This site is the archived OWASP Foundation Wiki and is no longer accepting Account Requests.
To view the new OWASP Foundation website, please visit https://owasp.org
Difference between revisions of "Reviewing code for Cross-Site Request Forgery issues"
(→An eye for an eye, A request for a request) |
m (Added navigation to facilitate sequential reading online) |
||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{LinkBar | |
| + | | useprev=PrevLink | prev=Reviewing Code for Cross-Site Scripting | lblprev= | ||
| + | | usemain=MainLink | main=OWASP Code Review Guide Table of Contents | lblmain=Table of Contents | ||
| + | | usenext=NextLink | next=Reviewing Code for Logging Issues | lblnext= | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
| + | ==Overview== | ||
| + | [[CSRF]] is an attack which forces an end user to execute unwanted actions on a web application in which he/she is currently authenticated. With a little help of social engineering (like sending a link via email/chat), an attacker may force the users of a web application to execute actions of the attacker's choosing. A successful CSRF exploit can compromise end user data and operation in the case of a normal user. If the targeted end user is the administrator account, this can compromise the entire web application. | ||
==Related Security Activities== | ==Related Security Activities== | ||
| Line 8: | Line 15: | ||
See the OWASP article on [[CSRF]] Vulnerabilities. | See the OWASP article on [[CSRF]] Vulnerabilities. | ||
| − | ===How to | + | ===How to Test for CSRF Vulnerabilities=== |
| − | See the [[:Category:OWASP | + | See the [[:Category:OWASP Testing Project|OWASP Testing Guide]] article on how to [[Testing for CSRF (OWASP-SM-005)|Test for CSRF]] Vulnerabilities. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| − | CSRF is not the same as XSS (Cross Site Scripting) which forces malicious content to be served by a trusted website to an unsuspecting victim. Injected | + | CSRF is not the same as XSS (Cross Site Scripting), which forces malicious content to be served by a trusted website to an unsuspecting victim. Injected text is treated as executable by the browser, hence running the script. Used in Phishing, Trojan upload, Browser vulnerability weakness attacks….. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) (C-SURF) (Confused-Deputy) attacks are considered useful if the attacker knows the target is authenticated to a web based system. They only work if the target is logged into the system, and therefore have a small attack footprint. Other logical weaknesses also need to be present such as no transaction authorization required by the user. | |
| + | In effect CSRF attacks are used by an attacker to make a target system perform a function (Funds Transfer, Form submission etc..) via the target’s browser without the knowledge of the target user, at least until the unauthorized function has been committed. A primary target is the exploitation of “ease of use” features on web applications (One-click purchase), for example. | ||
| − | ==How | + | ==How They Work== |
| − | + | CSRF attacks work by sending a rogue HTTP request from an authenticated user's browser to the application, which then commits a transaction without authorization given by the target user. As long as the user is authenticated and a meaningful HTTP request is sent by the user’s browser to a target application, the application does not know if the origin of the request is a valid transaction or a link clicked by the user (that was, say, in an email) while the user is authenticated to the application. So, for example, using CSRF, an attacker makes the victim perform actions that they didn't intend to, such as logout, purchase item, change account information, or any other function provided by the vulnerable website. | |
| − | As long as the user is authenticated and a | ||
| − | So, | ||
| − | An Example below of a HTTP POST to a ticket vendor to purchase a number of tickets. | + | An Example below of a HTTP POST to a ticket vendor to purchase a number of tickets. |
POST http://TicketMeister.com/Buy_ticket.htm HTTP/1.1 | POST http://TicketMeister.com/Buy_ticket.htm HTTP/1.1 | ||
| Line 38: | Line 37: | ||
ticketId=ATHX1138&to=PO BOX 1198 DUBLIN 2&amount=10&date=11042008 | ticketId=ATHX1138&to=PO BOX 1198 DUBLIN 2&amount=10&date=11042008 | ||
| − | + | The response of the vendor is to acknowledge the purchase of the tickets: | |
| − | The response of the vendor is to acknowledge the purchase of the tickets: | ||
HTTP/1.0 200 OK | HTTP/1.0 200 OK | ||
| Line 53: | Line 51: | ||
</pge_data> | </pge_data> | ||
| − | ==How to | + | ==How to Locate the Potentially Vulnerable Code== |
| − | This issue is simple to detect but there may be compensating controls around the functionality of the application which may alert the user to a CSRF attempt. | + | This issue is simple to detect, but there may be compensating controls around the functionality of the application which may alert the user to a CSRF attempt. As long as the application accepts a well formed HTTP request and the request adheres to some business logic of the application CSRF shall work (From now on we assume the target user is logged into the system to be attacked). |
| − | As long as the application accepts a well formed HTTP request and the request adheres to some business logic of the application CSRF shall work (From now on we assume the target user is logged into the system to be attacked). | ||
