This site is the archived OWASP Foundation Wiki and is no longer accepting Account Requests.
To view the new OWASP Foundation website, please visit https://owasp.org
Difference between revisions of "OWASP Mobile Security Testing Guide"
(→The OWASP Security Principles) |
m (→Main Deliverables) |
||
| (306 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Main= | =Main= | ||
<!-- DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE THE TEXT ON NEXT LINE --> | <!-- DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE THE TEXT ON NEXT LINE --> | ||
| − | <div style="width:100%;height:160px;border:0,margin:0;overflow: hidden;">[[File: | + | <div style="width:100%;height:160px;border:0,margin:0;overflow: hidden;">[[File:OWASP_MSTG_Header.jpg|link=]]</div> |
| + | |||
| + | <div style="width:100%;height:90px;border:0,margin:0;overflow: hidden;">[[File: flagship_big.jpg|link=OWASP_Project_Stages#tab.3DLab_Projects]]</div> | ||
<!-- DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE THE TEXT ON NEXT LINE --> | <!-- DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE THE TEXT ON NEXT LINE --> | ||
{| style="padding: 0;margin:0;margin-top:10px;text-align:left;" |- | {| style="padding: 0;margin:0;margin-top:10px;text-align:left;" |- | ||
| − | | valign="top" style="border-right: 1px dotted gray;padding-right:25px;" | | + | | valign="top" style="border-right: 1px dotted gray;padding-right:25px;" | |
| + | |||
| + | == Maintenance notice == | ||
| + | |||
| + | This site is no longer maintained: please go to https://www2.owasp.org/www-project-mobile-security-testing-guide/ for our new website! | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Our Vision == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === '''"Define the industry standard for mobile application security."''' === | ||
| + | |||
| + | We are writing a security standard for mobile apps and a comprehensive testing guide that covers the processes, techniques, and tools used during a mobile app security test, as well as an exhaustive set of test cases that enables testers to deliver consistent and complete results. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Main Deliverables == | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| cellpadding="5" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[File:Mstg-cover-release-small2.jpg|200px|link=https://www.github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/]] | ||
| + | | '''Mobile Security Testing Guide (MSTG) - 1.1.3 Release''' | ||
| + | The [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/releases 1.1.3 Release] of the MSTG is a comprehensive manual for mobile app security testing and reverse engineering for iOS and Android mobile security testers with the following content: | ||
| + | # Mobile platform internals | ||
| + | # Security testing in the mobile app development lifecycle | ||
| + | # Basic static and dynamic security testing | ||
| + | # Mobile app reverse engineering and tampering | ||
| + | # Assessing software protections | ||
| + | # Detailed test cases that map to the requirements in the MASVS. | ||
| + | You can contribute and comment in the [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg GitHub Repo]. An online book version of the current master branch is available on [https://mobile-security.gitbook.io/mobile-security-testing-guide/ Gitbook]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Feel free to [https://leanpub.com/mobile-security-testing-guide download the ePub or Mobi] for $0 or contribute any amount you like. All funds raised through sales of this book go directly into the project budget and will be used to for technical editing and designing the book and fund production of future releases. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[File:masvs-mini-cover2.jpg|200px|link=https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-masvs/releases/tag/1.1.4]] | ||
| + | | '''Mobile App Security Requirements and Verification''' | ||
| + | The [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-masvs/releases/download/1.1.4/OWASP_Mobile_AppSec_Verification_Standard_1.1.4_Document.pdf OWASP Mobile Application Security Verification Standard (MASVS) version 1.1.4] is a standard for mobile app security. It can be used by mobile software architects and developers seeking to develop secure mobile applications, as well as security testers to ensure completeness and consistency of test results.You can find the sources on [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-masvs the Github repo]. We now have versions in the folllowing languages: Chinese, English, French, German, Japanese, Russian, and Spanish! Want to get a pdf/mobi/epub of the standard? Check [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-masvs/releases/ the release page on Github]. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[File:checklist.jpg|link=https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/tree/master/Checklists]] | ||
| + | | '''Mobile App Security Checklist''' | ||
| + | A checklist for use in security assessments. Also contains links to the MSTG test case for each requirement. The current release is [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/tree/master/Checklists can be found at Github in English, French, Spanish, Japanese and Korean]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:OWASP Project]] | ||
| + | [[Category:OWASP_Breakers]] | ||
| + | [[Category:OWASP_Document]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE THE TEXT ON NEXT LINE --> | ||
| + | | valign="top" style="padding-left:25px;width:200px;border-right: 1px dotted gray;padding-right:25px;" | | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Classifications== | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| width="200" cellpadding="2" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | rowspan="3" align="center" valign="top" width="50%" | [[File:Mature_projects.png|130px|link=https://www.owasp.org/index.php/OWASP_Project_Stages#Flagship_Projects|Flagship Project]] | ||
| + | | align="center" valign="top" width="50%" | [[File:Owasp-builders-small.png|link=Builders]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" valign="top" width="50%" | [[File:Owasp-breakers-small.png|link=Breakers]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" valign="top" width="50%" | [[File:Owasp-defenders-small.png|link=Defenders]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" valign="center" width="50%" | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" align="center" | [[File:CC-License-4.0.png|link=https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" align="center" | [[File:Project_Type_Files_DOC.jpg|link=]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Project Leaders == | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="color:#ff0000">[https://www.owasp.org/index.php/User:Sven_Schleier Sven Schleier] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://www.owasp.org/index.php/User:Jeroenwillemsen Jeroen Willemsen] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [mailto:[email protected] Carlos Holguera] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Training == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Oct 2019: MSTG Hands-on at [https://appsecday.io/training/#session-mobile OWASP AppSec Day Melbourne] | ||
| + | * Oct 2018: MSTG Hands-on at [https://appsecus2018.sched.com/event/F00G/2-day-training-mobile-security-testing-guide-hands-on OWASP AppSec USA] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Presentations == | ||
| + | * OWASP AppSec Day Melbourne October 2019 - [https://appsecday.io/schedule/#session-7 Fixing Mobile AppSec] | ||
| + | * OWASP Global AppSec Amsterdam September 2019 | ||
| + | * r2con in Barcelona September 2019 - [https://rada.re/con/2019/agenda.html# radare2 and Frida in the OWASP Mobile Security Testing Guide] | ||
| + | * Open Security summit 2019 - [[File:Mstg 101 summit 2019.pdf|101 & onboarding slides]] & [[File:Mstg outcome summit 2019.pdf|MSTG outcome keynote]] | ||
| + | * OWASP Kyiv April 2019 - [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BTkXlsTQtlI&feature=youtu.be OWASP MSTG in real life] | ||
| + | * AppDevcon (Amsterdam), March 2019 - [https://appdevcon.nl/session/securing-your-mobile-app-with-the-owasp-mobile-security-testing-guide/ Securing your mobile app with the OWASP Mobile Security Testing Guide] | ||
| + | * OWASP BeNeLux days 2018 - Fast forwarding mobile security with the MSTG, November 2018 - [https://www.owasp.org/images/c/c4/OWASP_BeNeLux_2018_Jeroen_Willemsen_-_Fast_forwarding_Mobile_Security_with_the_MSTG_compressed.pdf slides] | ||
| + | * OWASP Germany days 2018 - Introduction to Mobile Security Testing, November 2018 - [https://owasp.github.io/german-owasp-day/archive/2018/ slides] | ||
| + | * DBS AppSecCon (Singapore) - Fixing Mobile AppSec, October 2018 | ||
| + | * OWASP Bay Area Chapter - Mobile Testing Workshop, October 2018 | ||
| + | * OWASP AppSec USA - Fixing Mobile AppSec, October 2018 | ||
| + | * CSC 2018 - A Perspective on Mobile Security in IoT and how OWASP can Help - [https://fr.slideshare.net/RomualdSZKUDLAREK/mobile-security-at-owasp-masvs-and-mstg slides]. | ||
| + | * OWASP North Sweden Umea - Mobile Security Essentials | ||
| + | * OWASP Gotentburg - Mobile Security Essentials [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HLeAIScDMNM Introduction into OMTG] and [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Yeybnej03lw All about the keying material] | ||
| + | * OWASP Day Indonesia 2017 - Fixing Mobile AppSec | ||
| + | * Confidence (Krakow, Poland) - Pawel Rzepa - Testing Mobile Applications | ||
| + | * OWASP AppSec EU 2017 - [http://sched.co/A66j Fixing Mobile AppSec] - [https://2017.appsec.eu/presos/Developer/Fixing%20Mobile%20AppSec%20The%20OWASP%20Mobile%20Project-%20Bernhard%20Mueller%20and%20Sven%20Schleier%20-%20OWASP_AppSec-Eu_2017.pdf Slides], [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=THJVzf-u7Iw Video] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Licensing == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The guide is licensed under the [https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/ Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 license], so you can copy, distribute and transmit the work, and you can adapt it, and use it commercially, but all provided that you attribute the work and if you alter, transform, or build upon this work, you may distribute the resulting work only under the same or similar license to this one. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | =How-To= | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Using the OWASP Mobile App Security Verification Standard, Testing Guide and Checklist == | ||
| + | |||
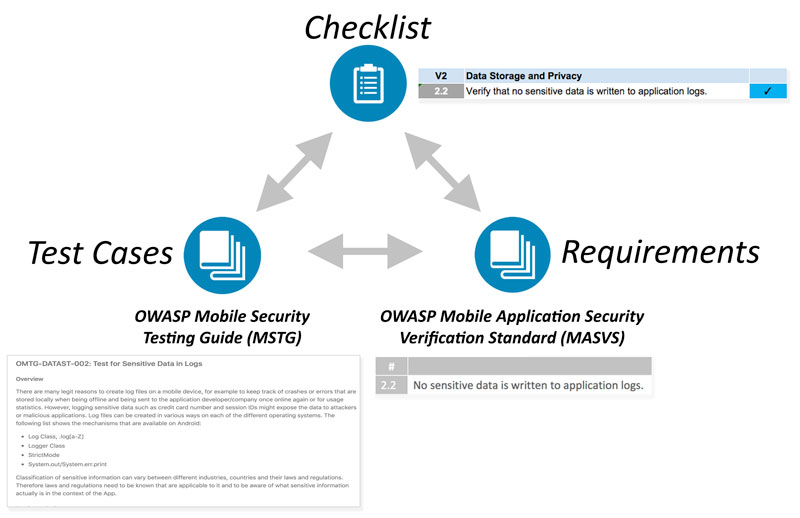
| + | The documents produced in this project cover many aspects of mobile application security, from the high-level requirements to the nitty-gritty implementation details and test cases. They can be used to plan and verify security controls during any phase of mobile app development, as well as during pre-release code review and penetration testing. | ||
| + | |||
