system will attempt a delta update every 24 hours.
- What is the NVD mirror feature?
- For organizations that run Dependency-Check, it is possible to specify an alternate URL for the NIST/NVD data. This allows organizations with many Dependency-Check instances to take advantage of an internal mirror for faster access. The NIST/NVD data feed can be used by specifying http://HOSTNAME/CONTEXT/nist/FILENAME. For example: http://localhost:8080/dtrack/nist/nvdcve-2.0-2002.xml.gz. The NVD mirror is automatically updated every 24 hours.
- What is the relationship between Dependency-Check and Dependency-Track?
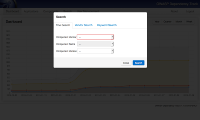
- OWASP Dependency-Check is a tool which can identify third party components (via the file system) and based on evidence collected from the files (vendor, library name, version, etc) determine if there are known vulnerabilities in the National Vulnerability Database. Dependency-Check consists of several modules including the core library along with plugins for Ant, Maven and Jenkins. Dependency-Check is ideal for use in development workflows (continuous integration) and for conducting security assessments and audits.
- OWASP Dependency-Track is an asset management application for tracking use of third-party components across every application and version. Dependency-Track incorporates the Dependency-Check core engine and will track the number and severity of vulnerabilities in third-party components over time. Dependency-Track is ideal for situations where use of vulnerable components in production applications need to be carefully tracked and where access to files for every application is not feasible.
- What are some common use cases for using Dependency-Track?
- A custom software provider can track use of components they've used in their clients projects. By monitoring Dependency-Track, the provider can proactively inform clients of new vulnerabilities, potentially increase billable hours by suggesting mitigation, and increase the security and satisfaction of their clients.
- A client calls a technical support department to report use of a vulnerable component. After verification, instead of closing the case, the support engineer can query Dependency-Track to find additional uses of said component in other applications they support. This allows the support department to play a proactive role in identifying vulnerable components for the applications they support.
- A independent software vendor needs to keep track of all third party components and their licenses for every version of every product they build. Dependency-Track can fulfill this legal or contractual requirement.
- A hardware device vendor with embedded software (home routers, IoT device, etc) can document all software including operating systems, applications and utilities used in specific revisions of hardware and proactively monitor each configuration for vulnerabilities.
- How often does Dependency-Track check for vulnerabilities?
- Dependency-Track will automatically perform a Dependency-Check analysis for all components it tracks every 24 hours. For components that are added in the user interface, a Dependency-Check analysis will be performed on that component within a minute of it being added.
This project would not be possible without the existence of the OWASP_Dependency_Check project. Special thanks to Jeremy Long and the Dependency-Check core team for their hard work.
Dependency-Track Core Team
- Steve Springett
Past Contributors
- Nikhil Chitlur Navakiran
Sponsors
Development of OWASP Dependency-Track is sponsored in part by Axway.
As of February 2015, the priorities are:
- Enhance dashboard to provide additional control over data being visualized
- Update UI libraries and begin testing with Microsoft Edge
- Auto-populate Dependency-Track database with library identification from Dependency-Check
- Add support for tracking end-of-life dates
- Integrate ThreadFix support
- Translate into other languages
- Promote use of Dependency-Track
Involvement in the development and promotion of Dependency-Track is actively encouraged! You do not have to be a security expert in order to contribute. Some of the ways you can help:
Localization
Are you fluent in another language? Can you help translate Dependency-Track into that language?
Front-End Gurus
Want to provide design or an implementation for a way to visualize data? There's a lot of potential opportunities in this area. Let us know if you can help.
Feedback
Please use the Dependency-Track mailing list for feedback:
- What you like?
- What you don't like?
- What could be improved?
- v1.0.0 (19 Feb 2015)
- Initial general availability release.
| PROJECT INFO What does this OWASP project offer you? |
RELEASE(S) INFO What releases are available for this project? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||