This site is the archived OWASP Foundation Wiki and is no longer accepting Account Requests.
To view the new OWASP Foundation website, please visit https://owasp.org
Testing for Format String
OWASP Testing Guide v3 Table of Contents
This article is part of the OWASP Testing Guide v3. The entire OWASP Testing Guide v3 can be downloaded here.
OWASP at the moment is working at the OWASP Testing Guide v4: you can browse the Guide here
Brief Summary
This section describes how to test for format string attacks that can be used to crash a program or to execute harmful code. The problem stems from the use of unfiltered user input as the format string parameter in certain C functions that perform formatting, such as printf().
Description of the Issue
Various C-Style languages provision formatting of output by means of functions like printf( ), fprintf( ) etc.
Formatting is governed by a parameter to these functions termed as format type specifier, typically %s, %c etc.
The vulnerability arises when format functions are called with inadequate parameters validation and user controlled data.
A simple example would be printf(argv[1]). In this case the type specifier has not been explicitly declared, allowing a user to pass characters such as %s, %n, %x to the application by means of command line argument argv[1].
This situation tends to become precarious since a user who can supply format specifiers can perform the following malicious actions:
Enumerate Process Stack: This allows an adversary to view stack organization of the vulnerable process by supplying format strings, such as %x or %p, which can lead to leakage of sensitive information. It can also be used to extract canary values when the application is protected with a stack protection mechanism. Coupled with a stack overflow, this information can be used to bypass the stack protector.
Control Execution Flow: This vulnerability can also facilitate arbitrary code execution since it allows writing 4 bytes of data to an address supplied by the adversary. The specifier %n comes handy for overwriting various function pointers in memory with address of the malicious payload. When these overwritten function pointers get called, execution passes to the malicious code.
Denial of Service: If the adversary is not in a position to supply malicious code for execution, the vulnerable application can be crashed by supplying a sequence of %x followed by %n.
Black Box testing and example
The key to testing format string vulnerabilities is supplying format type specifiers in application input.
For example, consider an application that processes the URL string http://xyzhost.com/html/en/index.htm or accepts inputs from forms. If a format string vulnerability exists in one of the routines processing this information, supplying a URL like http://xyzhost.com/html/en/index.htm%n%n%n or passing %n in one of the form fields might crash the application creating a core dump in the hosting folder.
Format string vulnerabilities manifest mainly in web servers, application servers, or web applications utilizing C/C++ based code or CGI scripts written in C. In most of these cases, an error reporting or logging function like syslog( ) has been called insecurely.
When testing CGI scripts for format string vulnerabilities, the input parameters can be manipulated to include %x or %n type specifiers. For example a legitimate request like
http://hostname/cgi-bin/query.cgi?name=john&code=45765
can be altered to
http://hostname/cgi-bin/query.cgi?name=john%x.%x.%x&code=45765%x.%x
If a format string vulnerability exists in the routine processing this request, the tester will be able to see stack data being printed out to browser.
If code is unavailable, the process of reviewing assembly fragments (also known as reverse engineering binaries) would yield substantial information about format string bugs.
Take the instance of code (1) :
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
printf("The string entered is\n");
printf(“%s”,argv[1]);
return 0;
}
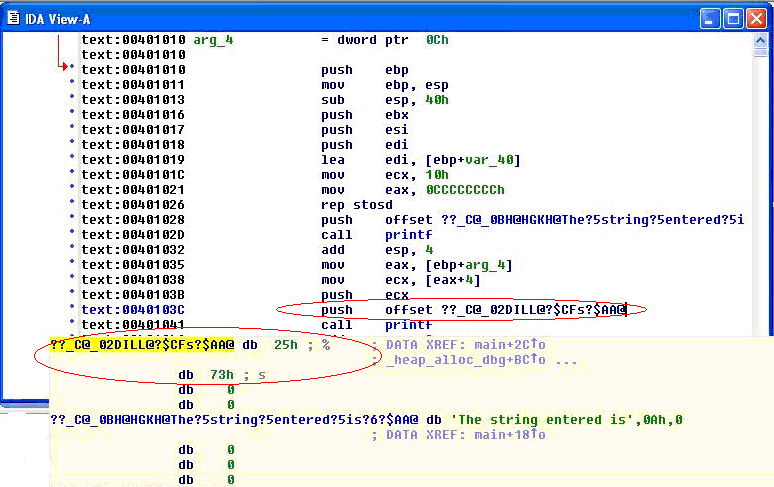
when the disassembly is examined using IDA Pro, the address of a format type specifier being pushed on the stack is clearly visible before a call to printf is made.
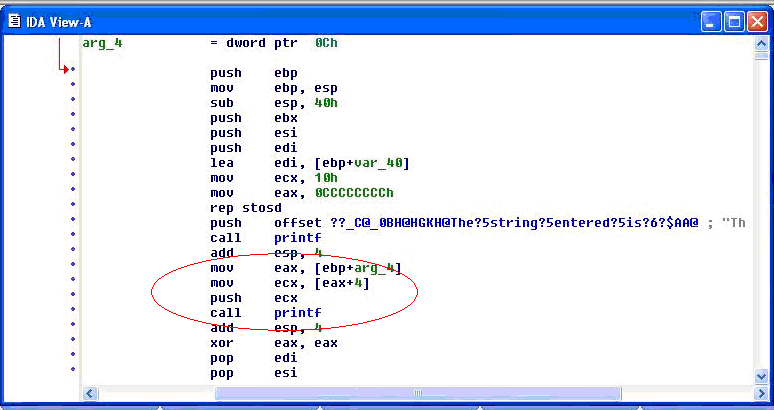
On the other hand, when the same code is compiled without “%s” as an argument , the variation in assembly is apparent. As seen below, there is no offset being pushed on the stack before calling printf.
Gray Box testing and example
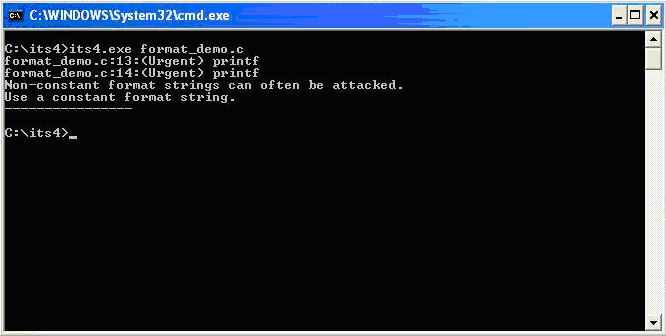
While performing code reviews, nearly all format string vulnerabilities can be detected by use of static code analysis tools. Subjecting the code shown in (1) to ITS4, which is a static code analysis tool, gives the following output.
The functions that are primarily responsible for format string vulnerabilities are ones that treat format specifiers as optional. Therefore when manually reviewing code, emphasis can be given to functions such as:
printf fprintf sprintf snprintf vfprintf vprintf vsprintf vsnprintf
There can be several formatting functions that are specific to the development platform. These should also be reviewed for absence of format strings once their argument usage has been understood.
References
Whitepapers
- Analysis of format string bugs - http://julianor.tripod.com/format-bug-analysis.pdf
- Format functions manual page - http://www.die.net/doc/linux/man/man3/fprintf.3.html
Tools
- ITS4: "A static code analysis tool for identifying format string vulnerabilities using source code" - http://www.cigital.com/its4
- A disassembler for analyzing format bugs in assembly - http://www.datarescue.com/idabase
- An exploit string builder for format bugs - http://seclists.org/lists/pen-test/2001/Aug/0014.html