| + | # The [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-masvs/releases Mobile Application Security Verification Standard (MASVS)] contains generic security requirements along with mappings to verification levels that can be chosen depending on the overall need for security. | ||
| + | # The [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/releases Mobile Security Testing Guide (MSTG)] provides verification instructions for each requirement in the MASVS, as well as security best practices for apps on each supported mobile operating system (currently Android and iOS). It is also useful as a standalone learning resource and reference guide for mobile application security testers. | ||
| + | # The [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/tree/master/Checklists Mobile App Security Checklist] can be used to apply the MASVS requirements during practical assessments. It also conveniently links to the MSTG test case for each requirement, making mobile penetration testing a breeze. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is important to note that the security standard, testing guide and checklists are closely related: They all map to the same basic set of requirements. Depending on the context, the documents can be used stand-alone or in combination to achieve different objectives. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Overview-800px.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | For example, the MASVS requirements may be used in the planning and architecture design stages, while the checklist and testing guide may serve as a baseline for manual security testing or as a template for automated security tests. | ||
| − | + | == Mobile App Security Testing == | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/tree/master/Checklists checklist] works great as a reference during mobile app security assessments. You can walk through the requirements one-by-one - for more information on each requirement, simply click on the link in the "Testing procedures" column. Or, fill out the checklist at the end of an assessment to ensure completeness. | |
| − | + | == Security Engineering in the SDLC == | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Properly defined security requirements are an important part of the Secure SDLC. The [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-masvs/releases/download/0.9.2/OWASP_Mobile_AppSec_Verification_Standard_v0.9.2.pdf MASVS] levels can be used along with threat modeling to determine the appropriate set of security controls for a particular mobile app. MASVS V1 also lists requirements pertaining to the architecture and design of the mobile apps, as well as general processes and activities that should be part of the development process. | |
| − | + | == Mobile App Security Education == | |
| − | + | The [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg Mobile Security Testing Guide] can be used as a standalone learning resource. Its main chapters contain general how-tos and tutorials that cover a variety of topics from mobile OS internals to advanced reverse engineering techniques. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | = Sponsorship Packages = | |
| + | With the Mobile Security Testing Guide sponsorship packages, we offer companies opportunities to create brand awareness and maximize visibility in the mobile security space. A limited amount of sponsorship packages will be made available shortly through our crowdfunding campaign. | ||
| − | + | The following packages will be available (or [[:File:MSTG-Sponsor-Packages.pdf|download as PDF]] ): | |
| − | + | === Good Samaritan (USD 500) === | |
| + | * Listed as supporter on the project website and GitHub | ||
| + | * Listed as supporter in the printed and ebook versions | ||
| + | * 5 Paperback Books | ||
| − | == | + | === Honourable Benefactor (USD 2,000 / 8 Available) === |
| + | * Small company logo in the “Honourable Benefactors” section on project website and Github | ||
| + | * Small company logo on the sponsors page of the printed and ebook versions | ||
| + | * 10 Paperback Books | ||
| − | + | === God Mode Sponsor (USD 4,000 / 5 Available) === | |
| − | + | * Large company logo in the “God mode sponsors” section on project website and Github | |
| − | + | * Large company logo on the sponsors page of the printed and ebook versions | |
| − | + | * 20 Paperback Books | |
| − | + | == Pre-book a package == | |
| − | + | Contact [mailto:sven.schleier@owasp.org Sven Schleier] to reserve your slot. We will contact you as soon as the packages become available. | |
| − | + | ==Why Sponsors?== | |
| − | + | As it turns out, writing a book to a professional standard is a challenging task, even more so if there's 50+ authors that aren't necessarily native speakers. Also, professional editors, graphic designers and layouters don't work for free. Thus, some funds are needed to make the tech book a reality. | |
| − | + | 100% of the funds raised go directly into the project budget and will be used to fund production of the final release, including: | |
| − | + | * Editing and proofreading by professional editors | |
| + | * Graphic design and layout | ||
| − | + | Any leftover funds will be donated to the OWASP Foundation to the mobile security project for future use. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | =News= | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==October 2nd, 2019: MSTG Playground release! == | |
| + | Want more training apps? We hear you! We just released the MSTG-Android-Java & MSTG-Android-Kotlin for Android and the MSTG-JWT app for iOS. Come and check it out at [https://github.com/OWASP/MSTG-Hacking-Playground/releases the release page] ! With special thanks to Sven Schleier(@sushi2k), Wen Bin Kong (@kongwenbin), Nikhil Soni (@nikhil), and Ryan Teoh (@ryantzj)! | ||
| − | + | ==October 2nd, 2019: MSTG Project joins Hacktoberfest! == | |
| − | + | We are joining the #hacktoberfest October 2-31. Check out our issues [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/labels/Hacktoberfest at Github]. Register at https://hacktoberfest.digitalocean.com. | |
| + | |||
| + | ==September 17th, 2019: Xamarin experiment! == | ||
| + | We have launched a react-native experiment based on our compliancy checklist. Want to teach others how to validate React NAtive apps against the MASVS? Check [https://drive.google.com/open?id=1UL1yLRREJwXfe0HlrcX-IuvPYQM7lTtG this Google sheet]!. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == September 6th, 2019: Flutter experiment! == | ||
| + | We have launched a react-native experiment based on our compliancy checklist. Want to teach others how to validate React NAtive apps against the MASVS? Check [https://drive.google.com/open?id=1wHK3VI1cU1xmYrCu9yb5OHKUEeLIPSkC this Google sheet]!. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == September 6th, 2019: React native experiment! == | ||
| + | We have launched a react-native experiment based on our compliancy checklist. Want to teach others how to validate React NAtive apps against the MASVS? Check [https://drive.google.com/open?id=1P5FZ_Bup5eSPOmkePZA8cIpKGOKvngkN this Google sheet]!. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == August 29th, 2019: Carlos Holguera joins the leaderteam == | ||
| + | We are happy to announce that Carlos Holguera joins us as an official MSTG Author and co-leader! With a team of 3 we hope to march further as that would make our lives easier given that all of this hard work is done by volunteers! | ||
| + | |||
| + | == August 4th, 2019: OSS Release! == | ||
| + | After a lot of work, we finally have a new release of the MSTG! Want to know more? Head over to the [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/releases Github release page] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == August 2nd, 2019: Project promoted to Flagship status! == | ||
| + | We have been awarded Flagship status! We are very grateful and excited about this! We could not have done this without our team of awesome volunteers that have committed to the project, wrote issues, and supported us in many other ways. A special thanks goes out to OWASP and especially Harold Blankenship for facilitating us to function as a project and for leading the project review at OWASP Appsec Tel-Aviv! | ||
| + | Thank you! | ||
| + | |||
| + | == June 5th, 2019: New release of the MASVS == | ||
| + | As the summit is progressing, so are we! We have just released a new version of the MASVS (1.1.4). Want to know more? Head over to the [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-masvs/releases Github release page]! | ||
| + | |||
| + | == May 21nd, 2019: New release of the MSTG == | ||
| + | As part of the preparations for the Open Security Summit, we have released a new version of the MSTG. Want to know more? Head over to the [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/releases Github release page] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == May 7th, 2019: New release of the MSTG == | ||
| + | After many changes, we decided it was time to create a new release in order to improve the book version! Want to know more? Head over to the [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/releases Github release page] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == April 15th, 2019: Book version, project promotion & preparation for the summit == | ||
| + | Given that most news is already shared via OWASP Slack over the last quarter, we still see that it is good to share a summary of all of the good things outside of Slack using this news section. In this update we have a lot to share! While we started off this year with an improved version of the MASVS and MSTG, things have not been quiet: there has been a huge development in master of the MSTG and many issues have been raised and fixed. In the meantime, we have worked on an actual print of the book! While an early version is available through Hulu (no link supplied, google and buy at your own risk), we are working on making a better version of that book. In the mean time we have filed for a project promotion to Flagship! | ||
| + | Next a lot more cool things happened: with the now official publication of [https://csrc.nist.gov/news/2019/nist-publishes-sp-800-163-rev-1 NIST Special Publication (SP) 800-163 Revision 1], the MASVS and MSTG are getting more mainstream ;-). The MASVS & MSTG are mentioned in various other upcoming programs/standards/recommendations as well, which is really a recognition of the hard work put in by the community. We are proud to be part of such a great project! | ||
| + | Next, we are preparing to join the [https://opensecsummit.org/tracks/mobile/ Open Security Summit] again! Already three people will be on site, and at least one remoting, but we would love to work with more people at the project again! | ||
| + | Want to know more? Please get in touch via Slack and join the #project-mobile_omtg channel or follow us on [https://twitter.com/OWASP_MSTG Twitter]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == January 15th, 2019: Release of improved checklist == | ||
