This site is the archived OWASP Foundation Wiki and is no longer accepting Account Requests.
To view the new OWASP Foundation website, please visit https://owasp.org
Difference between revisions of "OWASP Enterprise Application Security Project"
m |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | === Main === | |
== Objective == | == Objective == | ||
| − | The OWASP Enterprise Application Security Project (OWASP-EAS) exists to provide guidance to people involved in the procurement, design, implementation or sign-off of large scale ( | + | The OWASP Enterprise Application Security Project (OWASP-EAS) exists to provide guidance to people involved in the procurement, design, implementation or sign-off of large scale (i.e. 'Enterprise') applications. |
| − | == | + | == The purpose of the project == |
| − | Enterprise applications security is one of the major topics in overall security area because those applications | + | Enterprise applications security is one of the major topics in overall security area because those applications control money and resources, and any security violation can result in significant money loss. The purpose of this project is to aware people about enterprise application security problems and create guidelines and tools for enterprise application security assessment. |
== Our Subprojects == | == Our Subprojects == | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
Here are our primary goals: | Here are our primary goals: | ||
| − | 1 Aware people about enterprise | + | 1 Aware people about enterprise application security vulnerabilities by releasing annual statistics of enterprise business application security vulnerabilities. |
Subproject [[Enterprise Business Application Vulnerability Statistics]] | Subproject [[Enterprise Business Application Vulnerability Statistics]] | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
[[Projects/OWASP Enterprise Application Security Project|Statistics]] | [[Projects/OWASP Enterprise Application Security Project|Statistics]] | ||
| − | 2 Help companies to begin assessment of enterprise applicatios by creating | + | 2 Help companies to begin assessment of enterprise applicatios by creating Subproject [[Enterprise Business Application Security Implementation Assessment Guide]] |
| − | Subproject [[Enterprise Business Application Security | + | 3 Help software companies to improve security of their solutions by creating Subproject [[Enterprise Business Application Security Vulnerability Testing Guide v1]] |
| − | + | 4 Develop free tools for Enterprise business applicatioons assessment | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | 4 Develop | ||
Subproject [[Enterprise Business Application Security Software]] | Subproject [[Enterprise Business Application Security Software]] | ||
| Line 37: | Line 33: | ||
Have a look at the [[OWASP Enterprise Application Security Project/Roadmp]] | Have a look at the [[OWASP Enterprise Application Security Project/Roadmp]] | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Statistics === | ||
== Objective == | == Objective == | ||
| − | This document is the first statistics report which will be repeated annually | + | This document is the first statistics report which will be repeated annually including tendencies and changes in Enterprise Business Application Security area. |
== Purpose == | == Purpose == | ||
| − | This document | + | This document will show the results of statistical research in the Business Application security area made by ERPscan Research Group and OWASP-EAS project. The purpose of this document is to raise awareness about Enterprise Business Application security by showing the current number of vulnerabilities found in those applications, how critical those are and what tendences we see. |
== Intro == | == Intro == | ||
| − | Business applications like ERP, CRM, SRM and others are one of the major topics within the field of computer security as these applications store business data and any vulnerability in these applications will cause a significant monetary loss. Nonetheless people still | + | Business applications like ERP, CRM, SRM, and others are one of the major topics within the field of computer security as these applications store business data, and any vulnerability in these applications will cause a significant monetary loss. Nonetheless, people still do not pay much attention to Enterprise Business Application, judging by our and our collegues' research and assessment data. |
| + | Business applications are very large and complex systems that consist of different components such as Database server, Front-end, Web server, Application server and other parts. Also, those systems rely on different hardware and software that can have their own vulnerabilities. | ||
| + | Overall security of an Enterprise Business Application consist of different layers, such as: | ||
