This site is the archived OWASP Foundation Wiki and is no longer accepting Account Requests.
To view the new OWASP Foundation website, please visit https://owasp.org
Difference between revisions of "HttpOnly"
m |
Markgordon (talk | contribs) m (Corrected a spelling error) (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| (64 intermediate revisions by 12 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| − | The goal of this section is to introduce, discuss, and provide language specific mitigation techniques for | + | The goal of this section is to introduce, discuss, and provide language specific mitigation techniques for HttpOnly. |
| − | <h3 style=color:#4682B4> <u> Who developed | + | <h3 style="color:#4682B4"> <u> Who developed HttpOnly? When? </u> </h3> |
| − | According to | + | According to a daily blog article by [http://www.networkcomputing.com/careers/no-cookie-you/1270585242 Jordan Wiens, “No cookie for you!”], HttpOnly cookies were first implemented in 2002 by Microsoft Internet Explorer developers for Internet Explorer 6 SP1. |
| − | |||
| − | <h3 style=color:#4682B4> <u> What is | + | <h3 style="color:#4682B4"> <u> What is HttpOnly? </u> </h3> |
| − | According to the [http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms533046.aspx Microsoft Developer Network], | + | According to the [http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms533046.aspx Microsoft Developer Network], HttpOnly is an ''additional flag'' included in a Set-Cookie HTTP response header. Using the HttpOnly flag when generating a cookie helps mitigate the risk of client side script accessing the protected cookie (if the browser supports it). |
*The example below shows the syntax used within the '''HTTP response header''': | *The example below shows the syntax used within the '''HTTP response header''': | ||
| − | Set-Cookie: <name>=<value>[; < | + | Set-Cookie: <name>=<value>[; <Max-Age>=<age>] |
[; expires=<date>][; domain=<domain_name>] | [; expires=<date>][; domain=<domain_name>] | ||
[; path=<some_path>][; secure][; HttpOnly] | [; path=<some_path>][; secure][; HttpOnly] | ||
| − | If the | + | If the HttpOnly flag (optional) is included in the HTTP response header, the cookie cannot be accessed through client side script (again if the browser supports this flag). As a result, even if a cross-site scripting '''(XSS)''' flaw exists, and a user accidentally accesses a link that exploits this flaw, the browser (primarily Internet Explorer) will not reveal the cookie to a third party. |
| − | If a browser does not support | + | If a browser does not support HttpOnly and a website attempts to set an HttpOnly cookie, the HttpOnly flag will be ignored by the browser, thus creating a traditional, script accessible cookie. As a result, the cookie (typically your session cookie) becomes vulnerable to theft of modification by malicious script. [http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms533046.aspx Mitigating]. |
| − | <h3 style=color:#4682B4> <u> Mitigating XSS using | + | <h3 style="color:#4682B4"> <u>Mitigating the Most Common XSS attack using HttpOnly</u> </h3> |
| − | According to [http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms972826.aspx Michael Howard], Senior Security Program Manager in the Secure Windows Initiative group at Microsoft, the majority of XSS attacks | + | According to [http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms972826.aspx Michael Howard], Senior Security Program Manager in the Secure Windows Initiative group at Microsoft, the majority of XSS attacks target theft of session cookies. A server could help mitigate this issue by setting the HttpOnly flag on a cookie it creates, indicating the cookie should not be accessible on the client. |
| − | If | + | If a browser that supports HttpOnly detects a cookie containing the HttpOnly flag, and client side script code attempts to read the cookie, the browser ''returns an empty string'' as the result. This causes the attack to fail by preventing the malicious (usually XSS) code from sending the data to an attacker's website. |
| − | <h5 style=color:#2E8B57> <u> Using Java to Set | + | <h5 style="color:#2E8B57"> <u>Using Java to Set HttpOnly</u> </h5> |
| − | + | Since Java Enterprise Edition 6 (JEE 6), which adopted Java Servlet 3.0 technology, it's programmatically easy to set the HttpOnly flag on a cookie. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | In fact <code>setHttpOnly</code> and <code>isHttpOnly</code> methods are available in the <code>Cookie</code> interface [http://java.sun.com/javaee/6/docs/api/javax/servlet/http/Cookie.html#setHttpOnly%28boolean%29], and also for session cookies (JSESSIONID) [http://java.sun.com/javaee/6/docs/api/javax/servlet/SessionCookieConfig.html#setHttpOnly%28boolean%29]: | |
| − | + | Cookie cookie = getMyCookie("myCookieName"); | |