| + | We released a new version of the checklist! This version has adaptable references so that it can be used with newer versions of the MSTG as well. This version is currently available in French and English and we hope to add the Russian, Japanese, German and Spanish version soon! Want to know more? Take a look at [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/releases/tag/1.1-excel our release page!]. We would like to thank our volunteers for their effort to deliver these easy to use checklists! | ||
| + | |||
| + | == January 3rd, 2019: Multilnaguage Release 1.1.2 of the MASVS== | ||
| + | We released the 1.1.2 version of the OWASP MAVS! This is the first version in Chinese, English, French, German, Japanese, Russian, and Spanish! Exactly: we just added French, German, Japanese and Chinese! Obviously this would not be possible without all the volunteers that helped us with translations, feedback, updating, and automating the release proces! We are grateful for the awesome team that pulled this off! Want to see the result? Take a look at [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-masvs/releases/tag/1.1.2 our release page!] | ||
| − | == | + | == November 39th, 2018: Release 1.1.0 of the MSTG== |
| + | We released the 1.1.0 version of the OWASP MSTG! Now all requirements of the MASVS have at least one covering testcase. We would like to thank all of our contributors for their hard work! Want to check it out? [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-masvs/releases Check the releases!]. | ||
| − | + | == Oktober 28th, 2018: Call for Company references== | |
| − | + | We are looking for company references that are using or have used the OWASP-MSTG and/or MASVS. If you have done so and are ok with being mentioned: please email to [email protected]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | The | + | == Oktober 28th, 2018: The MASVS is getting more translations== |
| + | Thanks to Romuald, Koki and many others, new translations of the MASVS are popping up. We now have a Japanese translation added and the French, German and Persian translations are in development. Each of them will be released the moment our release-automation of the MASVS is completed. Until then: feel free to checkout the sources! | ||
| − | + | == Oktober 18th, 2018: The MSTG is now officially an OWASP Lab Project!== | |
| + | During AppSec US 2018 in San Jose the Mobile Security Testing Guide was reviewed by several volunteers to assess the maturity of the project. As a result our request for project graduation to lab status was granted. The reviews can be found here [https://docs.google.com/a/owasp.org/document/d/1WiHln8igTE5noquodwWCo_VuRmvnpQtEhGV6z-P37EU/edit?usp=drive_web]. | ||
| − | + | Thanks to Harold Blankenship for organising the project review event during AppSec US and for pushing things forward for all the OWASP projects and of course to all people that took the effort to review our project! | |
| − | + | == Oktober 13th, 2018: MSTG 1.0.2 released & Twitter account!== | |
| − | + | While working hard towards the 1.1.0 milestone of the MSTG, we released the 1.0.2 version. From now onward we have better PDF, Epub and Mobi files! We hope to port this to the MASVS after the Github release. We now have an official [https://twitter.com/OWASP_MSTG Twitter account: @OWASP_MSTG]! | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | == September 21th, 2018: MASVS automation started == | ||
| + | Now that the document generation process for the MSTG has been optimized enough for milestone 1.1.0 (and we reached #1000 in Github of issues and Pull requests), we have started to improve the MASVS releasing mechanism. This will be further improved after Appsec USA and the release of 1.1.0 of the MSTG. | ||
| − | + | == September 16th, 2018: MSTG 1.0.1 released == | |
| + | The Mobile Security Testing Guide version 1.0.1 has been released using our automated release system (based on tagging). See the CHANGELOG.md for all the changes. We now have added pdf support and improved our .docx quiet a lot. We will further improve the release process for the pdf and epubs after milestone 1.1.0. | ||
| − | == | + | == September 1st, 2018: Mobile Security Testing Guide mentioned in NIST SP-163r1 == |
| + | The Mobile Security Testing Guide is now reference in [https://csrc.nist.gov/CSRC/media/Publications/sp/800-163/rev-1/error/documents/sp800-163r1-draft.pdf NIST SP 800-163 Revision 1] . | ||
| − | + | == Augustus 2nd, 2018: Mobile App Security Verification Standard Releases == | |
| − | + | A lot has happened & we are happy to announce that version 1.1 of the MASVS got released! Not just in English, but in Spanis and Russian as well. Want to know more? [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-masvs/releases check the releases!]. | |
| − | + | We would like to thank our Russian and Spanish speaking volunteers that have put quiet some effort in translating the document! | |
| − | + | Lastly, we would like to announce that not all minor version releases will be in this news-section, unless something really important changed. Do you want to have the latest version of the MASVS? Just check Github! | |
| − | + | == June 16th, 2018: Jeroen Willemsen joins as project lead == | |
| + | Jeroen Willemsen has joined as a proejct leader for the OMTG project. | ||
| + | == June 15th, 2018: Mobile Security Testing Guide - Release 1.0 == | ||
| + | The Mobile Security Testing Guide is now [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg#reading-the-mobile-security-testing-guide available for download in various formats] . This is the first release of the MSTG and is a great community effort. We want to thank [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/graphs/contributors all contributors] through this great journey. Thank you! | ||
| − | == | + | == January 13th, 2018: Mobile App Security Verification Standard Release 1.0 == |
| + | [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-masvs/releases/download/1.0/OWASP_Mobile_AppSec_Verification_Standard_v1.0.pdf Version 1.0] of the MASVS is now [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-masvs/releases/download/1.0/OWASP_Mobile_AppSec_Verification_Standard_v1.0.pdf available for download] . This release contains several bug fixes and modifications to security requirements and is our first release. | ||
| − | + | == September 14th, 2017: Mobile App Security Verification Standard Update == | |
| − | + | Version 0.9.4 of the MASVS is now [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-masvs/releases/tag/0.9.4 available for download] . This release contains several bug fixes and modifications to security requirements. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == July 5th, 2017: Sponsorship Packages Announced == | |
| − | + | We are happy to announce that a limited amount of [[:File:MSTG-Sponsor-Packages.pdf|sponsorship packages]] will be made available shortly through our crowdfunding campaign. With these packages, we offer companies opportunities to create brand awareness and maximize visibility in the mobile security space. 100% of the funds raised go directly into the project budget and will be used to fund production of the final release. | |
| − | + | == June 17th, 2017: The OWASP Mobile Security Testing Guide - Summit Preview == | |
| + | |||
| + | The MSTG Summit Preview is an experimental proof-of-concept book created on the OWASP Summit 2017 in London. The goal was to improve the authoring process and book deployment pipeline, as well as to demonstrate the viability of the project. Note that the content is not final and will likely change significantly in subsequent releases. | ||
| − | + | Download the ebook [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/releases/download/1.0/owasp-mstg-summit-edition.epub here]. | |
| − | |||
| − | == | + | == Mobile Security Testing Workshop on the OWASP Summit 2017 == |
| + | |||
| + | The OWASP MSTG team is organizing a 5-days mobile security track on the OWASP Summit 2017. The track consists of a series of book sprints, each of which focuses on producing content for a specific section in the OWASP MSTG, as well as proof-reading and editing the existing content. The goal is to make as much progress on the guide as is humanly possible. Depending on the number of participants, we’ll split into sub-groups to work on different subsections or topic areas. | ||
| − | + | === How to Join === | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Join up for the working session(s) you like by following the link(s) on the [http://owaspsummit.org/Working-Sessions/Mobile-Security/ mobile security track page], then hitting the "Edit this page here" link at the bottom, and adding yourself to the "participants" field. Signing up is not mandatory, but helps us to better organize the sessions. Don’t worry though if your session of choice happens on the "wrong" day - you can always simply stop by and we’ll brief you on your topic of choice. After all, this is the Woodstock of appsec! | |
| − | + | Mobile security track main page: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | http://owaspsummit.org/Working-Sessions/Mobile-Security/ | |
| − | + | Mobile security track schedule: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | http://owaspsummit.org/schedule/tracks/Mobile-Security.html/ | |
| − | |||
| − | == | + | == April 5th, 2017: Mobile App Security Verification Standard Update == |
| + | |||
| + | Version 0.9.3 of the MASVS is now [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-masvs/releases/tag/0.9.3 available for download] . This release contains several bug fixes and modifications to security requirements: | ||
| − | + | * Merged requirements 7.8 and 7.9 into for simplification | |
| − | + | * Removed Anti-RE controls 8.1 and 8.2 | |
| − | + | * Updated MSTG links to current master | |
| − | + | * Section "Environmental Interaction" renamed to "Platform Interaction" | |
| + | * Removed To-dos | ||
| + | * Fixed some wording & spelling issues | ||
| − | + | == January 31st, 2017: Mobile App Security Verification Standard v0.9.2 Available For Download == | |
| + | |||
| + | The Mobile App Security Verification Standard (MASVS) has undergone a major revision, including a re-design of the security model and verification levels. We also revised many security requirements to address the multitude of [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-masvs/issues?q=is%3Aissue%20 issues raised on GitHub]. The result is MASVS v0.9.2, which is now [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-masvs/releases/tag/0.9.2 available for download in PDF format]. | ||
| − | + | As the MASVS is nearing maturity, we have decided to freeze the requirements until the Mobile Testing Guide and checklists "catch up" (due to the one-to-one mapping between requirements in the MASVS and MSTG, changes to the requirements make it necessary to update the other documents as well, causing repeated effort). Unless major issues pop up, the current list will therefore remain in place until MASVS/MSTG v1.0, and further changes will be reserved for v1.1 or later releases. | |
