This site is the archived OWASP Foundation Wiki and is no longer accepting Account Requests.
To view the new OWASP Foundation website, please visit https://owasp.org
Difference between revisions of "Reporting"
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
Each finding should be clear and concise and give the reader of the report a full understanding of the issue at hand. | Each finding should be clear and concise and give the reader of the report a full understanding of the issue at hand. | ||
| − | Here is the report: | + | Here is the report (see https://www.owasp.org/index.php/Testing_Checklist for the complete list of tests): |
<center>[[Image:tablerep.PNG]]</center> | <center>[[Image:tablerep.PNG]]</center> | ||
Revision as of 11:49, 1 November 2008
OWASP Testing Guide v3 Table of Contents
This article is part of the OWASP Testing Guide v3. The entire OWASP Testing Guide v3 can be downloaded here.
OWASP at the moment is working at the OWASP Testing Guide v4: you can browse the Guide here
Performing the technical side of the assessment is only half of the overall assessment process; the final product is the production of a well-written, and informative, report. A report should be easy to understand and highlight all the risks found during the assessment phase and appeal to both management and technical staff.
The report needs to have three major sections and be created in a manner that allows each section to be split off and printed and given to the appropriate teams, such as the developers or system managers.
The sections generally recommended are:
I. Executive Summary
The executive summary sums up the overall findings of the assessment and gives managers, or system owners, an idea of the overall risk faced. The language used should be more suited to people who are not technically aware and should include graphs or other charts which show the risk level. It is recommended that a summary be included, which details when the testing commenced and when it was completed.
Another section, which is often overlooked, is a paragraph on implications and actions. This allows the system owners to understand what is required to be done in order to ensure the system remains secure.
II. Technical Management Overview
The technical management overview section often appeals to technical managers who require more technical detail than found in the executive summary. This section should include details about the scope of the assessment, the targets included and any caveats, such as system availability etc. This section also needs to include an introduction on the risk rating used throughout the report and then finally a technical summary of the findings.
III Assessment Findings
The last section of the report is the section, which includes detailed technical detail about the vulnerabilities found, and the approaches needed to ensure they are resolved. This section is aimed at a technical level and should include all the necessary information for the technical teams to understand the issue and be able to solve it.
The findings section should include:
- A reference number for easy reference with screenshots
- The affected item
- A technical description of the issue
- A section on resolving the issue
- The risk rating and impact value
Each finding should be clear and concise and give the reader of the report a full understanding of the issue at hand.
Here is the report (see https://www.owasp.org/index.php/Testing_Checklist for the complete list of tests):
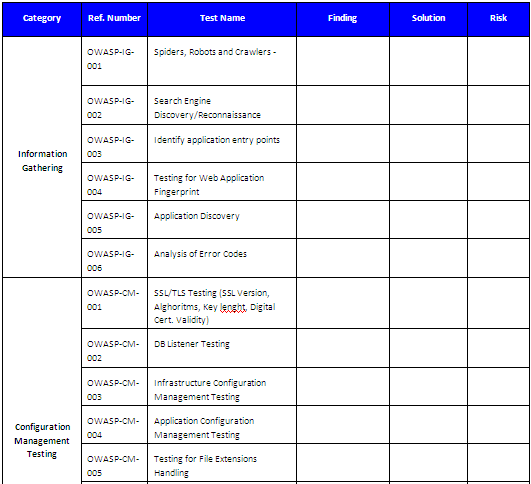
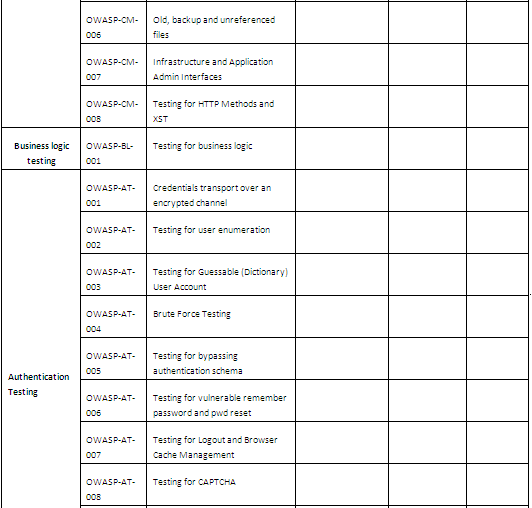
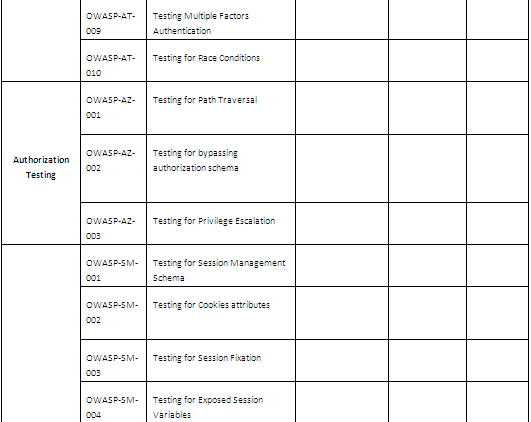
IV Toolbox
This section is often used to describe the commercial and open-source tools that were used in conducting the assessment. When custom scripts/code are utilized during the assessment, it should be disclosed in this section or noted as attachment. It is often appreciated by the customer when the methodology used by the consultants is included. It gives them an idea of the thoroughness of the assessment and also an idea what areas were included.