| − | + | cookie.setHttpOnly(true); | |
| − | |||
| − | ' | + | Moreover, since JEE 6 it's also declaratively easy setting <code>HttpOnly</code> flag in a session cookie by applying the following configuration in the deployment descriptor <code>WEB-INF/web.xml</code>: |
| + | <session-config> | ||
| + | <cookie-config> | ||
| + | <http-only>true</http-only> | ||
| + | </cookie-config> | ||
| + | </session-config> | ||
| − | < | + | For Java Enterprise Edition versions ''prior'' to JEE 6 a common '''workaround''' is to overwrite the <code>SET-COOKIE</code> HTTP response header with a session cookie value that explicitly appends the <code>HttpOnly</code> flag: |
| + | String sessionid = request.getSession().getId(); | ||
| + | // be careful overwriting: JSESSIONID may have been set with other flags | ||
| + | response.setHeader("SET-COOKIE", "JSESSIONID=" + sessionid + "; HttpOnly"); | ||
| − | *By ''default'', '''.NET 2.0''' sets the | + | In this context, overwriting, despite appropriate for the <code>HttpOnly</code> flag, is discouraged because the JSESSIONID may have been set with other flags. A better workaround is taking care of the previously set flags or using the [[ESAPI#Java_EE]] library: in fact the <code>addCookie</code> method of the <code>SecurityWrapperResponse</code> [http://code.google.com/p/owasp-esapi-java/source/browse/tags/esapi-2.0.1/src/main/java/org/owasp/esapi/filters/SecurityWrapperResponse.java] takes care of previously set flags for us. So we could write a servlet filter as the following one: |
| + | public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException { | ||
| + | HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = (HttpServletRequest) request; | ||
| + | HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse = (HttpServletResponse) response; | ||
| + | // if errors exist then create a sanitized cookie header and continue | ||
| + | SecurityWrapperResponse securityWrapperResponse = new SecurityWrapperResponse(httpServletResponse, "sanitize"); | ||
| + | Cookie[] cookies = httpServletRequest.getCookies(); | ||
| + | if (cookies != null) { | ||
| + | for (int i = 0; i < cookies.length; i++) { | ||
| + | Cookie cookie = cookies[i]; | ||
| + | if (cookie != null) { | ||
| + | // ESAPI.securityConfiguration().getHttpSessionIdName() returns JSESSIONID by default configuration | ||
| + | if (ESAPI.securityConfiguration().getHttpSessionIdName().equals(cookie.getName())) { | ||
| + | securityWrapperResponse.addCookie(cookie); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | filterChain.doFilter(request, response); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | Some web application servers, that implement JEE 5, and servlet containers that implement Java Servlet 2.5 (part of JEE 5), also allow creating HttpOnly session cookies: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Tomcat 6''' In <code>context.xml</code> set the <code>context</code> tag's attribute <code>useHttpOnly</code> [http://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-6.0-doc/config/context.html#Common_Attributes] as follow: | ||
| + | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> | ||
| + | <Context path="/myWebApplicationPath" useHttpOnly="true"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''JBoss 5.0.1''' and '''JBOSS EAP 5.0.1''' In <code>\server\<myJBossServerInstance>\deploy\jbossweb.sar\context.xml</code> set the <code>SessionCookie</code> tag [https://community.jboss.org/message/598558#598558] as follow: | ||
| + | <Context cookies="true" crossContext="true"> | ||
| + | <SessionCookie secure="true" httpOnly="true" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * <b>IBM Websphere</b> offer HTTPOnly for session cookies as a configuration option. | ||
| + | http://pic.dhe.ibm.com/infocenter/tivihelp/v33r1/topic/com.ibm.mam.inswas.doc/install/t_configuringthehttponlyattribute.html | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h5 style="color:#2E8B57"> <u>Using .NET to Set HttpOnly</u> </h5> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *By ''default'', '''.NET 2.0''' sets the HttpOnly attribute for | ||
*#Session ID | *#Session ID | ||
*#Forms Authentication cookie | *#Forms Authentication cookie | ||
| − | In .NET 2.0, | + | In .NET 2.0, HttpOnly can also be set via the HttpCookie object for all custom application cookies |
*Via '''web.config''' in the system.web/httpCookies element | *Via '''web.config''' in the system.web/httpCookies element | ||
<httpCookies httpOnlyCookies="true" …> | <httpCookies httpOnlyCookies="true" …> | ||
*Or '''programmatically''' | *Or '''programmatically''' | ||
| + | C# Code: | ||
HttpCookie myCookie = new HttpCookie("myCookie"); | HttpCookie myCookie = new HttpCookie("myCookie"); | ||
myCookie.HttpOnly = true; | myCookie.HttpOnly = true; | ||
Response.AppendCookie(myCookie); | Response.AppendCookie(myCookie); | ||