| − | + | The MASVS is a community effort to establish security requirements for designing, developing and testing secure mobile apps on iOS and Android. Join the [https://owasp.slack.com/messages/project-mobile_omtg/details/ OWASP Mobile Security Project Slack Channel] to meet the project members! You can sign up for an account [https://join.slack.com/t/owasp/shared_invite/enQtNjExMTc3MTg0MzU4LTViMDg1MmJiMzMwZGUxZjgxZWQ1MTE0NTBlOTBhNjhhZDIzZTZiNmEwOTJlYjdkMzAxMGVhNDkwNDNiNjZiOWQ here]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | {| | + | == January 28th, 2017: Mobile Crackmes and Reversing Tutorials == |
| + | {| cellpadding="5" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | [[File:uncrackable-250.png|link=]] | |
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | A key goal of the OWASP Mobile Testing Project is to build the ultimate learning resource and reference guide for mobile app reversers. As hands-on hacking is by far the best way to learn, we'd like to link most of the content to practical examples. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Starting now, we'll be adding [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/tree/master/Crackmes crackmes for Android and iOS] to the [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg GitHub repo] that will then be used as examples throughout the guide. The goal is to collect enough resources for demonstrating the most important tools and techniques in our guide, plus additional crackmes for practicing. For starters there are three challenges: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | * [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/tree/master/OMTG-Files/02_Crackmes/01_Android/01_License_Validation Android License Validator] | |
| − | + | * [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/tree/master/Crackmes/iOS/Level_01/ Uncrackable App for iOS Level 1] | |
| − | + | * [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/tree/master/Crackmes/iOS/Level_02/ Uncrackable App for iOS Level 2] | |
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | One of these three already has a [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/blob/master/Document/0x05b-Reverse-Engineering-and-Tampering-Android.md#symbolicexec documented solution] in the guide. Tutorials for solving the other two [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/blob/master/OMTG-Files/02_Crackmes/List_of_Crackmes.md still need to be added]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === We Need More Authors and Contributors! === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Maybe you have noticed that [https://rawgit.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/master/Generated/OWASP-MSTG-Table-of-Contents.html the reverse engineering sections in the Mobile Testing Guide are incomplete]. The reason: We're still in the starting stages and don't have a lot of authors and contributors (in fact, 99% of the reversing content was produced by one guy). We'd love to welcome *you* as a contributor of crackmes, tutorials, writeups, or simply new ideas for this project. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== What You Can Do ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The OWASP MSTG is an open project and there's a lot of flexibility - it mostly depends on your skill set and willingness to commit your time. That said, the some areas that need help are: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Solving crackmes and contributing a tutorial to the guide (preferable a technique that's not already documented. Check the [https://rawgit.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/master/Generated/OWASP-MSTG-Table-of-Contents.html TOC] first). | ||
| + | * Writing and adding new crackmes along with solutions (should also describe something not already in the guide. Cracking white-boxes, dynamic analysis using an emulator / introspection, etc. etc.). | ||
| + | * General reversing write-ups to describe specific processes and techniques | ||
| + | * Help us figure out [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/blob/master/Document/0x07b-Assessing_Software_Protections.md resiliency testing processes] and [https://github.com/b-mueller/obfuscation-metrics obfuscation metrics] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The reversing part of the guide consists of the following chapters: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/blob/master/Document/0x05-Testing-Processes-and-Techniques.md#tampering-and-reverse-engineering Tampering and Reverse Engineering - General Overview] | ||
| + | * [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/blob/master/Document/0x05b-Reverse-Engineering-and-Tampering-Android.md#tampering-and-reverse-engineering-on-android Tampering and Reverse Engineering on Android] | ||
| + | * [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/blob/master/Document/0x05d-Reverse-Engineering-and-Tampering-iOS.md#tampering-and-reverse-engineering-on-ios Tampering and Reverse Engineering on iOS] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== How To Join ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Read the [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/blob/master/authors_guide.md author's guide] first, and join the [https://owasp.slack.com/messages/project-mobile_omtg/details/ OWASP Mobile Security Project Slack Channel], where you'll find all the other project members. You can sign up for an account [https://join.slack.com/t/owasp/shared_invite/enQtNjExMTc3MTg0MzU4LTViMDg1MmJiMzMwZGUxZjgxZWQ1MTE0NTBlOTBhNjhhZDIzZTZiNmEwOTJlYjdkMzAxMGVhNDkwNDNiNjZiOWQ here]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == January 22nd, 2017: Mobile Testing Guide TOC Available == | ||
| + | |||
| + | As of now, we'll be auto-generating a [https://rawgit.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/master/Generated/OWASP-MSTG-Table-of-Contents.html table of contents] out of the current MSTG master branch. This reflects the current state of the guide, and should make it easier to coordinate work between authors. A short-term goal is to finalize the structure of the guide so we get a clearer picture of what will be included in the final document. Lead authors are encouraged to complete the outline of their respective chapters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''On another note, we still need additional authors to help with all sections of the guide, including mobile operating system overviews, testing processes and techniques, and reverse engineering.''' Especially iOS authors are in short supply! As usual, ping us on the [https://owasp.slack.com/messages/project-mobile_omtg/details/ Slack Channel] if you want to contribute. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == December 4th, 2016: Call For Authors: The Ultimate Open-Source Mobile App Reverse Engineering Guide == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Reverse engineering is an art, and describing every available facet of it would fill a whole library. The sheer range techniques and possible specializations is mind-blowing: One can spend years working on a very specific, isolated sub-problem, such as automating malware analysis or developing novel de-obfuscation methods. For mobile app security testers, it can be challenging to filter through the vast amount of information and build a working methodology. Things become even more problematic when one is tasked to assess apps that are heavily obfuscated and have anti-tampering measures built in. | ||
| + | |||
| + | One of the main goals in the MSTG is to build the ultimate resource for mobile reverse engineers. This includes not only basic static and dynamic analysis, but also advanced de-obfuscation, scripting and automation. Obviously, writing all this content is a lot of work, both in terms of general content and OS-specific how-tos. We're therefore looking for talented authors that want to join the project early on. Topics include the following: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Basic Hybrid Static/Dynamic Analysis | ||
| + | * Code Injection and Dynamic Instrumentation (Substrate, FRIDA) | ||
| + | * Dynamic Binary Instrumentation (Valgrind, PIE) | ||
| + | * Analysis Frameworks (Metasm / Miasm) | ||
| + | * Symbolic Execution | ||
| + | * DCA and DPA attacks on white-box crypto | ||
| + | * Dynamic analysis frameworks (PANDA / DroidScope,...) | ||
| + | * Anything else we might have missed | ||
| + | |||
| + | === What is in for me? === | ||
| + | |||
| + | All of this is unpaid, volunteer work. However, depending on your contribution, you will be named in the "lead authors" or "contributors" list, and you'll be able to point to the fact that you co-authored the guide. You'll also be contributing to the field, helping others who are just starting out, and in turn becoming a happier person yourself (reaping the full benefits of your altruism). | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Where do I sign up? === | ||
| + | |||
| + | First of all, have a look at the existing RE chapters outline: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/blob/master/Document/0x05-Testing-Processes-and-Techniques.md#tampering-and-reverse-engineering Generic / Introduction] | ||
| + | * [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/blob/master/Document/0x05b-Reverse-Engineering-and-Tampering-Android.md Android] | ||
| + | * [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/blob/master/Document/0x05d-Reverse-Engineering-and-Tampering-iOS.md#tampering-and-reverse-engineering-on-ios iOS] | ||
| + | |||
| + | You'll probably immediately have ideas on how you can contribute. If that's the case, read the [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/blob/master/authors_guide.md author's guide] first. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then contact [https://github.com/b-mueller Bernhard Mueller] - ideally directly on the [https://owasp.slack.com/messages/project-mobile_omtg/details/ OWASP Mobile Security Project Slack Channel], where you'll find all the other project members. You can sign up for an account [https://join.slack.com/t/owasp/shared_invite/enQtNjExMTc3MTg0MzU4LTViMDg1MmJiMzMwZGUxZjgxZWQ1MTE0NTBlOTBhNjhhZDIzZTZiNmEwOTJlYjdkMzAxMGVhNDkwNDNiNjZiOWQ here]. | ||
=FAQs= | =FAQs= | ||
| − | + | == Project Roadmap == | |
| − | + | The current project Roadmap can be found in our Github Project: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/projects/2 | |
| + | |||
| + | This Github Project summarizes the status of the tickets we are working on for the latest milestone. | ||
| + | A list of the planned milestones are available in Github Isses: https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/milestones | ||