| + | • Network architecture security | ||
| + | • OS security | ||
| + | • Database security | ||
| + | • Application security | ||
| + | • Front-end security | ||
| − | Every described layer may have | + | Every described layer may have its own vulnerabilities that can give attacker full access to business data even if other layers are completely secured. In this document, all the popular applications from described levels and their vulnerabilities will be shown. The purpose of this document is to increase awareness of Business Application security. |
== Links == | == Links == | ||
| Line 57: | Line 62: | ||
Surveys: | Surveys: | ||
| − | [http://dsecrg.com Business applications vulnerability statistics 2009 and future trends] - Presentation by Dmitry Evdokimov and | + | [http://dsecrg.com Business applications vulnerability statistics 2009 and future trends] - Presentation by Dmitry Evdokimov and Dmitry Chastukhin |
[https://www.owasp.org/images/6/6b/SAP_Security_in_figures_-_a_global_survey_2007-2011._OWASP-EAS.pdf SAP Security In Figures – A Global Survey 2007-2011] | [https://www.owasp.org/images/6/6b/SAP_Security_in_figures_-_a_global_survey_2007-2011._OWASP-EAS.pdf SAP Security In Figures – A Global Survey 2007-2011] | ||
| Line 65: | Line 70: | ||
[http://www.oracle.com/security/critical-patch-update.html Oracle Secalert CPU page with latest vulnerabilities] | [http://www.oracle.com/security/critical-patch-update.html Oracle Secalert CPU page with latest vulnerabilities] | ||
| − | |||
== Authors == | == Authors == | ||
| − | Alexander Polyakov, Alexey | + | Alexander Polyakov, Alexey Tyurin, Dmitry Chastukhin, Dmitry Evdokimov (ERPScan Research Group) |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | === Development of guides === | |
== Objective == | == Objective == | ||
| − | This document | + | This document will describe different areas of program vulnerabilities that can be found in Enterprise Business applications and ERP systems. |
== Purpose == | == Purpose == | ||
| − | The purpose of this document to | + | The purpose of this document is to increase awareness of the developers of Enterprise Business software. Here, we will collect top software vulnerabilities in server side and frontend side that can exist in Business Applications. |
== Intro == | == Intro == | ||
| − | There are many different languages and technologies that can be used | + | There are many different languages and technologies that can be used to develop business applications and write costom code. Here, we will try to categorize it first by dividing into Server and Client side. Top 10 list of vulnerabilities for both areas will be shown. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Main == | == Main == | ||
| Line 114: | Line 113: | ||
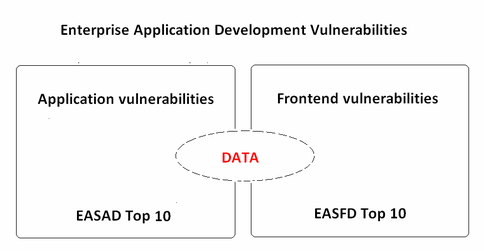
== Top 10 Server vulnerabilities (EASAD) == | == Top 10 Server vulnerabilities (EASAD) == | ||
| − | + | 1 XSS | |
| + | 2 Improper Access Control | ||
| + | 3 Information disclosure | ||
| + | 4 Command/code injection in proprietary language | ||
| + | 5 SQL Injection | ||
| + | 6 Missing Encryption of Sensitive Data | ||
| + | 7 Buffer overflows | ||
| + | 8 Path traversal | ||
| + | 9 CSRF | ||
| + | 10 Use of a Broken or Risky Cryptographic Algorithm | ||
== Top 10 Frontend vulnerabilities (EASFD) == | == Top 10 Frontend vulnerabilities (EASFD) == | ||
| − | 1 Buffer overflows (ActiveX ) | + | 1 Buffer overflows (ActiveX ) |
| − | + | 2 Exposed Dangerous Method or Function (ActiveX) | |
| − | + | 3 Insecure scripting server access | |
| + | 4 File handling Frontend vulnerabilities | ||
| + | 5 Use of a Broken or Risky Cryptographic Algorithm | ||
| + | 6 Cleartext Storage of Sensitive Information | ||
| + | 7 Use of Hard-coded Password | ||
| + | 8 Lack of integrity checking for front-end application | ||
| + | 9 Cleartext Transmission of Sensitive Information | ||
| + | 10 Vulnerable remote services | ||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
| − | + | coming soon | |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 130: | Line 145: | ||
== Authors == | == Authors == | ||
| − | Alexander Polyakov ( | + | Alexander Polyakov (ERPScan Research Group) |
| + | Mikhail Markevich | ||
| + | Dmitry Evdokimov (ERPScan Research Group) | ||
| + | Alexey Sintsov (ERPScan Research Group) | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | === Implementation guides === | |
== Objective == | == Objective == | ||
| − | This document | + | This document will describe different areas of secure implementation of Enterprise Business Applications and ERP systems. Here, we will mainly focus on security architecture and configuration threats because program errors are well described in the "Software vulnerabilities" topic. |
== Purpose == | == Purpose == | ||