| + | |||
| + | VB.NET Code: | ||
| + | Dim myCookie As HttpCookie = new HttpCookie("myCookie") | ||
| + | myCookie.HttpOnly = True | ||
| + | Response.AppendCookie(myCookie) | ||
*However, in '''.NET 1.1''', you would have to do this ''manually'', e.g., | *However, in '''.NET 1.1''', you would have to do this ''manually'', e.g., | ||
| − | Response.Cookies[cookie].Path += "; | + | Response.Cookies[cookie].Path += ";HttpOnly"; |
| + | |||
| + | <h5 style="color:#2E8B57"> <u>Using Python (cherryPy) to Set HttpOnly</u> </h5> | ||
| − | < | + | Python Code (cherryPy):<br> |
| + | To use HTTP-Only cookies with Cherrypy sessions just add the following line in your configuration file:<br> | ||
| + | tools.sessions.httponly = True<br> | ||
| + | If you use SLL you can also make your cookies secure (encrypted) to avoid "man-in-the-middle" cookies reading with:<br> | ||
| + | tools.sessions.secure = True<br> | ||
| − | + | <h5 style="color:#2E8B57"> <u> Using PHP to set HttpOnly </u> </h5> | |
| − | + | PHP supports setting the HttpOnly flag since version 5.2.0 (November 2006). | |
| − | + | ||
| + | For session cookies managed by PHP, the flag is set either permanently in php.ini [http://www.php.net/manual/en/session.configuration.php#ini.session.cookie-httponly PHP manual on ''HttpOnly''] through the parameter: | ||
| + | session.cookie_httponly = True | ||
| + | or in and during a script via the function[http://pl.php.net/manual/en/function.session-set-cookie-params.php]: | ||
| + | void session_set_cookie_params ( int $lifetime [, string $path [, string $domain | ||
| + | [, bool $secure= false [, bool $httponly= false ]]]] ) | ||
| + | For application cookies last parameter in setcookie() sets HttpOnly flag[http://pl.php.net/setcookie]: | ||
| + | bool setcookie ( string $name [, string $value [, int $expire= 0 [, string $path | ||
| + | [, string $domain [, bool $secure= false [, bool $httponly= false ]]]]]] ) | ||
| + | ===Web Application Firewalls=== | ||
| + | If code changes are infeasible, web application firewalls can be used to add HttpOnly to session cookies: | ||
| − | + | * Mod_security - using SecRule and Header directives[http://blog.modsecurity.org/2008/12/fixing-both-missing-httponly-and-secure-cookie-flags.html] | |
| − | * | + | * ESAPI WAF[http://code.google.com/p/owasp-esapi-java/downloads/list] using ''add-http-only-flag'' directive[http://www.slideshare.net/llamakong/owasp-esapi-waf-appsec-dc-2009] |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Browsers Supporting HttpOnly== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Using WebGoat's HttpOnly lesson, the following web browsers have been tested for HttpOnly support. If the browsers enforces HttpOnly, a client side script will be unable to read or write the session cookie. However, there is currently no prevention of reading or writing the session cookie via a XMLHTTPRequest. | |
| − | |||
| − | = | + | Note: These results may be out of date as this page is not well maintained. A great page that is focused on keeping up with the status of browsers is at: http://www.browserscope.org/?category=security. Just look at the HttpOnly column. The Browserscope site does not provide as much detail on HttpOnly as this page, but provides lots of other details this page does not. |
| − | + | Our results as of Feb 2009 are listed below in '''table 1'''. | |
| − | {| | + | {| width="100%" border="2" align="center" |
| − | |+ '''Table 1:''' Browsers Supporting | + | |+ '''Table 1:''' Browsers Supporting HttpOnly |
|- | |- | ||
! style="background:black; color:white" | '''Browser''' | ! style="background:black; color:white" | '''Browser''' | ||
! style="background:black; color:white" | '''Version''' | ! style="background:black; color:white" | '''Version''' | ||
| − | ! style="background:black; color:white" | ''' | + | ! style="background:black; color:white" | '''Prevents Reads''' |
| + | ! style="background:black; color:white" | '''Prevents Writes''' | ||
| + | ! style="background:black; color:white" | '''Prevents Read within XMLHTTPResponse*''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Microsoft Internet Explorer | | Microsoft Internet Explorer | ||
| − | | align="center" | 6 (SP1) - | + | | align="center" | 8 Beta 2 |
| − | | align="center" | | + | | align="center" | Yes |
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | | align="center" | Partially (set-cookie is protected, but not set-cookie2, see [http://www.microsoft.com/technet/security/bulletin/ms08-069.mspx]). Fully patched IE8 passes http://ha.ckers.org/httponly.cgi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Microsoft Internet Explorer | ||
| + | | align="center" | 7 | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | | align="center" | Partially (set-cookie is protected, but not set-cookie2, see [http://www.microsoft.com/technet/security/bulletin/ms08-069.mspx]). Fully patched IE7 passes http://ha.ckers.org/httponly.cgi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Microsoft Internet Explorer | ||