==How can I participate in your project?== | ==How can I participate in your project?== | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | '''We are searching for additional authors, reviewers and editors.''' The best way to get started is to browse the [https://b-mueller.gitbooks.io/owasp-mobile-security-testing-guide/content/ existing content]. Also, check the [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/projects/1 project dashboard] for a list of open tasks. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Drop a us line on the [https://owasp.slack.com/messages/project-mobile_omtg/details/) Slack channel] before you start working on a topic. This helps us to keep track of what everyone is doing and prevent conflicts. You can create a Slack account here: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://join.slack.com/t/owasp/shared_invite/enQtNjExMTc3MTg0MzU4LWQ2Nzg3NGJiZGQ2MjRmNzkzN2Q4YzU1MWYyZTdjYjA2ZTA5M2RkNzE2ZjdkNzI5ZThhOWY5MjljYWZmYmY4ZjM owasp slack invite] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Before you start contributing, please read our brief [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/blob/master/style_guide.md style guide] which contains a few basic writing rules. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If there's something you really want to see in the guide, or you want to suggest an improvement, create an issue [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/issues issue] or ping us on [https://owasp.slack.com/messages/project-mobile_omtg/details/ Slack]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Where do you guys need help the most?== | ||
| + | |||
| + | There's a lot of areas where you can help out: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Writing original content, such as describing testing processes and writing test cases. We're all doing this in our spare time, which unfortunately means that things sometimes slow down to a crawl. If you're knowledgeable in some area and have time available, we'd be incredibly thankful to anyone who contributes, even if it's only one or two test cases. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Reviewing content and giving feedback. The proper channel for questions and feedback is the GitHub issues system of the respective repo, contacting us on [https://owasp.slack.com/messages/project-mobile_omtg/details/ OWASP Mobile Security Project Slack Channel] is another possibility. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Developing tools. For example, we still don't have an automated way of generating checklists out of the GitHub repo. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Contributing to auxiliary projects: There are various projects that we support at this moment, consider: [https://github.com/OWASP/Mobile-Threatmodel the mobile threatmodel project] and our own [https://github.com/OWASP/MSTG-Hacking-Playground Hacking playground]. In the past, there was the [https://github.com/b-mueller/obfuscation-metrics obfuscation metrics project] is an auxiliary project that deals with specific forms of control flow and data obfuscation. This project needs experts in advanced obfuscation / de-obfuscation. Please contact us if you have experience in this area. | ||
==If I am not a programmer can I participate in your project?== | ==If I am not a programmer can I participate in your project?== | ||
| − | Yes, you can certainly participate in the project if you are not a programmer or technical. The project needs different skills and expertise and different times during its development. Currently, we are looking for researchers, writers, graphic designers, and a project administrator. | + | Yes, you can certainly participate in the project if you are not a programmer or technical. The project needs different skills and expertise and different times during its development. Currently, we are looking for researchers, writers, graphic designers, and a project administrator. |
| + | |||
| + | ==I contributed to the original Google Doc, but I'm not credited in the new version of the MSTG? == | ||
| + | As we migrated some of the existing content, we did our best to backtrack the original authors and credit them appropriately. We also added a [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/blob/master/Document/0x02-Frontispiece.md revision history] that lists all the authors from old Google Docs. If you are not on that list but feel you should be, please contact [https://github.com/sushi2k Sven] and he'll fix it. Or better yet, re-join the author's team and start contributing to the new guide. | ||
= Acknowledgements = | = Acknowledgements = | ||
| − | ==Contributors== | + | == Acknowledgments == |
| + | |||
| + | === Authors === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Bernhard Mueller ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Bernhard is a cyber security specialist with a talent in hacking all kinds of systems. During more than a decade in the industry, he has published many zero-day exploits for software such as MS SQL Server, Adobe Flash Player, IBM Director, Cisco VOIP and ModSecurity. If you can name it, he has probably broken it at least once. His pioneering work in mobile security was commended with a BlackHat "Best Research" Pwnie Award. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Sven Schleier ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sven is an experienced penetration tester and security architect who specialized in implementing secure SDLC for web application, iOS and Android apps. He is a project leader for the OWASP Mobile Security Testing Guide and the creator of OWASP Mobile Hacking Playground. Sven also supports the community with free hands-on workshops on web and mobile app security testing. He has published several security advisories and a white papers about a range of security topics. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Jeroen Willemsen ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Jeroen is a principal security architect at Xebia with a passion for mobile security and risk management. He has supported companies as a security coach, a security engineer and as a full-stack developer, which makes him a jack of all trades. He loves explaining technical subjects: from security issues to programming challenges. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Carlos Holguera ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Carlos is a security engineer leading the mobile penetration testing team at ESCRYPT. He has gained many years of hands-on experience in the field of security testing for mobile apps and embedded systems such as automotive control units and IoT devices. He is passionate about reverse engineering and dynamic instrumentation of mobile apps and is continuously learning and sharing his knowledge. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Co-Authors === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Romuald Szkudlarek ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Romuald is a passionate cyber security & privacy professional with over 15 years of experience in the Web, Mobile, IoT and Cloud domains. During his career, he has been dedicating spare time to a variery of projects with the goal of advancing the sectors of software and security. He is also teaching at various institutions. He holds CISSP, CSSLP and CEH credentials. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Jeroen Beckers ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Jeroen is the mobile security lead at NVISO where he is responsible for quality assurance on mobile security projects and for R&D on all things mobile. He worked as a Flash developer during high school and college, but switched to a career in cybersecurity once he graduated and now has more than 5 years of experience in mobile security. He loves sharing his knowledge with other people, as is demonstrated by his many talks & trainings at colleges, universities, clients and conferences. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Top Contributors === | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Pawel Rzepa | ||
| + | * Francesco Stillavato | ||
| + | * Henry Hoggard | ||
| + | * Andreas Happe | ||
| + | * Kyle Benac | ||
| + | * Alexander Anthuk | ||
| + | * Wen Bin Kong | ||
| + | * Abdessamad Temmar | ||
| + | * Bolot Kerimbaev | ||
| + | * Cláudio André | ||
| + | * Slawomir Kosowski | ||
| + | * Abderrahmane Aftahi | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Contributors === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Contributors have contributed quality content and have at least 50 additions logged in the GitHub repository. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Abderrahmane Aftahi, Jin Kung Ong, Koki Takeyama, Sjoerd Langkemper, Gerhard Wagner, Michael Helwig, Pece Milosev, Ryan Teoh, Denis Pilipchuk, Dharshin De Silva, Anatoly Rosencrantz, Abhinav Sejpal, José Carlos Andreu, Dominique Righetto, Raul Siles, Daniel Ramirez Martin, Yogesh Sharma, Enrico Verzegnassi, Nick Epson, Emil Tostrup, Prathan Phongthiproek, Tom Welch, Luander Ribeiro, Heaven L. Hodges, Dario Incalza, Akanksha Bana, Oguzhan Topgul, Vikas Gupta, Sijo Abraham, David Fern, Pishu Mahtani, Anuruddha E., Shiv Sahni | ||
| − | + | === Reviewers === | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * Anant Shrivastava | |
| + | * Sjoerd Langkemper | ||
| − | + | === Others === | |
| − | + | The full list of contributors, including those with less than 50 additions logged, is available on [https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/graphs/contributors GitHub]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | = | + | === Sponsors === |
| + | While both the MASVS and the MSTG are created and maintained by the community on a voluntary basis, sometimes a little bit of outside help is required. We therefore thank our sponsors for providing the funds to be able to hire technical editors. Note that their sponsorship does not influence the content of the MASVS or MSTG in any way. The sponsorship packages are described on the OWASP Project Wiki. | ||
| − | + | '''Honourable Benefactor''' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:NowSecure logo.png|SecureNow|x50px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | === Old Version - MSTG "Beta" on Google Drive === | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The Mobile Security Testing Guide was initiated by [https://www.owasp.org/index.php/User:Milan_Singh_Thakur Milan Singh Thakur] in 2015. The original document was hosted on Google Drive. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Authors:''' | |
| − | + | Mirza Ali, Stephen Corbiaux, Ryan Dewhurst, Mohammad Hamed Dadpour, David Fern, Ali Yazdani, Bao Lee, Anto Joseph, Nutan Kumar Panda, Rahil Parikh, Julian Schütte, Abhinav Sejpal, Anant Shrivastava, Pragati Singh, Milan Singh Thakur, Stephanie Vanroelen, Gerhard Wagner | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Reviewers:''' | |
| + | Andrew Muller, Jonathan Carter, Stephanie Vanroelen, Milan Singh Thakur | ||
<!-- DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE THE TEXT ON NEXT LINE --> | <!-- DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE THE TEXT ON NEXT LINE --> | ||
| − | __NOTOC__ <headertabs /> | + | __NOTOC__ <headertabs></headertabs> |
| − | [[Category:OWASP Project]] [[Category:OWASP_Builders]] [[Category:OWASP_Defenders]] [[Category:OWASP_Document]] | + | [[Category:OWASP Project]] |
| + | [[Category:OWASP_Builders]] | ||
| + | [[Category:OWASP_Defenders]] | ||
| + | [[Category:OWASP_Document]] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:15, 1 November 2019
Maintenance noticeThis site is no longer maintained: please go to https://www2.owasp.org/www-project-mobile-security-testing-guide/ for our new website!
