This site is the archived OWASP Foundation Wiki and is no longer accepting Account Requests.
To view the new OWASP Foundation website, please visit https://owasp.org
Difference between revisions of "OWASP LAPSE Project"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==== Main ==== | ==== Main ==== | ||
| + | '''LAPSE+: The Security Scanner for Java EE Applications''' | ||
| − | |||
== News == | == News == | ||
| − | * 4/23/2011 - LAPSE+ | + | * 4/23/2011 - LAPSE+ released. |
| − | * 8/23/2006 - version 2.5.5 released (see http://suif.stanford.edu/~livshits/work/lapse/download.html) | + | * 8/23/2006 - version 2.5.5 released (see http://suif.stanford.edu/~livshits/work/lapse/download.html). |
| − | * 8/22/2006 - OWASP LAPSE Project Created | + | * 8/22/2006 - OWASP LAPSE Project Created. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| − | + | [[Image:LapseLogo.png|thumb|300px|left]] | |
LAPSE+ is a security scanner for detecting vulnerabilities of untrusted data injection in Java EE Applications. It has been developed as a plugin for Eclipse Java Development Environment, working specifically with Eclipse Helios and Java 1.6 or higher. LAPSE+ is based on the GPL software LAPSE, developed by [http://suif.stanford.edu/~livshits/ Benjamin Livshits] as part of the [http://suif.stanford.edu/~livshits/work/griffin/ Griffin Software Security Project]. This new release of the plugin developed by [http://www.evalues.es/index.php/en.html Evalues Lab] of [http://www.uc3m.es Universidad Carlos III de Madrid] provides more features to analyze the propagation of the malicious data through the application and includes the identification of new vulnerabilities. | LAPSE+ is a security scanner for detecting vulnerabilities of untrusted data injection in Java EE Applications. It has been developed as a plugin for Eclipse Java Development Environment, working specifically with Eclipse Helios and Java 1.6 or higher. LAPSE+ is based on the GPL software LAPSE, developed by [http://suif.stanford.edu/~livshits/ Benjamin Livshits] as part of the [http://suif.stanford.edu/~livshits/work/griffin/ Griffin Software Security Project]. This new release of the plugin developed by [http://www.evalues.es/index.php/en.html Evalues Lab] of [http://www.uc3m.es Universidad Carlos III de Madrid] provides more features to analyze the propagation of the malicious data through the application and includes the identification of new vulnerabilities. | ||
| − | + | LAPSE+ is based on the static analysis of code to detect the source and the sink of a vulnerability. The source of a vulnerability refers to the injection of untrusted data, e.g. in the parameters of an HTTP request or a Cookie. The sink of a vulnerability refers to the process of data modification to manipulate the behaviour of the application, such as a servlet response or a HTML page. The vulnerability sources can lead to sinks by simple assignments, method calls or parameters passing. When it is possible to reach a vulnerability sink from a vulnerability source then we have a vulnerability in our application. | |
| − | |||
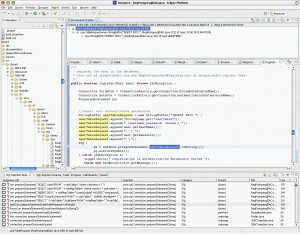
| − | + | [[Image:screenshot.jpg|thumb|300px|right|LAPSE in action (click to see a bigger image)]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
The vulnerabilities detected by LAPSE+ are related to the injection of untrusted data to manipulate the behavior of the application. These type of vulnerabilities are defined by OWASP as the most common vulnerabilities in web applications. The detection of these kind of vulnerabilities is performed in three steps: | The vulnerabilities detected by LAPSE+ are related to the injection of untrusted data to manipulate the behavior of the application. These type of vulnerabilities are defined by OWASP as the most common vulnerabilities in web applications. The detection of these kind of vulnerabilities is performed in three steps: | ||
| − | Vulnerability Source. The first step consist of detecting the points of code that can be source of an attack of malicious data injection. | + | * '''Vulnerability Source.''' The first step consist of detecting the points of code that can be source of an attack of malicious data injection. |
| − | Vulnerability Sink. After detecting the points of code that can be target of data injection, LAPSE+ identifies the points that can propagate the attack and manipulate the behaviour of the application. | + | * '''Vulnerability Sink.''' After detecting the points of code that can be target of data injection, LAPSE+ identifies the points that can propagate the attack and manipulate the behaviour of the application. |
| − | Provenance Tracker. Finally, we check if it is possible to reach a Vulnerability Source from a Vulnerability Sink performing the backward propagation through the different assignations. If this occurs, we have a vulnerability in our code. | + | * '''Provenance Tracker.''' Finally, we check if it is possible to reach a Vulnerability Source from a Vulnerability Sink performing the backward propagation through the different assignations. If this occurs, we have a vulnerability in our code. |
What should you do to avoid these vulnerabilities in your code? How do we protect Web applications from exploits? The proper way to deal with these types of attacks is by sanitizing the tainted input. Please refer to the OWASP guide to find out more about Web application security. | What should you do to avoid these vulnerabilities in your code? How do we protect Web applications from exploits? The proper way to deal with these types of attacks is by sanitizing the tainted input. Please refer to the OWASP guide to find out more about Web application security. | ||
Revision as of 15:27, 15 March 2011
Main
LAPSE+: The Security Scanner for Java EE Applications
News
- 4/23/2011 - LAPSE+ released.