| + | | align="center" | 6 (SP1) | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | | align="center" | No | ||
| + | | align="center" | No (Possible that ms08-069 fixed IE 6 too, please verify with http://ha.ckers.org/httponly.cgi and update this page!) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Microsoft Internet Explorer | ||
| + | | align="center" | 6 (fully patched) | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | | align="center" | Unknown | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Mozilla Firefox | | Mozilla Firefox | ||
| − | | align="center" | | + | | align="center" | 3.0.0.6+ |
| − | | align="center" | | + | | align="center" | Yes |
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes (see [http://manicode.blogspot.com/2009/02/firefox-3006-httponly-champion.html]) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Netscape Navigator | | Netscape Navigator | ||
| − | | align="center" | 9. | + | | align="center" | 9.0b3 |
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| align="center" | No | | align="center" | No | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Opera | | Opera | ||
| − | | align="center" | 9. | + | | align="center" | 9.23 |
| + | | align="center" | No | ||
| + | | align="center" | No | ||
| + | | align="center" | No | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Opera | ||
| + | | align="center" | 9.50 | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | | align="center" | No | ||
| + | | align="center" | No | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Opera | ||
| + | | align="center" | 11 | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | | align="center" | Unknown | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Safari | ||
| + | | align="center" | 3.0 | ||
| + | | align="center" | No | ||
| + | | align="center" | No | ||
| + | | align="center" | No (almost yes, see [https://bugs.webkit.org/show_bug.cgi?id=10957]) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Safari | ||
| + | | align="center" | 5 | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | iPhone (Safari) | ||
| + | | align="center" | iOS 4 | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Google's Chrome | ||
| + | | align="center" | Beta (initial public release) | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | | align="center" | No | ||
| + | | align="center" | No (almost yes, see [https://bugs.webkit.org/show_bug.cgi?id=10957]) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Google's Chrome | ||
| + | | align="center" | 12 | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | | align="center" | Yes | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Android | ||
| + | | align="center" | Android 2.3 | ||
| + | | align="center" | Unknown | ||
| + | | align="center" | Unknown | ||
| align="center" | No | | align="center" | No | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | <nowiki>*</nowiki> An attacker could still | + | <nowiki>*</nowiki> An attacker could still read the session cookie in a response to an '''[http://ha.ckers.org/blog/20070719/firefox-implements-httponly-and-is-vulnerable-to-xmlhttprequest/ XmlHttpRequest]'''. |
| + | |||
| + | As of 2011, 99% of browsers and most web application frameworks support HttpOnly<ref>[http://blog.fortify.com/blog/2011/11/02/Misunderstandings-on-HttpOnly-Cookie Misunderstandings on HttpOnly Cookie]</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Using WebGoat to Test for HttpOnly Support == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The goal of this section is to provide a step-by-step example of testing your browser for HttpOnly support. | ||
| − | = | + | <h3 style="color:#4682B4"> <u> WARNING</u> </h3> |
| − | The | + | The OWASP WEBGOAT HttpOnly lab is broken and does not show IE 8 Beta 2 with ms08-069 as complete in terms of HttpOnly XMLHTTPRequest header leakage protection. This error is being tracked via http://code.google.com/p/webgoat/issues/detail?id=18. |
| − | <h3 style=color:#4682B4> <u> Getting Started </u> </h3> | + | <h3 style="color:#4682B4"> <u> Getting Started </u> </h3> |
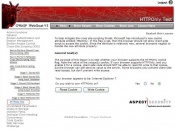
| − | [[Image:Click_link.JPG|thumb|175px|right|Figure 1 - Accessing WebGoat's | + | [[Image:Click_link.JPG|thumb|175px|right|Figure 1 - Accessing WebGoat's HttpOnly Test Lesson]] |
| − | Assuming you have | + | Assuming you have installed and launched WebGoat, begin by navigating to the '''‘HttpOnly Test’ lesson''' located within the Cross-Site Scripting ('''XSS''') category. After loading the ‘HttpOnly Test’ lesson, as shown in '''figure 1''', you are now able to begin testing web browsers supporting HttpOnly. |