Our Vision"Define the industry standard for mobile application security."We are writing a security standard for mobile apps and a comprehensive testing guide that covers the processes, techniques, and tools used during a mobile app security test, as well as an exhaustive set of test cases that enables testers to deliver consistent and complete results. Main Deliverables
|
Classifications
Project LeadersTraining
Presentations
LicensingThe guide is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 license, so you can copy, distribute and transmit the work, and you can adapt it, and use it commercially, but all provided that you attribute the work and if you alter, transform, or build upon this work, you may distribute the resulting work only under the same or similar license to this one. | |||||||||||||||
Using the OWASP Mobile App Security Verification Standard, Testing Guide and Checklist
The documents produced in this project cover many aspects of mobile application security, from the high-level requirements to the nitty-gritty implementation details and test cases. They can be used to plan and verify security controls during any phase of mobile app development, as well as during pre-release code review and penetration testing.
- The Mobile Application Security Verification Standard (MASVS) contains generic security requirements along with mappings to verification levels that can be chosen depending on the overall need for security.
- The Mobile Security Testing Guide (MSTG) provides verification instructions for each requirement in the MASVS, as well as security best practices for apps on each supported mobile operating system (currently Android and iOS). It is also useful as a standalone learning resource and reference guide for mobile application security testers.
- The Mobile App Security Checklist can be used to apply the MASVS requirements during practical assessments. It also conveniently links to the MSTG test case for each requirement, making mobile penetration testing a breeze.
It is important to note that the security standard, testing guide and checklists are closely related: They all map to the same basic set of requirements. Depending on the context, the documents can be used stand-alone or in combination to achieve different objectives.
For example, the MASVS requirements may be used in the planning and architecture design stages, while the checklist and testing guide may serve as a baseline for manual security testing or as a template for automated security tests.
Mobile App Security Testing
The checklist works great as a reference during mobile app security assessments. You can walk through the requirements one-by-one - for more information on each requirement, simply click on the link in the "Testing procedures" column. Or, fill out the checklist at the end of an assessment to ensure completeness.
Security Engineering in the SDLC
Properly defined security requirements are an important part of the Secure SDLC. The MASVS levels can be used along with threat modeling to determine the appropriate set of security controls for a particular mobile app. MASVS V1 also lists requirements pertaining to the architecture and design of the mobile apps, as well as general processes and activities that should be part of the development process.
Mobile App Security Education
The Mobile Security Testing Guide can be used as a standalone learning resource. Its main chapters contain general how-tos and tutorials that cover a variety of topics from mobile OS internals to advanced reverse engineering techniques.
With the Mobile Security Testing Guide sponsorship packages, we offer companies opportunities to create brand awareness and maximize visibility in the mobile security space. A limited amount of sponsorship packages will be made available shortly through our crowdfunding campaign.
The following packages will be available (or download as PDF ):
Good Samaritan (USD 500)
- Listed as supporter on the project website and GitHub
- Listed as supporter in the printed and ebook versions
- 5 Paperback Books
Honourable Benefactor (USD 2,000 / 8 Available)
- Small company logo in the “Honourable Benefactors” section on project website and Github
- Small company logo on the sponsors page of the printed and ebook versions
- 10 Paperback Books
God Mode Sponsor (USD 4,000 / 5 Available)
- Large company logo in the “God mode sponsors” section on project website and Github
- Large company logo on the sponsors page of the printed and ebook versions
- 20 Paperback Books
Pre-book a package
Contact Sven Schleier to reserve your slot. We will contact you as soon as the packages become available.
Why Sponsors?
As it turns out, writing a book to a professional standard is a challenging task, even more so if there's 50+ authors that aren't necessarily native speakers. Also, professional editors, graphic designers and layouters don't work for free. Thus, some funds are needed to make the tech book a reality.
100% of the funds raised go directly into the project budget and will be used to fund production of the final release, including:
- Editing and proofreading by professional editors
- Graphic design and layout
Any leftover funds will be donated to the OWASP Foundation to the mobile security project for future use.
October 2nd, 2019: MSTG Playground release!
Want more training apps? We hear you! We just released the MSTG-Android-Java & MSTG-Android-Kotlin for Android and the MSTG-JWT app for iOS. Come and check it out at the release page ! With special thanks to Sven Schleier(@sushi2k), Wen Bin Kong (@kongwenbin), Nikhil Soni (@nikhil), and Ryan Teoh (@ryantzj)!
October 2nd, 2019: MSTG Project joins Hacktoberfest!
We are joining the #hacktoberfest October 2-31. Check out our issues at Github. Register at https://hacktoberfest.digitalocean.com.
September 17th, 2019: Xamarin experiment!
We have launched a react-native experiment based on our compliancy checklist. Want to teach others how to validate React NAtive apps against the MASVS? Check this Google sheet!.
September 6th, 2019: Flutter experiment!
We have launched a react-native experiment based on our compliancy checklist. Want to teach others how to validate React NAtive apps against the MASVS? Check this Google sheet!.
September 6th, 2019: React native experiment!
We have launched a react-native experiment based on our compliancy checklist. Want to teach others how to validate React NAtive apps against the MASVS? Check this Google sheet!.
August 29th, 2019: Carlos Holguera joins the leaderteam
We are happy to announce that Carlos Holguera joins us as an official MSTG Author and co-leader! With a team of 3 we hope to march further as that would make our lives easier given that all of this hard work is done by volunteers!
August 4th, 2019: OSS Release!
After a lot of work, we finally have a new release of the MSTG! Want to know more? Head over to the Github release page
August 2nd, 2019: Project promoted to Flagship status!
We have been awarded Flagship status! We are very grateful and excited about this! We could not have done this without our team of awesome volunteers that have committed to the project, wrote issues, and supported us in many other ways. A special thanks goes out to OWASP and especially Harold Blankenship for facilitating us to function as a project and for leading the project review at OWASP Appsec Tel-Aviv! Thank you!
June 5th, 2019: New release of the MASVS
As the summit is progressing, so are we! We have just released a new version of the MASVS (1.1.4). Want to know more? Head over to the Github release page!
May 21nd, 2019: New release of the MSTG
As part of the preparations for the Open Security Summit, we have released a new version of the MSTG. Want to know more? Head over to the Github release page
May 7th, 2019: New release of the MSTG
After many changes, we decided it was time to create a new release in order to improve the book version! Want to know more? Head over to the Github release page
April 15th, 2019: Book version, project promotion & preparation for the summit
Given that most news is already shared via OWASP Slack over the last quarter, we still see that it is good to share a summary of all of the good things outside of Slack using this news section. In this update we have a lot to share! While we started off this year with an improved version of the MASVS and MSTG, things have not been quiet: there has been a huge development in master of the MSTG and many issues have been raised and fixed. In the meantime, we have worked on an actual print of the book! While an early version is available through Hulu (no link supplied, google and buy at your own risk), we are working on making a better version of that book. In the mean time we have filed for a project promotion to Flagship! Next a lot more cool things happened: with the now official publication of NIST Special Publication (SP) 800-163 Revision 1, the MASVS and MSTG are getting more mainstream ;-). The MASVS & MSTG are mentioned in various other upcoming programs/standards/recommendations as well, which is really a recognition of the hard work put in by the community. We are proud to be part of such a great project! Next, we are preparing to join the Open Security Summit again! Already three people will be on site, and at least one remoting, but we would love to work with more people at the project again! Want to know more? Please get in touch via Slack and join the #project-mobile_omtg channel or follow us on Twitter.
January 15th, 2019: Release of improved checklist
We released a new version of the checklist! This version has adaptable references so that it can be used with newer versions of the MSTG as well. This version is currently available in French and English and we hope to add the Russian, Japanese, German and Spanish version soon! Want to know more? Take a look at our release page!. We would like to thank our volunteers for their effort to deliver these easy to use checklists!
