This site is the archived OWASP Foundation Wiki and is no longer accepting Account Requests.
To view the new OWASP Foundation website, please visit https://owasp.org
CRV2 SecCommsdotNet
ASP.NET Configurations
Since web requests through physical tiers of an application crosses different communication channels, it must be considered how the application must be secure for each of these channels. Most of the security configurations occurs on different files found in the application such as the web.config file or in the server such as the policy files. The following information highlights the most important aspects to secure communications in ASP.NET applications
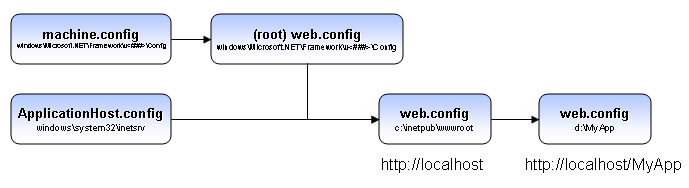
IIS 7 Configurations
In IIS 7 there is a new configuration system which affects the hierarchy level and how one file can inherit from another. The following figure resumes how this work and the location of each file (Aguilar, 2006)
Password protection and sensitive information
The web.config files might include sensitive information in the connection strings such as database passwords, mail server user names among others.
Sections that are required to be encrypted are:
<appSettings>. This section contains custom application settings. <connectionStrings>. This section contains connection strings. <identity>. This section can contain impersonation credentials. <sessionState>. This section contains the connection string for the out-of-process session state provider.
Passwords and user names contained in a <connectionstring> section should be encrypted. ASP.NET allows you to encrypt this information by using the functionality aspnet_regiis .This utility is found in the installed .NET framework under the folder
%windows%\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v2.0.50727
You can specify the section you need to encrypt by using the command:
aspnet_regiis -pef sectiontobeencryoted .
Encrypting sections in Web.Config file
Even though encrypting sections is possible, not all sections can be encrypted, specifically, sections that are read before user code is run. The following sections cannot be encrypted:
*<processModel> *<runtime> *<mscorlib> *<startup> *<system.runtime.remoting> *<configProtectedData> *<satelliteassemblies> *<cryptographySettings> *<cryptoNameMapping> *<cryptoClasses>
Machine-Level RSA key container or User-Level Key Containers
Encrypting a single file has its disadvantages when this file is moved to another servers. In this case, the user of an RSA key container is strongly advice. The RSAProtectedConfigurationProvider supports machine-level and user-level key containers for key storage.
RSA machine key containers are stored in the following folder:
\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\Microsoft\Crypto\RSA\MachineKeys
User Key Container
When the application that needs to be protected is in a shared hosting environment and protection of sensitive data cannot be accessible to other applications, the user key container is strongly recommended. In this case each application should have a separate identity. RSA user-level key containers are stored in the following folder:
\Documents and Settings\{UserName}\Application Data\Microsoft\Crypto\RSA
IIS configurations
Depending on the version of IIS that must be configured, it is important to revise some of its settings which can comprise security in the server.
Trust level
The trust level is a set of Code Access Security permissions granted to an application within a hosting environment. These are defined using policy files. Depending on the trust level that must be configured, it is possible to grant FULL, HIGH, MEDIUM, LOW or MINIMAL level. The ASP.NET host does not apply any additional policy to applications that are running at the full-trust level.
Example:
<system.web>
<securityPolicy>
<trustLevel name="Full" policyFile="internal"/>
</securityPolicy>
</system.web>
Lock Trust Levels
In the .NET framework web.config file is possible to lock applications from changing their trust level This file is found at:
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\{version}\CONFIG
The following example shows how to lock 2 different application configuration trust levels (MSDN, 2013)
<configuration>
<location path="application1" allowOverride="false">
<system.web>
<trust level="High" />
</system.web>
</location>
<location path="application2" allowOverride="false">
<system.web>
<trust level="Medium" />
</system.web>
</location>
</configuration>
References
Aguilar Carlos ,2006 "The new Configuration System in IIS 7" available at http://blogs.msdn.com/b/carlosag/archive/2006/04/25/iis7configurationsystem.aspx MSDN, 2013 . How to: Lock ASP.NET Configuration Settings available at http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms178693.aspx (Last accessed on 14 July, 2013)