This site is the archived OWASP Foundation Wiki and is no longer accepting Account Requests.
To view the new OWASP Foundation website, please visit https://owasp.org
Difference between revisions of "CRV2 FrameworkSpecIssuesASPNetStrongAssembiles"
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
At the command prompt, type the following: | At the command prompt, type the following: | ||
al sources options | al sources options | ||
| + | |||
| + | Remarks | ||
| + | All Visual Studio compilers produce assemblies. However, if you have one or more modules (metadata without a manifest), you can use Al.exe to create an assembly with the manifest in a separate file. | ||
| + | To install assemblies in the cache, remove assemblies from the cache, or list the contents of the cache, use the Global Assembly Cache Tool (Gacutil.exe). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The following command creates an executable file t2a.exe with an assembly from the t2.netmodule module. The entry point is the Main method in MyClass. | ||
| + | al t2.netmodule /target:exe /out:t2a.exe /main:MyClass.Main | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/wd40t7ad(v=vs.80).aspx | ||
| + | http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/c405shex(v=vs.110).aspx | ||
| + | http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/k5b5tt23(v=vs.80).aspx | ||
Revision as of 01:29, 1 July 2013
Strongly Named assemblies
Creating Strongly Named Assemblies provides a unique identification to an assembly. A unique digital signature is specifically created for it. By default strongly names assemblies can only access other ones. The strong name guarantee its uniqueness because it relies on unique key pairs. Furthermore, it provides a very strong integrity check.
Signing tools
In order to create a Strongly name assembly there are a set of tools and steps that you need to follow
Using Visual Studio
In order to use Visual Studio to create a Strongly Named Assembly, it is necessary to have a copy of the public/private key pair file. Its is also possible to create this pair key in Visual Studio
In Visual Studio 2005, the C#, Visual Basic, and Visual J# integrated development environments (IDEs) allow you to generate key pairs and sign assemblies without the need to create a key pair using Sn.exe(Strong Name Tool). These IDEs have a Signing tab in the Project Designer. . The use of the AssemblyKeyFileAttribute to identify key file pairs has been made obsolete in Visual Studio 2005.
The following figure ilustrates the process done by the compiler
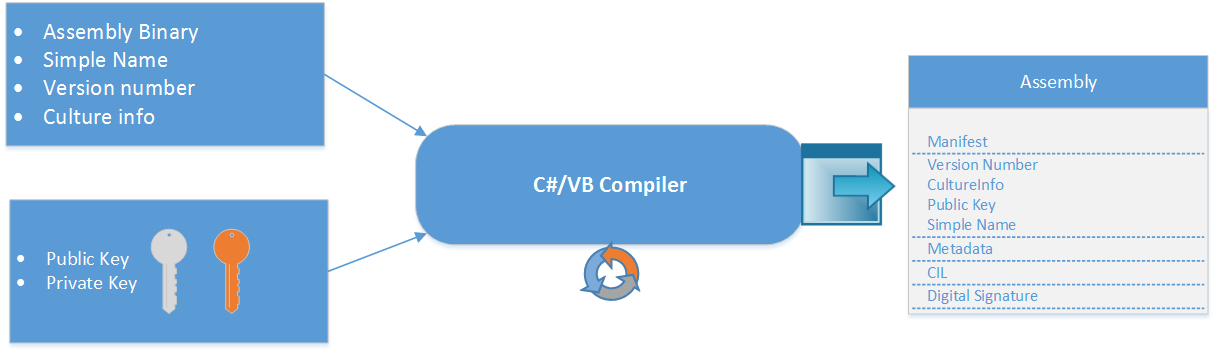
Using Strong Name tool
The Sign Tool is a command-line tool that digitally signs files, verifies signatures in files, or time stamps files. The Sign Tool is not supported on Microsoft Windows NT, Windows Me, Windows 98, or Windows 95. In case you aren't using the "Visual Studio Command Prompt" (Start >> Microsoft Visual Studio 2010 >> Visual Studio Tools >> Visual Studio Command Prompt (2010)) you can locate sn.exe at %ProgramFiles%\Microsoft SDKs\Windows\v7.0A\bin\sn.exe
The following command creates a new, random key pair and stores it in keyPair.snk.
sn -k keyPair.snk
The following command stores the key in keyPair.snk in the container MyContainer in the strong name CSP.
sn -i keyPair.snk MyContainer
The following command extracts the public key from keyPair.snk and stores it in publicKey.snk.
sn -p keyPair.snk publicKey.snk
The following command displays the public key and the token for the public key contained in publicKey.snk.
sn -tp publicKey.snk
The following command verifies the assembly MyAsm.dll.
sn -v MyAsm.dll
The following command deletes MyContainer from the default CSP.
sn -d MyContainer
Using the Assembly Linker(AI.exe)
This tool is automatically installed with Visual Studio and with the Windows SDK. To run the tool, we recommend that you use the Visual Studio Command Prompt or the Windows SDK Command Prompt (CMD Shell). These utilities enable you to run the tool easily, without navigating to the installation folder. For more information, see Visual Studio and Windows SDK Command Prompts.
If you have Visual Studio installed on your computer: On the taskbar, click Start, click All Programs, click Visual Studio, click Visual Studio Tools, and then click Visual Studio Command Prompt. -or- If you have the Windows SDK installed on your computer: On the taskbar, click Start, click All Programs, click the folder for the Windows SDK, and then click Command Prompt (or CMD Shell).
At the command prompt, type the following:
al sources options
Remarks All Visual Studio compilers produce assemblies. However, if you have one or more modules (metadata without a manifest), you can use Al.exe to create an assembly with the manifest in a separate file. To install assemblies in the cache, remove assemblies from the cache, or list the contents of the cache, use the Global Assembly Cache Tool (Gacutil.exe).
The following command creates an executable file t2a.exe with an assembly from the t2.netmodule module. The entry point is the Main method in MyClass.
al t2.netmodule /target:exe /out:t2a.exe /main:MyClass.Main
References
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/wd40t7ad(v=vs.80).aspx http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/c405shex(v=vs.110).aspx http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/k5b5tt23(v=vs.80).aspx