| − | <h3 style=color:#4682B4> <u> Lesson Goal </u> </h3> | + | <h3 style="color:#4682B4"> <u> Lesson Goal </u> </h3> |
| − | If the | + | If the ''HttpOnly flag'' is set, then your browser should not allow a client-side script to access the session cookie. Unfortunately, since the attribute is relatively new, several browsers may neglect to handle the new attribute properly. |
| − | The '''purpose''' of this lesson is to test whether your browser supports the ''' | + | The '''purpose''' of this lesson is to test whether your browser supports the '''HttpOnly cookie flag'''. ''Note the value of the'' '''''unique2u cookie'''''. If your browser supports HttpOnly, and you ''enable'' it for a cookie, a client-side script should NOT be able to read OR write to that cookie, but the browser can still send its value to the server. However, some browsers only prevent client side read access, but do not prevent write access. |
| − | <h3 style=color:#4682B4> <u> Testing Web Browsers for | + | <h3 style="color:#4682B4"> <u> Testing Web Browsers for HttpOnly Support </u> </h3> |
| − | The following test was performed on two browsers, '''Internet Explorer 7''' and '''Opera 9.22''', to demonstrate the results when the | + | The following test was performed on two browsers, '''Internet Explorer 7''' and '''Opera 9.22''', to demonstrate the results when the HttpOnly flag is enforced properly. As you will see, IE7 properly enforces the HttpOnly flag, whereas Opera does not properly enforce the HttpOnly flag. |
| − | <h5 style=color:#2E8B57> <u> Disabling | + | <h5 style="color:#2E8B57"> <u> Disabling HttpOnly </u> </h5> |
| − | 1) Select the option to '''turn | + | 1) Select the option to '''turn HttpOnly off''' as shown below in '''figure 2'''. |
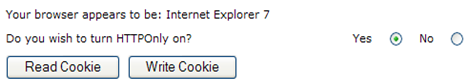
| − | [[Image:Fig2-Disabling_HTTPOnly.PNG|frame|center|Figure 2 - Disabling | + | [[Image:Fig2-Disabling_HTTPOnly.PNG|frame|center|Figure 2 - Disabling HttpOnly]] |
| − | 2) After turning | + | 2) After turning HttpOnly off, select the '''“Read Cookie”''' button. |
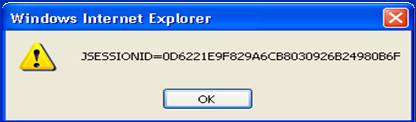
| − | *An alert dialog box will display on the screen notifying you that ''since | + | *An alert dialog box will display on the screen notifying you that ''since HttpOnly was not enabled'', the '''‘unique2u’ cookie''' was successfully read as shown below in '''figure 3'''. |
| − | [[Image:Fig3-Read_HTTPOnly_Off.PNG|frame|center|Figure 3 - Cookie Successfully Read with | + | [[Image:Fig3-Read_HTTPOnly_Off.PNG|frame|center|Figure 3 - Cookie Successfully Read with HttpOnly Off]] |
| − | 3) With | + | 3) With HttpOnly remaining disabled, select the '''“Write Cookie” ''' button. |
| − | *An alert dialog box will display on the screen notifying you that ''since | + | *An alert dialog box will display on the screen notifying you that ''since HttpOnly was not enabled'', the '''‘unique2u’ cookie''' was successfully modified on the client side as shown below in '''figure 4'''. |
| − | [[Image:Fig4-Write_HTTPOnly_Off.PNG|frame|center|Figure 4 - Cookie Successfully Written with | + | [[Image:Fig4-Write_HTTPOnly_Off.PNG|frame|center|Figure 4 - Cookie Successfully Written with HttpOnly Off]] |
| − | *As you have seen thus far, '''browsing without | + | *As you have seen thus far, '''browsing without HttpOnly''' on is a potential '''''threat'''''. Next, we will '''enable HttpOnly''' to demonstrate how this flag protects the cookie. |
| − | <h5 style=color:#2E8B57> <u> Enabling | + | <h5 style="color:#2E8B57"> <u> Enabling HttpOnly </u> </h5> |
| − | 4) Select the ''radio button'' to enable | + | 4) Select the ''radio button'' to enable HttpOnly as shown below in '''figure 5'''. |
| − | [[Image:Fig5-Turning_HTTPOnly_On.PNG|frame|center|Figure 5 - Enabling | + | [[Image:Fig5-Turning_HTTPOnly_On.PNG|frame|center|Figure 5 - Enabling HttpOnly]] |
| − | 5) After enabling | + | 5) After enabling HttpOnly, select the '''"Read Cookie"''' button. |
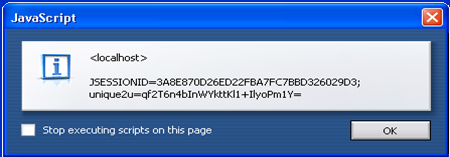
| − | *If the browser enforces the | + | *If the browser enforces the HttpOnly flag properly, an alert dialog box will display only the session ID rather than the contents of the '''‘unique2u’ cookie''' as shown below in '''figure 6'''. |
[[Image:Fig6-Cookie_Read_Protection.PNG|frame|center|Figure 6 - Enforced Cookie Read Protection]] | [[Image:Fig6-Cookie_Read_Protection.PNG|frame|center|Figure 6 - Enforced Cookie Read Protection]] | ||
| − | *However, if the browser does not enforce the | + | *However, if the browser does not enforce the HttpOnly flag properly, an alert dialog box will display both the '''‘unique2u’ cookie''' and session ID as shown below in '''figure 7'''. |
[[Image:Fig7-No_Cookie_Read_Protection.PNG|frame|center|Figure 7 - Unenforced Cookie Read Protection]] | [[Image:Fig7-No_Cookie_Read_Protection.PNG|frame|center|Figure 7 - Unenforced Cookie Read Protection]] | ||