January 3rd, 2019: Multilnaguage Release 1.1.2 of the MASVS
We released the 1.1.2 version of the OWASP MAVS! This is the first version in Chinese, English, French, German, Japanese, Russian, and Spanish! Exactly: we just added French, German, Japanese and Chinese! Obviously this would not be possible without all the volunteers that helped us with translations, feedback, updating, and automating the release proces! We are grateful for the awesome team that pulled this off! Want to see the result? Take a look at our release page!
November 39th, 2018: Release 1.1.0 of the MSTG
We released the 1.1.0 version of the OWASP MSTG! Now all requirements of the MASVS have at least one covering testcase. We would like to thank all of our contributors for their hard work! Want to check it out? Check the releases!.
Oktober 28th, 2018: Call for Company references
We are looking for company references that are using or have used the OWASP-MSTG and/or MASVS. If you have done so and are ok with being mentioned: please email to [email protected].
Oktober 28th, 2018: The MASVS is getting more translations
Thanks to Romuald, Koki and many others, new translations of the MASVS are popping up. We now have a Japanese translation added and the French, German and Persian translations are in development. Each of them will be released the moment our release-automation of the MASVS is completed. Until then: feel free to checkout the sources!
Oktober 18th, 2018: The MSTG is now officially an OWASP Lab Project!
During AppSec US 2018 in San Jose the Mobile Security Testing Guide was reviewed by several volunteers to assess the maturity of the project. As a result our request for project graduation to lab status was granted. The reviews can be found here [1].
Thanks to Harold Blankenship for organising the project review event during AppSec US and for pushing things forward for all the OWASP projects and of course to all people that took the effort to review our project!
Oktober 13th, 2018: MSTG 1.0.2 released & Twitter account!
While working hard towards the 1.1.0 milestone of the MSTG, we released the 1.0.2 version. From now onward we have better PDF, Epub and Mobi files! We hope to port this to the MASVS after the Github release. We now have an official Twitter account: @OWASP_MSTG!
September 21th, 2018: MASVS automation started
Now that the document generation process for the MSTG has been optimized enough for milestone 1.1.0 (and we reached #1000 in Github of issues and Pull requests), we have started to improve the MASVS releasing mechanism. This will be further improved after Appsec USA and the release of 1.1.0 of the MSTG.
September 16th, 2018: MSTG 1.0.1 released
The Mobile Security Testing Guide version 1.0.1 has been released using our automated release system (based on tagging). See the CHANGELOG.md for all the changes. We now have added pdf support and improved our .docx quiet a lot. We will further improve the release process for the pdf and epubs after milestone 1.1.0.
September 1st, 2018: Mobile Security Testing Guide mentioned in NIST SP-163r1
The Mobile Security Testing Guide is now reference in NIST SP 800-163 Revision 1 .
Augustus 2nd, 2018: Mobile App Security Verification Standard Releases
A lot has happened & we are happy to announce that version 1.1 of the MASVS got released! Not just in English, but in Spanis and Russian as well. Want to know more? check the releases!. We would like to thank our Russian and Spanish speaking volunteers that have put quiet some effort in translating the document! Lastly, we would like to announce that not all minor version releases will be in this news-section, unless something really important changed. Do you want to have the latest version of the MASVS? Just check Github!
June 16th, 2018: Jeroen Willemsen joins as project lead
Jeroen Willemsen has joined as a proejct leader for the OMTG project.
June 15th, 2018: Mobile Security Testing Guide - Release 1.0
The Mobile Security Testing Guide is now available for download in various formats . This is the first release of the MSTG and is a great community effort. We want to thank all contributors through this great journey. Thank you!
January 13th, 2018: Mobile App Security Verification Standard Release 1.0
Version 1.0 of the MASVS is now available for download . This release contains several bug fixes and modifications to security requirements and is our first release.
September 14th, 2017: Mobile App Security Verification Standard Update
Version 0.9.4 of the MASVS is now available for download . This release contains several bug fixes and modifications to security requirements.
July 5th, 2017: Sponsorship Packages Announced
We are happy to announce that a limited amount of sponsorship packages will be made available shortly through our crowdfunding campaign. With these packages, we offer companies opportunities to create brand awareness and maximize visibility in the mobile security space. 100% of the funds raised go directly into the project budget and will be used to fund production of the final release.
June 17th, 2017: The OWASP Mobile Security Testing Guide - Summit Preview
The MSTG Summit Preview is an experimental proof-of-concept book created on the OWASP Summit 2017 in London. The goal was to improve the authoring process and book deployment pipeline, as well as to demonstrate the viability of the project. Note that the content is not final and will likely change significantly in subsequent releases.
Download the ebook here.
Mobile Security Testing Workshop on the OWASP Summit 2017
The OWASP MSTG team is organizing a 5-days mobile security track on the OWASP Summit 2017. The track consists of a series of book sprints, each of which focuses on producing content for a specific section in the OWASP MSTG, as well as proof-reading and editing the existing content. The goal is to make as much progress on the guide as is humanly possible. Depending on the number of participants, we’ll split into sub-groups to work on different subsections or topic areas.
How to Join
Join up for the working session(s) you like by following the link(s) on the mobile security track page, then hitting the "Edit this page here" link at the bottom, and adding yourself to the "participants" field. Signing up is not mandatory, but helps us to better organize the sessions. Don’t worry though if your session of choice happens on the "wrong" day - you can always simply stop by and we’ll brief you on your topic of choice. After all, this is the Woodstock of appsec!
Mobile security track main page:
http://owaspsummit.org/Working-Sessions/Mobile-Security/
Mobile security track schedule:
http://owaspsummit.org/schedule/tracks/Mobile-Security.html/
April 5th, 2017: Mobile App Security Verification Standard Update
Version 0.9.3 of the MASVS is now available for download . This release contains several bug fixes and modifications to security requirements:
* Merged requirements 7.8 and 7.9 into for simplification * Removed Anti-RE controls 8.1 and 8.2 * Updated MSTG links to current master * Section "Environmental Interaction" renamed to "Platform Interaction" * Removed To-dos * Fixed some wording & spelling issues
January 31st, 2017: Mobile App Security Verification Standard v0.9.2 Available For Download
The Mobile App Security Verification Standard (MASVS) has undergone a major revision, including a re-design of the security model and verification levels. We also revised many security requirements to address the multitude of issues raised on GitHub. The result is MASVS v0.9.2, which is now available for download in PDF format.
As the MASVS is nearing maturity, we have decided to freeze the requirements until the Mobile Testing Guide and checklists "catch up" (due to the one-to-one mapping between requirements in the MASVS and MSTG, changes to the requirements make it necessary to update the other documents as well, causing repeated effort). Unless major issues pop up, the current list will therefore remain in place until MASVS/MSTG v1.0, and further changes will be reserved for v1.1 or later releases.
The MASVS is a community effort to establish security requirements for designing, developing and testing secure mobile apps on iOS and Android. Join the OWASP Mobile Security Project Slack Channel to meet the project members! You can sign up for an account here.
January 28th, 2017: Mobile Crackmes and Reversing Tutorials

|
A key goal of the OWASP Mobile Testing Project is to build the ultimate learning resource and reference guide for mobile app reversers. As hands-on hacking is by far the best way to learn, we'd like to link most of the content to practical examples. Starting now, we'll be adding crackmes for Android and iOS to the GitHub repo that will then be used as examples throughout the guide. The goal is to collect enough resources for demonstrating the most important tools and techniques in our guide, plus additional crackmes for practicing. For starters there are three challenges: |
One of these three already has a documented solution in the guide. Tutorials for solving the other two still need to be added.
We Need More Authors and Contributors!
Maybe you have noticed that the reverse engineering sections in the Mobile Testing Guide are incomplete. The reason: We're still in the starting stages and don't have a lot of authors and contributors (in fact, 99% of the reversing content was produced by one guy). We'd love to welcome *you* as a contributor of crackmes, tutorials, writeups, or simply new ideas for this project.
What You Can Do
The OWASP MSTG is an open project and there's a lot of flexibility - it mostly depends on your skill set and willingness to commit your time. That said, the some areas that need help are:
- Solving crackmes and contributing a tutorial to the guide (preferable a technique that's not already documented. Check the TOC first).
- Writing and adding new crackmes along with solutions (should also describe something not already in the guide. Cracking white-boxes, dynamic analysis using an emulator / introspection, etc. etc.).
- General reversing write-ups to describe specific processes and techniques
- Help us figure out resiliency testing processes and obfuscation metrics
The reversing part of the guide consists of the following chapters:
- Tampering and Reverse Engineering - General Overview
- Tampering and Reverse Engineering on Android
- Tampering and Reverse Engineering on iOS
How To Join
Read the author's guide first, and join the OWASP Mobile Security Project Slack Channel, where you'll find all the other project members. You can sign up for an account here.
January 22nd, 2017: Mobile Testing Guide TOC Available
As of now, we'll be auto-generating a table of contents out of the current MSTG master branch. This reflects the current state of the guide, and should make it easier to coordinate work between authors. A short-term goal is to finalize the structure of the guide so we get a clearer picture of what will be included in the final document. Lead authors are encouraged to complete the outline of their respective chapters.
