This site is the archived OWASP Foundation Wiki and is no longer accepting Account Requests.
To view the new OWASP Foundation website, please visit https://owasp.org
Enterprise Business Application Security Implementation Assessment
Implementation guides
Objective
This document will describe different areas of secure implementation of Enterprise Business Applications and ERP systems. Here, we will mainly focus on security architecture and configuration threats because program errors are well described in the "Software vulnerabilities" topic.
Purpose
The purpose of this document is to increase awareness of the administrators of Business Application security and help them to start a self-assessment of their systems and find the most critical violations.
Intro
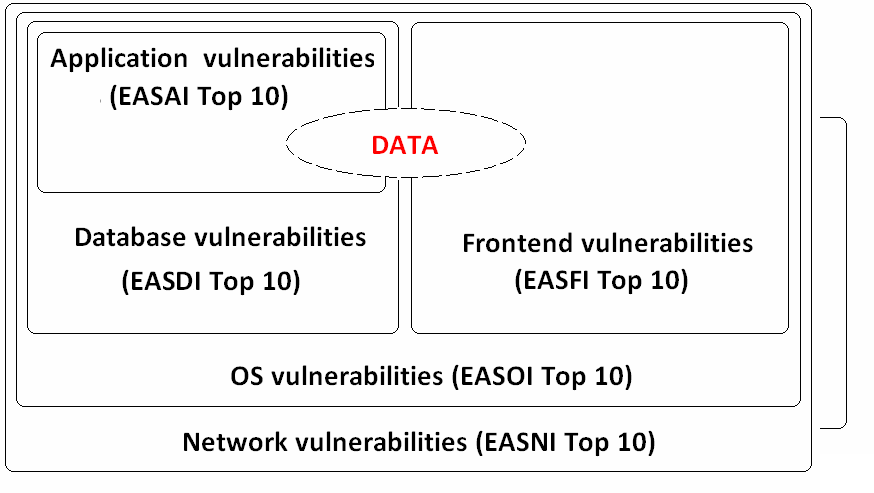
Enterprise Business Applications (like ERP, it is any software system that has been designed to support and automate the business process of medium and large business) are very large systems that consist of different components such as Database server, Front-end, Web server, Application server and other parts. Also, those systems rely on different hardware and software that can have their own vulnerabilities. Every described layer may have its own vulnerabilities and misconfigurations that can give attacker full access to business data even if other layers are completely secured.
All the data was collected and categorized during our big practice of assessing the security of popular Business Applications such as SAP ERP, Oracle E-Business Suite, Oracle Peoplesoft, JD-Edwards and other less known or custom applications.
Main
Overall security of Enterprise Business Application consists of different layers, including:
• Network architecture security
• OS security
• Database security
• Application security
• Front-end security
In this document, we will describe top 10 violations on every layer of Enterprise Business Application that can be easily assessed and mitigated.
Top 10 Network/Architecture issues
1 Lack of proper network filtration between EA and Corporate network
2 Lack or vulnerable encryption between corp net and EA Network
3 Lack of separation between Test, Dev, and Prod system<
4 Lack of encryption inside EA Network
5 Insecure trusted relations between components
6 Insecurely configured Internet facing applications
7 Vulnerable / default configuration of routers
8 Lack of frontend access filtration
9 Lack or misconfigured monitoring IDS/IPS
10 Insecure/unappropriate wireless comunications
Top 10 OS issues
1 Unnecessary enabled services
2 Missing 3rd party software patches
3 Insecure trust relations
4 Universal OS passwords
5 Missing OS patches
6 Lacking or misconfigured network access control
7 Lacking or misconfigured monitoring
8 Insecure internal acces control
9 Unencrypted remote access
10 Lack of password lockout/complexity checks
Top 10 Database issues
1 Default passwords for DB access
2 Lack of DB patch management
3 Unnecessary enabled DB features
4 Lack of password lockout/complexity checks
5 Unencrypted sensitive data transport / data
6 Lack or misconfigured network acess control
7 Extensive user and group privileges
8 Lacking or misconfigured audit
9 Insecure trust relations
10 Open additional interfaces
Top 10 Application issues
1 Lack of patch management
2 Default passwords for application access
3 SoD conficts
4 Unnecessary enabled application features
5 Open remote management interfaces
6 Lack of password lockout/complexity checks
7 Insecure options
8 Unecrypted communications
9 Insecure trust relations
10 Guest access
Top 10 Frontend issues
1 Vulnerable frontend applications
2 Lack of server trust check
3 Lack of encryption
4 Autocomplete enabled in the browser
5 Insecure browser scripting options
6 Insecure configuration
7 Insecure sortware distribution service
8 Lack of AV software
9 Password stored in configuration file
10 Sensitive information storage
Links
ERP Security:Myths Problems Solutions - by Alexander Polyakov and Ilya Medvedovsky
Authors
Alexander Polyakov Nikolay Mesherin Kirill Nikitenkov