| − | The purpose of this document to | + | The purpose of this document is to increase awareness of the administrators of Business Application security and help them to start a self-assessment of their systems and find the most critical violations. |
== Intro == | == Intro == | ||
| − | Enterprise Business Applications ( | + | Enterprise Business Applications (like ERP, it is any software system that has been designed to support and automate the business process of medium and large business) are very large systems that consist of different components such as Database server, Front-end, Web server, Application server and other parts. Also, those systems rely on different hardware and software that can have their own vulnerabilities. Every described layer may have its own vulnerabilities and misconfigurations that can give attacker full access to business data even if other layers are completely secured. |
| − | + | All the data was collected and categorized during our big practice of assessing the security of popular Business Applications such as SAP ERP, Oracle E-Business Suite, Oracle Peoplesoft, JD-Edwards and other less known or custom applications. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Main == | == Main == | ||
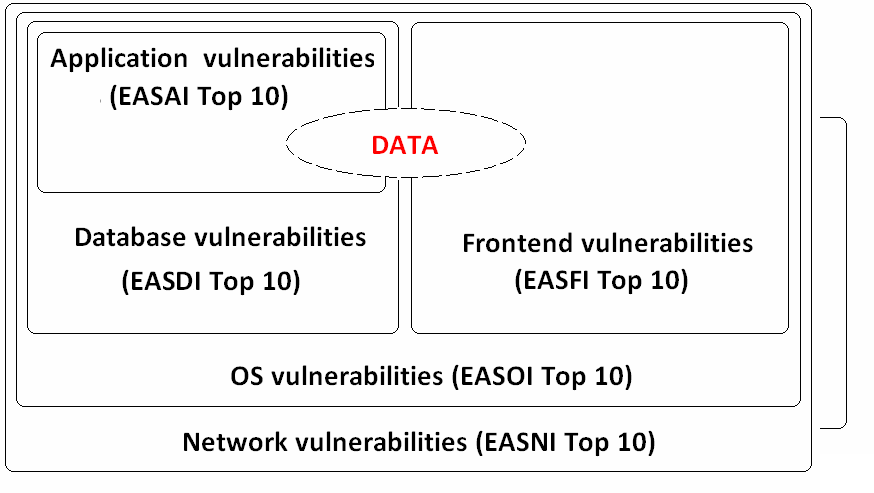
| − | Overall security of Enterprise Business Application consists of different layers | + | Overall security of Enterprise Business Application consists of different layers, including: |
| + | • Network architecture security | ||
| + | • OS security | ||
| + | • Database security | ||
| + | • Application security | ||
| + | • Front-end security | ||
| + | In this document, we will describe top 10 violations on every layer of Enterprise Business Application that can be easily assessed and mitigated. | ||
| − | |||
[[Image:Dev2.png]] | [[Image:Dev2.png]] | ||
| Line 164: | Line 183: | ||
== Top 10 Network/Architecture issues == | == Top 10 Network/Architecture issues == | ||
| − | 1 Lack of proper network filtration between EA and Corporate network | + | 1 Lack of proper network filtration between EA and Corporate network |
| + | 2 Lack or vulnerable encryption between corp net and EA Network | ||
| + | 3 Lack of separation between Test, Dev, and Prod system< | ||
| + | 4 Lack of encryption inside EA Network | ||
| + | 5 Insecure trusted relations between components | ||
| + | 6 Insecurely configured Internet facing applicatins | ||
| + | 7 Vulnerable / default configuration of routers | ||
| + | 8 Lack of frontend access filtration | ||
| + | 9 Lack or misconfigured monitoring IDS/IPS | ||
| + | 10 Insecure/unappropriate wireless comunications | ||
== Top 10 OS issues == | == Top 10 OS issues == | ||
| − | 1 Unnecessary | + | 1 Unnecessary enabled services |
| + | 2 Missing 3rd party software patches | ||
| + | 3 Insecure trust relations | ||
| + | 4 Universal OS passwords | ||
| + | 5 Missing OS patches | ||
| + | 6 Lacking or misconfigured network access control | ||
| + | 7 Lacking or misconfigured monitoring | ||
| + | 8 Insecure internal acces control | ||
| + | 9 Unencrypted remote access | ||
| + | 10 Lack of password lockout/complexity checks<br> | ||
== Top 10 Database issues == | == Top 10 Database issues == | ||
| − | 1 Default passwords for DB access | + | 1 Default passwords for DB access |
| + | 2 Lack of DB patch management | ||
| + | 3 Unnecessary enabled DB features | ||
| + | 4 Lack of password lockout/complexity checks | ||
| + | 5 Unencrypted sensitive data transport / data | ||
| + | 6 Lack or misconfigured network acess control | ||
| + | 7 Extensive user and group privileges | ||
| + | 8 Lacking or misconfigured audit | ||
| + | 9 Insecure trust relations | ||
| + | 10 Open additional interfaces | ||
== Top 10 Application issues == | == Top 10 Application issues == | ||
| − | 1 Lack of patch management | + | 1 Lack of patch management |
| + | 2 Default passwords for application access | ||
| + | 3 SoD conficts | ||
| + | 4 Unnecessary enabled application features | ||
| + | 5 Open remote management interfaces | ||
| + | 6 Lack of password lockout/complexity checks | ||
| + | 7 Insecure options | ||
| + | 8 Unecrypted communications | ||
| + | 9 Insecure trust relations | ||
| + | 10 Guest access | ||
== Top 10 Frontend issues == | == Top 10 Frontend issues == | ||
| − | 1 Vulnerable | + | 1 Vulnerable frontend applications |
| + | 2 Lack of server trust check | ||
| + | 3 Lack of encryption | ||
| + | 4 Autocomplete enabled in the browser | ||
| + | 5 Insecure browser scripting options | ||
| + | 6 Insecure configuration | ||
| + | 7 Insecure sortware distribution service | ||
| + | 8 Lack of AV software | ||
| + | 9 Password stored in configuration file | ||
| + | 10 Sensitive information storage | ||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