| − | By checking the page rendering we need to see if any unique identifiers are appended to the links rendered by the application in the user's browser | + | By checking the page rendering we need to see if any unique identifiers are appended to the links rendered by the application in the user's browser. If there is no unique identifier relating to each HTTP request to tie a HTTP request to the user, we are vulnerable. Session ID is not enough, as the session ID shall be sent anyway if a user clicks on a rogue link, as the user is authenticated already. |
| − | Session ID is | ||
| − | ===Transaction Drive Thru | + | ===Transaction Drive Thru=== |
==== An eye for an eye, A request for a request==== | ==== An eye for an eye, A request for a request==== | ||
| − | When an HTTP request is received by the application, one should | + | When an HTTP request is received by the application, one should examine the business logic to assess when a transaction request is sent to the application that the application does not simply execute, but responds to the request with another request for the user's password. |
Line | Line | ||
| Line 73: | Line 69: | ||
6 } | 6 } | ||
| − | In the above | + | In the above pseudo code, we would examine if an HTTP request to commit a transaction is received, and if the application responds to the user request for a confirmation (in this case re-enter a password). |
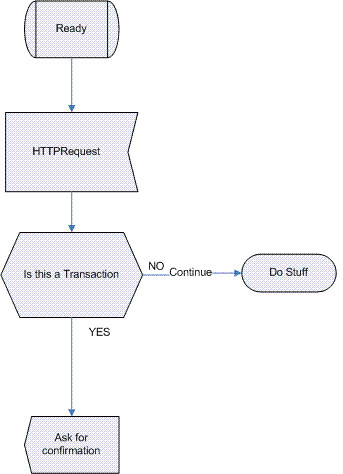
| − | The Flow below depicts the logic behind anti-CSRF transaction management: | + | The Flow below depicts the logic behind anti-CSRF transaction management: |
[[image:CSRF-Flow.GIF]] | [[image:CSRF-Flow.GIF]] | ||
==Vulnerable Patterns for CSRF== | ==Vulnerable Patterns for CSRF== | ||
| − | '''Any application that accepts HTTP requests from an authenticated user without having some control to verify that the HTTP request is unique to the | + | '''Any application that accepts HTTP requests from an authenticated user without having some control to verify that the HTTP request is unique to the user's session.''' (Nearly all web applications!!). Session ID is not in scope here as the rogue HTTP request shall also contain a valid session ID, as the user is authenticated already. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Good Patterns and procedures to prevent CSRF== | |
| − | + | Checking if the request has a valid session cookie is not enough, we need check if a unique identifier is sent with every HTTP request sent to the application. CSRF requests WON'T have this valid unique identifier. The reason CSRF requests won't have this unique request identifier is the unique ID is rendered as a hidden field on the page and is appended to the HTTP request once a link/button press is selected. The attacker will have no knowledge of this unique ID, as it is random and rendered dynamically per link, per page. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | # A list is complied prior to delivering the page to the user. The list contains all valid unique IDs generated for all links on a given page. The unique ID could be derived from a secure random generator such as SecureRandom for J2EE. . | ||
| + | # A unique ID is appended to each link/form on the requested page prior to being displayed to the user. | ||
| + | # Maintaining a list of unique IDs in the user session, the application checks if the unique ID passed with the HTTP request is valid for a given request. if the unique ID passed with the HTTP request is valid for a given request. | ||
| + | # If the unique ID is not present, terminate the user session and display an error to the user. | ||
| − | + | ==User Interaction== | |
| − | Upon | + | Upon committing to a transaction, such as fund transfer, display an additional decision to the user, such as a requirement for one’s password to be entered and verified prior to the transaction taking place. A CSRF attacker would not know the password of the user and therefore the transaction could not be committed via a stealth CSRF attack. |
| − | CSRF attacker would not know the password of the user and therefore the transaction could not be committed via a stealth CSRF attack. | ||
==Related Articles== | ==Related Articles== | ||
| − | + | [[CSRF Guard]] | |
| − | |||
| + | {{LinkBar | ||
| + | | useprev=PrevLink | prev=Reviewing Code for Cross-Site Scripting | lblprev= | ||
| + | | usemain=MainLink | main=OWASP Code Review Guide Table of Contents | lblmain=Table of Contents | ||
| + | | usenext=NextLink | next=Reviewing Code for Logging Issues | lblnext= | ||
| + | }} | ||
[[Category:OWASP Code Review Project]] | [[Category:OWASP Code Review Project]] | ||
[[Category:Identity Theft]] | [[Category:Identity Theft]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:35, 9 September 2010
Overview
CSRF is an attack which forces an end user to execute unwanted actions on a web application in which he/she is currently authenticated. With a little help of social engineering (like sending a link via email/chat), an attacker may force the users of a web application to execute actions of the attacker's choosing. A successful CSRF exploit can compromise end user data and operation in the case of a normal user. If the targeted end user is the administrator account, this can compromise the entire web application.
Related Security Activities
Description of CSRF Vulnerabilities
See the OWASP article on CSRF Vulnerabilities.
How to Test for CSRF Vulnerabilities
See the OWASP Testing Guide article on how to Test for CSRF Vulnerabilities.