| − | *Finally, we will test if the browser allows '''write access''' to the cookie with | + | *Finally, we will test if the browser allows '''write access''' to the cookie with HttpOnly enabled. |
6) Select the '''"Write Cookie"''' button. | 6) Select the '''"Write Cookie"''' button. | ||
| − | *If the browser enforces the | + | *If the browser enforces the HttpOnly flag properly, client side modification will be unsuccessful in writing to the '''‘unique2u’ cookie''' and an alert dialog box will display only containing the session ID as shown below in '''figure 8'''. |
[[Image:Fig6-Cookie_Read_Protection.PNG|frame|center|Figure 8 - Enforced Cookie Write Protection]] | [[Image:Fig6-Cookie_Read_Protection.PNG|frame|center|Figure 8 - Enforced Cookie Write Protection]] | ||
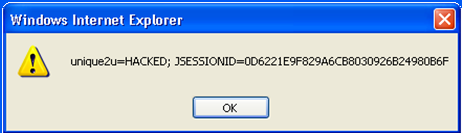
| − | *However, if the browser does not enforce the write protection property of | + | *However, if the browser does not enforce the write protection property of HttpOnly flag for the '''‘unique2u’ cookie''', the cookie will be successfully modified to ''HACKED'' on the client side as shown below in '''figure 9'''. |
[[Image:Fig9-No_Cookie_Write_Protection.PNG|frame|center|Figure 9 - Unenforced Cookie Write Protection]] | [[Image:Fig9-No_Cookie_Write_Protection.PNG|frame|center|Figure 9 - Unenforced Cookie Write Protection]] | ||
| Line 177: | Line 318: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| − | [ | + | # [https://cwe.mitre.org/data/definitions/1004.html CWE-1004: Sensitive Cookie Without 'HttpOnly' Flag] |
| − | + | # Wiens, Jordan [http://www.networkcomputing.com/careers/no-cookie-you/1270585242 "No cookie for you!"] | |
| − | + | # [http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms533046.aspx Mitigating Cross-site Scripting with HTTP-Only Cookies] | |
| − | + | # Howard, Michael. [http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms972826.aspx Some Bad News and Some Good News] | |
| − | + | # MSDN. [http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.web.httpcookie.httponly.aspx Setting the HttpOnly propery in .NET] | |
| + | # [http://seckb.yehg.net/2012/06/xss-gaining-access-to-httponly-cookie.html XSS: Gaining access to HttpOnly Cookie in 2012] | ||
| + | # [http://stackoverflow.com/questions/13147113/setting-an-httponly-cookie-with-javax-servlet-2-5 Setting HttpOnly in Java] | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 20:02, 24 August 2017
Overview
The goal of this section is to introduce, discuss, and provide language specific mitigation techniques for HttpOnly.
Who developed HttpOnly? When?
According to a daily blog article by Jordan Wiens, “No cookie for you!”, HttpOnly cookies were first implemented in 2002 by Microsoft Internet Explorer developers for Internet Explorer 6 SP1.
What is HttpOnly?
According to the Microsoft Developer Network, HttpOnly is an additional flag included in a Set-Cookie HTTP response header. Using the HttpOnly flag when generating a cookie helps mitigate the risk of client side script accessing the protected cookie (if the browser supports it).
- The example below shows the syntax used within the HTTP response header:
Set-Cookie: <name>=<value>[; <Max-Age>=<age>] [; expires=<date>][; domain=<domain_name>] [; path=<some_path>][; secure][; HttpOnly]
If the HttpOnly flag (optional) is included in the HTTP response header, the cookie cannot be accessed through client side script (again if the browser supports this flag). As a result, even if a cross-site scripting (XSS) flaw exists, and a user accidentally accesses a link that exploits this flaw, the browser (primarily Internet Explorer) will not reveal the cookie to a third party.
If a browser does not support HttpOnly and a website attempts to set an HttpOnly cookie, the HttpOnly flag will be ignored by the browser, thus creating a traditional, script accessible cookie. As a result, the cookie (typically your session cookie) becomes vulnerable to theft of modification by malicious script. Mitigating.
Mitigating the Most Common XSS attack using HttpOnly
According to Michael Howard, Senior Security Program Manager in the Secure Windows Initiative group at Microsoft, the majority of XSS attacks target theft of session cookies. A server could help mitigate this issue by setting the HttpOnly flag on a cookie it creates, indicating the cookie should not be accessible on the client.
If a browser that supports HttpOnly detects a cookie containing the HttpOnly flag, and client side script code attempts to read the cookie, the browser returns an empty string as the result. This causes the attack to fail by preventing the malicious (usually XSS) code from sending the data to an attacker's website.
Using Java to Set HttpOnly
Since Java Enterprise Edition 6 (JEE 6), which adopted Java Servlet 3.0 technology, it's programmatically easy to set the HttpOnly flag on a cookie.