- 8/23/2006 - version 2.5.5 released (see http://suif.stanford.edu/~livshits/work/lapse/download.html).
- 8/22/2006 - OWASP LAPSE Project Created.
Overview
LAPSE+ is a security scanner for detecting vulnerabilities of untrusted data injection in Java EE Applications. It has been developed as a plugin for Eclipse Java Development Environment, working specifically with Eclipse Helios and Java 1.6 or higher. LAPSE+ is based on the GPL software LAPSE, developed by Benjamin Livshits as part of the Griffin Software Security Project. This new release of the plugin developed by Evalues Lab of Universidad Carlos III de Madrid provides more features to analyze the propagation of the malicious data through the application and includes the identification of new vulnerabilities.
LAPSE+ is based on the static analysis of code to detect the source and the sink of a vulnerability. The source of a vulnerability refers to the injection of untrusted data, e.g. in the parameters of an HTTP request or a Cookie. The sink of a vulnerability refers to the process of data modification to manipulate the behaviour of the application, such as a servlet response or a HTML page. The vulnerability sources can lead to sinks by simple assignments, method calls or parameters passing. When it is possible to reach a vulnerability sink from a vulnerability source then we have a vulnerability in our application.
The vulnerabilities detected by LAPSE+ are related to the injection of untrusted data to manipulate the behavior of the application. These type of vulnerabilities are defined by OWASP as the most common vulnerabilities in web applications. The detection of these kind of vulnerabilities is performed in three steps:
- Vulnerability Source. The first step consist of detecting the points of code that can be source of an attack of malicious data injection.
- Vulnerability Sink. After detecting the points of code that can be target of data injection, LAPSE+ identifies the points that can propagate the attack and manipulate the behaviour of the application.
- Provenance Tracker. Finally, we check if it is possible to reach a Vulnerability Source from a Vulnerability Sink performing the backward propagation through the different assignations. If this occurs, we have a vulnerability in our code.
What should you do to avoid these vulnerabilities in your code? How do we protect Web applications from exploits? The proper way to deal with these types of attacks is by sanitizing the tainted input. Please refer to the OWASP guide to find out more about Web application security.
If you are interested in auditing a Java Web application, LAPSE helps you in the following ways:
- Identify taint sources
- Identify taint sinks
- Find paths between sources and sinks
LAPSE is inspired by existing lightweight security auditing tools such as RATS, pscan, and FlawFinder. Unlike those tools, however, LAPSE addresses vulnerabilities in Web applications. LAPSE is not intended as a comprehensive solution for Web application security, but rather as an aid in the code review process. Those looking for more comprehensive tools are encouraged to look at some of the tools produced by Fortify or Ounce Labs.
For now, LAPSE is housed at http://suif.stanford.edu/~livshits/work/lapse/
Feedback and Participation:
We hope you find the OWASP LAPSE Project useful. Please contribute to the Project by volunteering for one of the Tasks, sending your comments, questions, and suggestions to [email protected]. To join the OWASP LAPSE Project mailing list or view the archives, please visit the subscription page.
Project About
| PROJECT INFO What does this OWASP project offer you? |
RELEASE(S) INFO What releases are available for this project? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||