| − | [http://dsecrg.com ERP Security:Myths Problems Solutions] - by Alexander Polyakov and Ilya | + | [http://dsecrg.com ERP Security:Myths Problems Solutions] - by Alexander Polyakov and Ilya Medvedovsky |
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Authors == | == Authors == | ||
| − | Alexander Polyakov ( | + | Alexander Polyakov (ERPScan Research Group) |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Mikhail Markevich | Mikhail Markevich | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==== Project About ==== | ==== Project About ==== | ||
Revision as of 17:00, 17 December 2012
Main
Objective
The OWASP Enterprise Application Security Project (OWASP-EAS) exists to provide guidance to people involved in the procurement, design, implementation or sign-off of large scale (i.e. 'Enterprise') applications.
The purpose of the project
Enterprise applications security is one of the major topics in overall security area because those applications control money and resources, and any security violation can result in significant money loss. The purpose of this project is to aware people about enterprise application security problems and create guidelines and tools for enterprise application security assessment.
Our Subprojects
Here are our primary goals:
1 Aware people about enterprise application security vulnerabilities by releasing annual statistics of enterprise business application security vulnerabilities.
Subproject Enterprise Business Application Vulnerability Statistics
2 Help companies to begin assessment of enterprise applicatios by creating Subproject Enterprise Business Application Security Implementation Assessment Guide
3 Help software companies to improve security of their solutions by creating Subproject Enterprise Business Application Security Vulnerability Testing Guide v1
4 Develop free tools for Enterprise business applicatioons assessment
Subproject Enterprise Business Application Security Software
Project Roadmap
Have a look at the OWASP Enterprise Application Security Project/Roadmp
Statistics
Objective
This document is the first statistics report which will be repeated annually including tendencies and changes in Enterprise Business Application Security area.
Purpose
This document will show the results of statistical research in the Business Application security area made by ERPscan Research Group and OWASP-EAS project. The purpose of this document is to raise awareness about Enterprise Business Application security by showing the current number of vulnerabilities found in those applications, how critical those are and what tendences we see.
Intro
Business applications like ERP, CRM, SRM, and others are one of the major topics within the field of computer security as these applications store business data, and any vulnerability in these applications will cause a significant monetary loss. Nonetheless, people still do not pay much attention to Enterprise Business Application, judging by our and our collegues' research and assessment data. Business applications are very large and complex systems that consist of different components such as Database server, Front-end, Web server, Application server and other parts. Also, those systems rely on different hardware and software that can have their own vulnerabilities. Overall security of an Enterprise Business Application consist of different layers, such as: • Network architecture security • OS security • Database security • Application security • Front-end security
Every described layer may have its own vulnerabilities that can give attacker full access to business data even if other layers are completely secured. In this document, all the popular applications from described levels and their vulnerabilities will be shown. The purpose of this document is to increase awareness of Business Application security.
Links
Surveys:
Business applications vulnerability statistics 2009 and future trends - Presentation by Dmitry Evdokimov and Dmitry Chastukhin
SAP Security In Figures – A Global Survey 2007-2011
Links: SAP SDN page with latest vulnerabilities
Oracle Secalert CPU page with latest vulnerabilities
Authors
Alexander Polyakov, Alexey Tyurin, Dmitry Chastukhin, Dmitry Evdokimov (ERPScan Research Group)
Development of guides
Objective
This document will describe different areas of program vulnerabilities that can be found in Enterprise Business applications and ERP systems.
Purpose
The purpose of this document is to increase awareness of the developers of Enterprise Business software. Here, we will collect top software vulnerabilities in server side and frontend side that can exist in Business Applications.
Intro
There are many different languages and technologies that can be used to develop business applications and write costom code. Here, we will try to categorize it first by dividing into Server and Client side. Top 10 list of vulnerabilities for both areas will be shown.