In fact setHttpOnly and isHttpOnly methods are available in the Cookie interface [1], and also for session cookies (JSESSIONID) [2]:
Cookie cookie = getMyCookie("myCookieName");
cookie.setHttpOnly(true);
Moreover, since JEE 6 it's also declaratively easy setting HttpOnly flag in a session cookie by applying the following configuration in the deployment descriptor WEB-INF/web.xml:
<session-config> <cookie-config> <http-only>true</http-only> </cookie-config> </session-config>
For Java Enterprise Edition versions prior to JEE 6 a common workaround is to overwrite the SET-COOKIE HTTP response header with a session cookie value that explicitly appends the HttpOnly flag:
String sessionid = request.getSession().getId();
// be careful overwriting: JSESSIONID may have been set with other flags
response.setHeader("SET-COOKIE", "JSESSIONID=" + sessionid + "; HttpOnly");
In this context, overwriting, despite appropriate for the HttpOnly flag, is discouraged because the JSESSIONID may have been set with other flags. A better workaround is taking care of the previously set flags or using the ESAPI#Java_EE library: in fact the addCookie method of the SecurityWrapperResponse [3] takes care of previously set flags for us. So we could write a servlet filter as the following one:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = (HttpServletRequest) request;
HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse = (HttpServletResponse) response;
// if errors exist then create a sanitized cookie header and continue
SecurityWrapperResponse securityWrapperResponse = new SecurityWrapperResponse(httpServletResponse, "sanitize");
Cookie[] cookies = httpServletRequest.getCookies();
if (cookies != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < cookies.length; i++) {
Cookie cookie = cookies[i];
if (cookie != null) {
// ESAPI.securityConfiguration().getHttpSessionIdName() returns JSESSIONID by default configuration
if (ESAPI.securityConfiguration().getHttpSessionIdName().equals(cookie.getName())) {
securityWrapperResponse.addCookie(cookie);
}
}
}
}
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
Some web application servers, that implement JEE 5, and servlet containers that implement Java Servlet 2.5 (part of JEE 5), also allow creating HttpOnly session cookies:
- Tomcat 6 In
context.xmlset thecontexttag's attributeuseHttpOnly[4] as follow:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <Context path="/myWebApplicationPath" useHttpOnly="true">
- JBoss 5.0.1 and JBOSS EAP 5.0.1 In
\server\<myJBossServerInstance>\deploy\jbossweb.sar\context.xmlset theSessionCookietag [5] as follow:
<Context cookies="true" crossContext="true"> <SessionCookie secure="true" httpOnly="true" />
- IBM Websphere offer HTTPOnly for session cookies as a configuration option.
Using .NET to Set HttpOnly
- By default, .NET 2.0 sets the HttpOnly attribute for
- Session ID
- Forms Authentication cookie
In .NET 2.0, HttpOnly can also be set via the HttpCookie object for all custom application cookies
- Via web.config in the system.web/httpCookies element
<httpCookies httpOnlyCookies="true" …>
- Or programmatically
C# Code:
HttpCookie myCookie = new HttpCookie("myCookie");
myCookie.HttpOnly = true;
Response.AppendCookie(myCookie);
VB.NET Code:
Dim myCookie As HttpCookie = new HttpCookie("myCookie")
myCookie.HttpOnly = True
Response.AppendCookie(myCookie)
- However, in .NET 1.1, you would have to do this manually, e.g.,
Response.Cookies[cookie].Path += ";HttpOnly";
Using Python (cherryPy) to Set HttpOnly
Python Code (cherryPy):
To use HTTP-Only cookies with Cherrypy sessions just add the following line in your configuration file:
tools.sessions.httponly = True
If you use SLL you can also make your cookies secure (encrypted) to avoid "man-in-the-middle" cookies reading with:
tools.sessions.secure = True
Using PHP to set HttpOnly
PHP supports setting the HttpOnly flag since version 5.2.0 (November 2006).
For session cookies managed by PHP, the flag is set either permanently in php.ini PHP manual on HttpOnly through the parameter:
session.cookie_httponly = True
or in and during a script via the function[6]:
void session_set_cookie_params ( int $lifetime [, string $path [, string $domain
[, bool $secure= false [, bool $httponly= false ]]]] )
For application cookies last parameter in setcookie() sets HttpOnly flag[7]:
bool setcookie ( string $name [, string $value [, int $expire= 0 [, string $path
[, string $domain [, bool $secure= false [, bool $httponly= false ]]]]]] )
Web Application Firewalls
If code changes are infeasible, web application firewalls can be used to add HttpOnly to session cookies:
- Mod_security - using SecRule and Header directives[8]
- ESAPI WAF[9] using add-http-only-flag directive[10]
Browsers Supporting HttpOnly
Using WebGoat's HttpOnly lesson, the following web browsers have been tested for HttpOnly support. If the browsers enforces HttpOnly, a client side script will be unable to read or write the session cookie. However, there is currently no prevention of reading or writing the session cookie via a XMLHTTPRequest.
Note: These results may be out of date as this page is not well maintained. A great page that is focused on keeping up with the status of browsers is at: http://www.browserscope.org/?category=security. Just look at the HttpOnly column. The Browserscope site does not provide as much detail on HttpOnly as this page, but provides lots of other details this page does not.
