This site is the archived OWASP Foundation Wiki and is no longer accepting Account Requests.
To view the new OWASP Foundation website, please visit https://owasp.org
Difference between revisions of "OAT-011 Scraping"
(New page) |
(→Indicative Diagram) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
===Indicative Diagram=== | ===Indicative Diagram=== | ||
| − | + | [[File:OAT-011_Scraping.png|500px|link=]] | |
=== Description === | === Description === | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
* 281 Analyze Target | * 281 Analyze Target | ||
| − | === CWE Base / Class / Variant | + | === CWE Base / Class / Variant IDs === |
* 799 Improper Control of Interaction Frequency | * 799 Improper Control of Interaction Frequency | ||
| − | === WASC Threat | + | === WASC Threat IDs === |
* 21 Insufficient Anti-Automation | * 21 Insufficient Anti-Automation | ||
Latest revision as of 15:09, 16 February 2018
This is an automated threat. To view all automated threats, please see the Automated Threat Category page. The OWASP Automated Threat Handbook - Wed Applications (pdf, print), an output of the OWASP Automated Threats to Web Applications Project, provides a fuller guide to each threat, detection methods and countermeasures. The threat identification chart helps to correctly identify the automated threat.
Definition
OWASP Automated Threat (OAT) Identity Number
OAT-011
Threat Event Name
Scraping
Summary Defining Characteristics
Collect application content and/or other data for use elsewhere.
Indicative Diagram
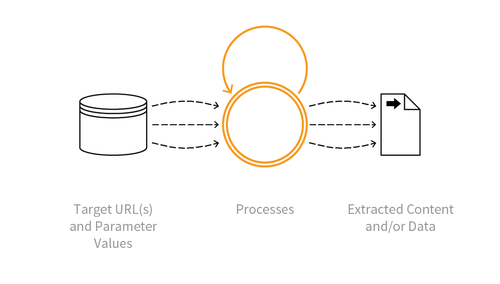
Description
Collecting accessible data and/or processed output from the application. Some scraping may use fake or compromised accounts, or the information may be accessible without authentication. The scraper may attempt to read all accessible paths and parameter values for web pages and APIs, collecting the responses and extracting data from them. Scraping may occur in real time, or be more periodic in nature. Some Scraping may be used to gain insight into how it is constructed and operates - perhaps for cryptanalysis, reverse engineering, or session analysis.
When another application is being used as an intermediary between the user(s) and the real application, see OAT-020 Account Aggregation. If the intent is to obtain cash or goods, see OAT-012 Cashing Out instead.
Other Names and Examples
API provisioning; Bargain hunting; Comparative shopping; Content scraping; Data aggregation; Database scraping; Farming; Harvesting; Meta search scraper; Mining; Mirroring; Pagejacking; Powering APIs; Ripping; Scraper bot; Screen scraping; Search / social media bot
See Also
Cross-References
CAPEC Category / Attack Pattern IDs
- 167 Lifting Sensitive Data from the Client
- 210 Abuse of Functionality
- 281 Analyze Target
CWE Base / Class / Variant IDs
- 799 Improper Control of Interaction Frequency
WASC Threat IDs
- 21 Insufficient Anti-Automation
- 42 Abuse of Functionality