Main
Crosslinks to CWE SANS OWASP and risks with descriptions will be added soon.
Top 10 Server vulnerabilities (EASAD)
1 XSS 2 Improper Access Control 3 Information disclosure 4 Command/code injection in proprietary language 5 SQL Injection 6 Missing Encryption of Sensitive Data 7 Buffer overflows 8 Path traversal 9 CSRF 10 Use of a Broken or Risky Cryptographic Algorithm
Top 10 Frontend vulnerabilities (EASFD)
1 Buffer overflows (ActiveX ) 2 Exposed Dangerous Method or Function (ActiveX) 3 Insecure scripting server access 4 File handling Frontend vulnerabilities 5 Use of a Broken or Risky Cryptographic Algorithm 6 Cleartext Storage of Sensitive Information 7 Use of Hard-coded Password 8 Lack of integrity checking for front-end application 9 Cleartext Transmission of Sensitive Information 10 Vulnerable remote services
Links
coming soon
Authors
Alexander Polyakov (ERPScan Research Group) Mikhail Markevich Dmitry Evdokimov (ERPScan Research Group) Alexey Sintsov (ERPScan Research Group)
Implementation guides
Objective
This document will describe different areas of secure implementation of Enterprise Business Applications and ERP systems. Here, we will mainly focus on security architecture and configuration threats because program errors are well described in the "Software vulnerabilities" topic.
Purpose
The purpose of this document is to increase awareness of the administrators of Business Application security and help them to start a self-assessment of their systems and find the most critical violations.
Intro
Enterprise Business Applications (like ERP, it is any software system that has been designed to support and automate the business process of medium and large business) are very large systems that consist of different components such as Database server, Front-end, Web server, Application server and other parts. Also, those systems rely on different hardware and software that can have their own vulnerabilities. Every described layer may have its own vulnerabilities and misconfigurations that can give attacker full access to business data even if other layers are completely secured.
All the data was collected and categorized during our big practice of assessing the security of popular Business Applications such as SAP ERP, Oracle E-Business Suite, Oracle Peoplesoft, JD-Edwards and other less known or custom applications.
Main
Overall security of Enterprise Business Application consists of different layers, including: • Network architecture security • OS security • Database security • Application security • Front-end security In this document, we will describe top 10 violations on every layer of Enterprise Business Application that can be easily assessed and mitigated.
Top 10 Network/Architecture issues
1 Lack of proper network filtration between EA and Corporate network 2 Lack or vulnerable encryption between corp net and EA Network 3 Lack of separation between Test, Dev, and Prod system< 4 Lack of encryption inside EA Network 5 Insecure trusted relations between components 6 Insecurely configured Internet facing applicatins 7 Vulnerable / default configuration of routers 8 Lack of frontend access filtration 9 Lack or misconfigured monitoring IDS/IPS 10 Insecure/unappropriate wireless comunications
Top 10 OS issues
1 Unnecessary enabled services
2 Missing 3rd party software patches
3 Insecure trust relations
4 Universal OS passwords
5 Missing OS patches
6 Lacking or misconfigured network access control
7 Lacking or misconfigured monitoring
8 Insecure internal acces control
9 Unencrypted remote access
10 Lack of password lockout/complexity checks
Top 10 Database issues
1 Default passwords for DB access 2 Lack of DB patch management 3 Unnecessary enabled DB features 4 Lack of password lockout/complexity checks 5 Unencrypted sensitive data transport / data 6 Lack or misconfigured network acess control 7 Extensive user and group privileges 8 Lacking or misconfigured audit 9 Insecure trust relations 10 Open additional interfaces
Top 10 Application issues
1 Lack of patch management 2 Default passwords for application access 3 SoD conficts 4 Unnecessary enabled application features 5 Open remote management interfaces 6 Lack of password lockout/complexity checks 7 Insecure options 8 Unecrypted communications 9 Insecure trust relations 10 Guest access
Top 10 Frontend issues
1 Vulnerable frontend applications 2 Lack of server trust check 3 Lack of encryption 4 Autocomplete enabled in the browser 5 Insecure browser scripting options 6 Insecure configuration 7 Insecure sortware distribution service 8 Lack of AV software 9 Password stored in configuration file 10 Sensitive information storage
Links
ERP Security:Myths Problems Solutions - by Alexander Polyakov and Ilya Medvedovsky
Authors
Alexander Polyakov (ERPScan Research Group) Mikhail Markevich
Project About
| PROJECT INFO What does this OWASP project offer you? |
RELEASE(S) INFO What releases are available for this project? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||