Our results as of Feb 2009 are listed below in table 1.
| Browser | Version | Prevents Reads | Prevents Writes | Prevents Read within XMLHTTPResponse* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Internet Explorer | 8 Beta 2 | Yes | Yes | Partially (set-cookie is protected, but not set-cookie2, see [11]). Fully patched IE8 passes http://ha.ckers.org/httponly.cgi |
| Microsoft Internet Explorer | 7 | Yes | Yes | Partially (set-cookie is protected, but not set-cookie2, see [12]). Fully patched IE7 passes http://ha.ckers.org/httponly.cgi |
| Microsoft Internet Explorer | 6 (SP1) | Yes | No | No (Possible that ms08-069 fixed IE 6 too, please verify with http://ha.ckers.org/httponly.cgi and update this page!) |
| Microsoft Internet Explorer | 6 (fully patched) | Yes | Unknown | Yes |
| Mozilla Firefox | 3.0.0.6+ | Yes | Yes | Yes (see [13]) |
| Netscape Navigator | 9.0b3 | Yes | Yes | No |
| Opera | 9.23 | No | No | No |
| Opera | 9.50 | Yes | No | No |
| Opera | 11 | Yes | Unknown | Yes |
| Safari | 3.0 | No | No | No (almost yes, see [14]) |
| Safari | 5 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| iPhone (Safari) | iOS 4 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Google's Chrome | Beta (initial public release) | Yes | No | No (almost yes, see [15]) |
| Google's Chrome | 12 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Android | Android 2.3 | Unknown | Unknown | No |
* An attacker could still read the session cookie in a response to an XmlHttpRequest.
As of 2011, 99% of browsers and most web application frameworks support HttpOnly<ref>Misunderstandings on HttpOnly Cookie</ref>.
Using WebGoat to Test for HttpOnly Support
The goal of this section is to provide a step-by-step example of testing your browser for HttpOnly support.
WARNING
The OWASP WEBGOAT HttpOnly lab is broken and does not show IE 8 Beta 2 with ms08-069 as complete in terms of HttpOnly XMLHTTPRequest header leakage protection. This error is being tracked via http://code.google.com/p/webgoat/issues/detail?id=18.
Getting Started
Assuming you have installed and launched WebGoat, begin by navigating to the ‘HttpOnly Test’ lesson located within the Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) category. After loading the ‘HttpOnly Test’ lesson, as shown in figure 1, you are now able to begin testing web browsers supporting HttpOnly.
Lesson Goal
If the HttpOnly flag is set, then your browser should not allow a client-side script to access the session cookie. Unfortunately, since the attribute is relatively new, several browsers may neglect to handle the new attribute properly.
The purpose of this lesson is to test whether your browser supports the HttpOnly cookie flag. Note the value of the unique2u cookie. If your browser supports HttpOnly, and you enable it for a cookie, a client-side script should NOT be able to read OR write to that cookie, but the browser can still send its value to the server. However, some browsers only prevent client side read access, but do not prevent write access.
Testing Web Browsers for HttpOnly Support
The following test was performed on two browsers, Internet Explorer 7 and Opera 9.22, to demonstrate the results when the HttpOnly flag is enforced properly. As you will see, IE7 properly enforces the HttpOnly flag, whereas Opera does not properly enforce the HttpOnly flag.
Disabling HttpOnly
1) Select the option to turn HttpOnly off as shown below in figure 2.
2) After turning HttpOnly off, select the “Read Cookie” button.
- An alert dialog box will display on the screen notifying you that since HttpOnly was not enabled, the ‘unique2u’ cookie was successfully read as shown below in figure 3.
3) With HttpOnly remaining disabled, select the “Write Cookie” button.
- An alert dialog box will display on the screen notifying you that since HttpOnly was not enabled, the ‘unique2u’ cookie was successfully modified on the client side as shown below in figure 4.
- As you have seen thus far, browsing without HttpOnly on is a potential threat. Next, we will enable HttpOnly to demonstrate how this flag protects the cookie.
Enabling HttpOnly
4) Select the radio button to enable HttpOnly as shown below in figure 5.
5) After enabling HttpOnly, select the "Read Cookie" button.
- If the browser enforces the HttpOnly flag properly, an alert dialog box will display only the session ID rather than the contents of the ‘unique2u’ cookie as shown below in figure 6.
- However, if the browser does not enforce the HttpOnly flag properly, an alert dialog box will display both the ‘unique2u’ cookie and session ID as shown below in figure 7.
- Finally, we will test if the browser allows write access to the cookie with HttpOnly enabled.
6) Select the "Write Cookie" button.
- If the browser enforces the HttpOnly flag properly, client side modification will be unsuccessful in writing to the ‘unique2u’ cookie and an alert dialog box will display only containing the session ID as shown below in figure 8.
- However, if the browser does not enforce the write protection property of HttpOnly flag for the ‘unique2u’ cookie, the cookie will be successfully modified to HACKED on the client side as shown below in figure 9.
References
- CWE-1004: Sensitive Cookie Without 'HttpOnly' Flag
- Wiens, Jordan "No cookie for you!"
- Mitigating Cross-site Scripting with HTTP-Only Cookies
- Howard, Michael. Some Bad News and Some Good News
- MSDN. Setting the HttpOnly propery in .NET
- XSS: Gaining access to HttpOnly Cookie in 2012
- Setting HttpOnly in Java
<references />