Introduction
CSRF is not the same as XSS (Cross Site Scripting), which forces malicious content to be served by a trusted website to an unsuspecting victim. Injected text is treated as executable by the browser, hence running the script. Used in Phishing, Trojan upload, Browser vulnerability weakness attacks…..
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) (C-SURF) (Confused-Deputy) attacks are considered useful if the attacker knows the target is authenticated to a web based system. They only work if the target is logged into the system, and therefore have a small attack footprint. Other logical weaknesses also need to be present such as no transaction authorization required by the user.
In effect CSRF attacks are used by an attacker to make a target system perform a function (Funds Transfer, Form submission etc..) via the target’s browser without the knowledge of the target user, at least until the unauthorized function has been committed. A primary target is the exploitation of “ease of use” features on web applications (One-click purchase), for example.
How They Work
CSRF attacks work by sending a rogue HTTP request from an authenticated user's browser to the application, which then commits a transaction without authorization given by the target user. As long as the user is authenticated and a meaningful HTTP request is sent by the user’s browser to a target application, the application does not know if the origin of the request is a valid transaction or a link clicked by the user (that was, say, in an email) while the user is authenticated to the application. So, for example, using CSRF, an attacker makes the victim perform actions that they didn't intend to, such as logout, purchase item, change account information, or any other function provided by the vulnerable website.
An Example below of a HTTP POST to a ticket vendor to purchase a number of tickets.
POST http://TicketMeister.com/Buy_ticket.htm HTTP/1.1 Host: ticketmeister User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X Mach-O;) Firefox/1.4.1 Cookie: JSPSESSIONID=34JHURHD894LOP04957HR49I3JE383940123K ticketId=ATHX1138&to=PO BOX 1198 DUBLIN 2&amount=10&date=11042008
The response of the vendor is to acknowledge the purchase of the tickets:
HTTP/1.0 200 OK Date: Fri, 02 May 2008 10:01:20 GMT Server: IBM_HTTP_Server Content-Type: text/xml;charset=ISO-8859-1 Content-Language: en-US X-Cache: MISS from app-proxy-2.proxy.ie Connection: close <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <pge_data> Ticket Purchased, Thank you for your custom. </pge_data>
How to Locate the Potentially Vulnerable Code
This issue is simple to detect, but there may be compensating controls around the functionality of the application which may alert the user to a CSRF attempt. As long as the application accepts a well formed HTTP request and the request adheres to some business logic of the application CSRF shall work (From now on we assume the target user is logged into the system to be attacked).
By checking the page rendering we need to see if any unique identifiers are appended to the links rendered by the application in the user's browser. If there is no unique identifier relating to each HTTP request to tie a HTTP request to the user, we are vulnerable. Session ID is not enough, as the session ID shall be sent anyway if a user clicks on a rogue link, as the user is authenticated already.
Transaction Drive Thru
An eye for an eye, A request for a request
When an HTTP request is received by the application, one should examine the business logic to assess when a transaction request is sent to the application that the application does not simply execute, but responds to the request with another request for the user's password.
Line
1 String actionType = Request.getParameter("Action");
2 if(actionType.equalsIgnoreCase("BuyStuff"){
4 Response.add("Please enter your password");
5 return Response;
6 }
In the above pseudo code, we would examine if an HTTP request to commit a transaction is received, and if the application responds to the user request for a confirmation (in this case re-enter a password).
The Flow below depicts the logic behind anti-CSRF transaction management:
Vulnerable Patterns for CSRF
Any application that accepts HTTP requests from an authenticated user without having some control to verify that the HTTP request is unique to the user's session. (Nearly all web applications!!). Session ID is not in scope here as the rogue HTTP request shall also contain a valid session ID, as the user is authenticated already.
Good Patterns and procedures to prevent CSRF
Checking if the request has a valid session cookie is not enough, we need check if a unique identifier is sent with every HTTP request sent to the application. CSRF requests WON'T have this valid unique identifier. The reason CSRF requests won't have this unique request identifier is the unique ID is rendered as a hidden field on the page and is appended to the HTTP request once a link/button press is selected. The attacker will have no knowledge of this unique ID, as it is random and rendered dynamically per link, per page.
- A list is complied prior to delivering the page to the user. The list contains all valid unique IDs generated for all links on a given page. The unique ID could be derived from a secure random generator such as SecureRandom for J2EE. .
- A unique ID is appended to each link/form on the requested page prior to being displayed to the user.
- Maintaining a list of unique IDs in the user session, the application checks if the unique ID passed with the HTTP request is valid for a given request. if the unique ID passed with the HTTP request is valid for a given request.
- If the unique ID is not present, terminate the user session and display an error to the user.
User Interaction
Upon committing to a transaction, such as fund transfer, display an additional decision to the user, such as a requirement for one’s password to be entered and verified prior to the transaction taking place. A CSRF attacker would not know the password of the user and therefore the transaction could not be committed via a stealth CSRF attack.
Related Articles