On another note, we still need additional authors to help with all sections of the guide, including mobile operating system overviews, testing processes and techniques, and reverse engineering. Especially iOS authors are in short supply! As usual, ping us on the Slack Channel if you want to contribute.
December 4th, 2016: Call For Authors: The Ultimate Open-Source Mobile App Reverse Engineering Guide
Reverse engineering is an art, and describing every available facet of it would fill a whole library. The sheer range techniques and possible specializations is mind-blowing: One can spend years working on a very specific, isolated sub-problem, such as automating malware analysis or developing novel de-obfuscation methods. For mobile app security testers, it can be challenging to filter through the vast amount of information and build a working methodology. Things become even more problematic when one is tasked to assess apps that are heavily obfuscated and have anti-tampering measures built in.
One of the main goals in the MSTG is to build the ultimate resource for mobile reverse engineers. This includes not only basic static and dynamic analysis, but also advanced de-obfuscation, scripting and automation. Obviously, writing all this content is a lot of work, both in terms of general content and OS-specific how-tos. We're therefore looking for talented authors that want to join the project early on. Topics include the following:
- Basic Hybrid Static/Dynamic Analysis
- Code Injection and Dynamic Instrumentation (Substrate, FRIDA)
- Dynamic Binary Instrumentation (Valgrind, PIE)
- Analysis Frameworks (Metasm / Miasm)
- Symbolic Execution
- DCA and DPA attacks on white-box crypto
- Dynamic analysis frameworks (PANDA / DroidScope,...)
- Anything else we might have missed
What is in for me?
All of this is unpaid, volunteer work. However, depending on your contribution, you will be named in the "lead authors" or "contributors" list, and you'll be able to point to the fact that you co-authored the guide. You'll also be contributing to the field, helping others who are just starting out, and in turn becoming a happier person yourself (reaping the full benefits of your altruism).
Where do I sign up?
First of all, have a look at the existing RE chapters outline:
You'll probably immediately have ideas on how you can contribute. If that's the case, read the author's guide first.
Then contact Bernhard Mueller - ideally directly on the OWASP Mobile Security Project Slack Channel, where you'll find all the other project members. You can sign up for an account here.
Project Roadmap
The current project Roadmap can be found in our Github Project:
https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/projects/2
This Github Project summarizes the status of the tickets we are working on for the latest milestone.
A list of the planned milestones are available in Github Isses: https://github.com/OWASP/owasp-mstg/milestones
How can I participate in your project?
We are searching for additional authors, reviewers and editors. The best way to get started is to browse the existing content. Also, check the project dashboard for a list of open tasks.
Drop a us line on the Slack channel before you start working on a topic. This helps us to keep track of what everyone is doing and prevent conflicts. You can create a Slack account here:
Before you start contributing, please read our brief style guide which contains a few basic writing rules.
If there's something you really want to see in the guide, or you want to suggest an improvement, create an issue issue or ping us on Slack.
Where do you guys need help the most?
There's a lot of areas where you can help out:
- Writing original content, such as describing testing processes and writing test cases. We're all doing this in our spare time, which unfortunately means that things sometimes slow down to a crawl. If you're knowledgeable in some area and have time available, we'd be incredibly thankful to anyone who contributes, even if it's only one or two test cases.
- Reviewing content and giving feedback. The proper channel for questions and feedback is the GitHub issues system of the respective repo, contacting us on OWASP Mobile Security Project Slack Channel is another possibility.
- Developing tools. For example, we still don't have an automated way of generating checklists out of the GitHub repo.
- Contributing to auxiliary projects: There are various projects that we support at this moment, consider: the mobile threatmodel project and our own Hacking playground. In the past, there was the obfuscation metrics project is an auxiliary project that deals with specific forms of control flow and data obfuscation. This project needs experts in advanced obfuscation / de-obfuscation. Please contact us if you have experience in this area.
If I am not a programmer can I participate in your project?
Yes, you can certainly participate in the project if you are not a programmer or technical. The project needs different skills and expertise and different times during its development. Currently, we are looking for researchers, writers, graphic designers, and a project administrator.
I contributed to the original Google Doc, but I'm not credited in the new version of the MSTG?
As we migrated some of the existing content, we did our best to backtrack the original authors and credit them appropriately. We also added a revision history that lists all the authors from old Google Docs. If you are not on that list but feel you should be, please contact Sven and he'll fix it. Or better yet, re-join the author's team and start contributing to the new guide.
Acknowledgments
Authors
Bernhard Mueller
Bernhard is a cyber security specialist with a talent in hacking all kinds of systems. During more than a decade in the industry, he has published many zero-day exploits for software such as MS SQL Server, Adobe Flash Player, IBM Director, Cisco VOIP and ModSecurity. If you can name it, he has probably broken it at least once. His pioneering work in mobile security was commended with a BlackHat "Best Research" Pwnie Award.
Sven Schleier
Sven is an experienced penetration tester and security architect who specialized in implementing secure SDLC for web application, iOS and Android apps. He is a project leader for the OWASP Mobile Security Testing Guide and the creator of OWASP Mobile Hacking Playground. Sven also supports the community with free hands-on workshops on web and mobile app security testing. He has published several security advisories and a white papers about a range of security topics.
Jeroen Willemsen
Jeroen is a principal security architect at Xebia with a passion for mobile security and risk management. He has supported companies as a security coach, a security engineer and as a full-stack developer, which makes him a jack of all trades. He loves explaining technical subjects: from security issues to programming challenges.
Carlos Holguera
Carlos is a security engineer leading the mobile penetration testing team at ESCRYPT. He has gained many years of hands-on experience in the field of security testing for mobile apps and embedded systems such as automotive control units and IoT devices. He is passionate about reverse engineering and dynamic instrumentation of mobile apps and is continuously learning and sharing his knowledge.
Co-Authors
Romuald Szkudlarek
Romuald is a passionate cyber security & privacy professional with over 15 years of experience in the Web, Mobile, IoT and Cloud domains. During his career, he has been dedicating spare time to a variery of projects with the goal of advancing the sectors of software and security. He is also teaching at various institutions. He holds CISSP, CSSLP and CEH credentials.
Jeroen Beckers
Jeroen is the mobile security lead at NVISO where he is responsible for quality assurance on mobile security projects and for R&D on all things mobile. He worked as a Flash developer during high school and college, but switched to a career in cybersecurity once he graduated and now has more than 5 years of experience in mobile security. He loves sharing his knowledge with other people, as is demonstrated by his many talks & trainings at colleges, universities, clients and conferences.
Top Contributors
- Pawel Rzepa
- Francesco Stillavato
- Henry Hoggard
- Andreas Happe
- Kyle Benac
- Alexander Anthuk
- Wen Bin Kong
- Abdessamad Temmar
- Bolot Kerimbaev
- Cláudio André
- Slawomir Kosowski
- Abderrahmane Aftahi
Contributors
Contributors have contributed quality content and have at least 50 additions logged in the GitHub repository.
Abderrahmane Aftahi, Jin Kung Ong, Koki Takeyama, Sjoerd Langkemper, Gerhard Wagner, Michael Helwig, Pece Milosev, Ryan Teoh, Denis Pilipchuk, Dharshin De Silva, Anatoly Rosencrantz, Abhinav Sejpal, José Carlos Andreu, Dominique Righetto, Raul Siles, Daniel Ramirez Martin, Yogesh Sharma, Enrico Verzegnassi, Nick Epson, Emil Tostrup, Prathan Phongthiproek, Tom Welch, Luander Ribeiro, Heaven L. Hodges, Dario Incalza, Akanksha Bana, Oguzhan Topgul, Vikas Gupta, Sijo Abraham, David Fern, Pishu Mahtani, Anuruddha E., Shiv Sahni
Reviewers
- Anant Shrivastava
- Sjoerd Langkemper
Others
The full list of contributors, including those with less than 50 additions logged, is available on GitHub.
Sponsors
While both the MASVS and the MSTG are created and maintained by the community on a voluntary basis, sometimes a little bit of outside help is required. We therefore thank our sponsors for providing the funds to be able to hire technical editors. Note that their sponsorship does not influence the content of the MASVS or MSTG in any way. The sponsorship packages are described on the OWASP Project Wiki.
Honourable Benefactor
Old Version - MSTG "Beta" on Google Drive
The Mobile Security Testing Guide was initiated by Milan Singh Thakur in 2015. The original document was hosted on Google Drive.
Authors:
Mirza Ali, Stephen Corbiaux, Ryan Dewhurst, Mohammad Hamed Dadpour, David Fern, Ali Yazdani, Bao Lee, Anto Joseph, Nutan Kumar Panda, Rahil Parikh, Julian Schütte, Abhinav Sejpal, Anant Shrivastava, Pragati Singh, Milan Singh Thakur, Stephanie Vanroelen, Gerhard Wagner
Reviewers:
Andrew Muller, Jonathan Carter, Stephanie Vanroelen, Milan Singh Thakur