This site is the archived OWASP Foundation Wiki and is no longer accepting Account Requests.
To view the new OWASP Foundation website, please visit https://owasp.org
Difference between revisions of "OWASP Benchmark Project"
| Line 342: | Line 342: | ||
please let [mailto:[email protected] me] know! | please let [mailto:[email protected] me] know! | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Documentation = | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==What is in the Benchmark?== | ||
| + | The Benchmark is a Java Maven project. Its primary component is thousands of test cases (e.g., BenchmarkTest00001.java) , each of which is a single Java servlet that contains a single vulnerability (either a true positive or false positive). The vulnerabilities span about a dozen different types currently and are expected to expand significantly in the future. | ||
| + | |||
| + | An expectedresults.csv is published with each version of the Benchmark (e.g., expectedresults-1.1.csv) and it specifically lists the expected results for each test case. Here’s what the first two rows in this file looks like for version 1.1 of the Benchmark: | ||
| + | |||
| + | # test name category real vulnerability CWE Benchmark version: 1.1 2015-05-22 | ||
| + | BenchmarkTest00001 crypto TRUE 327 | ||
| + | |||
| + | This simply means that the first test case is a crypto test case (use of weak cryptographic algorithms), this is a real vulnerability (as opposed to a false positive), and this issue maps to CWE 327. It also indicates this expected results file is for Benchmark version 1.1 (produced May 22, 2015). There is a row in this file for each of the tens of thousands of test cases in the Benchmark. Each time a new version of the Benchmark is published, a new corresponding results file is generated and each test case can be completely different from one version to the next. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Benchmark also comes with a bunch of different utilities, commands, and prepackaged open source security analysis tools, all of which can be executed through Maven goals, including: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Open source vulnerability detection tools to be run against the Benchmark | ||
| + | * A scorecard generator, which computes a scorecard for each of the tools you have results files for. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==What Can You Do With the Benchmark?== | ||
| + | * Compile all the software in the Benchmark project (e.g., mvn compile) | ||
| + | * Run a vulnerability detection tool against the Benchmark test cases to generate a results file for that tool. | ||
| + | ** These prepackaged open source tools have Maven goals for running these tools on the Benchmark. The following open source tools are currently supported: | ||
| + | *** PMD | ||
| + | *** FindBugs | ||
| + | *** FindBugs with the FindSecurityBugs extension for FindBugs | ||
| + | *** SonaryQube (support coming soon) | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Generate scorecards for each of the tools you have results files for. In addition to supporting the open source tools listed above, scorecards for the following commercial tools can also be generated: | ||
| + | ** Coverity Code Advisor | ||
| + | ** HP Fortify | ||
| + | ** IBM AppScan Source | ||
| + | ** Parasoft Jtest | ||
| + | ** Veracode SAST | ||
| + | |||
| + | The OWASP Benchmark project team can quickly generate new scorecard generators for other static analysis tools. We just don’t have access to any other licenses at this time in order to run them against the Benchmark. If you have a license, and can send us a tool generated results file, please send it to us, and we’ll generate a scorecard generator for it so that tool is now formally supported by the project. | ||
= Acknowledgements = | = Acknowledgements = | ||
Revision as of 17:39, 10 July 2015
OWASP Benchmark ProjectThe OWASP Benchmark for Security Automation (OWASP Benchmark) is a test suite designed to evaluate the speed, coverage, and accuracy of automated vulnerability detection tools and services (henceforth simply referred to as 'tools'). Without the ability to measure these tools, it is difficult to understand their value or interpret vendor claims. The OWASP Benchmark contains over 20,000 test cases that are fully runnable and exploitable. You can use the OWASP Benchmark with Static Application Security Testing (SAST) tools. A future goal is to support the evaluation of Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) tools like OWASP ZAP and Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST) tools. The current version of the Benchmark is implemented in Java. Future versions may expand to include other languages. Benchmark Project PhilosophySecurity tools (SAST, DAST, and IAST) are amazing when they find a complex vulnerability in your code. But they can drive everyone crazy with complexity, false alarms, and missed vulnerabilities. Using these tools without understanding their strengths and weaknesses can lead to a dangerous false sense of security. We are on a quest to measure just how good these tools are at discovering and properly diagnosing security problems in applications. We rely on the long history of military and medical evaluation of detection technology as a foundation for our research. Therefore, the test suite tests both real and fake vulnerabilities. There are four possible test outcomes in the Benchmark:
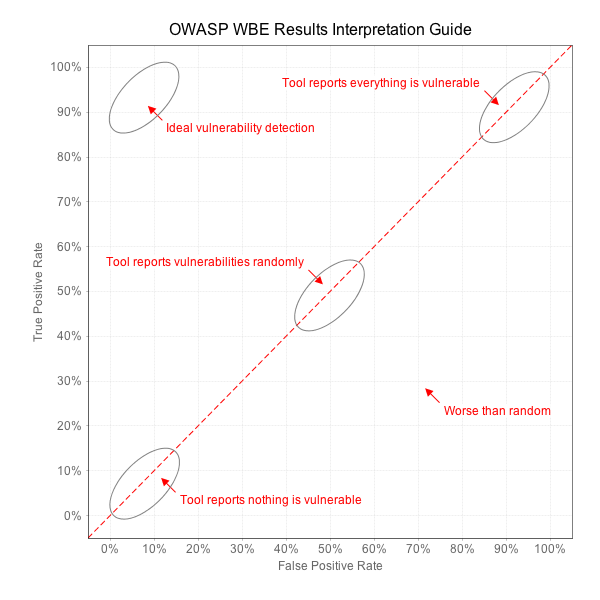
We can learn a lot about a tool from these four metrics. A tool that simply flags every line of code as vulnerable will perfectly identify all vulnerabilities in an application, but will also have 100% false positives. Similarly, a tool that reports nothing will have zero false positives, but will also identify zero real vulnerabilities. Imagine a tool that flips a coin to decide whether to report each vulnerability for every test case. The result would be 50% true positives and 50% false positives. We need a way to distinguish valuable security tools from these trivial ones. If you imagine the line that connects all these points, from 0,0 to 100,100 establishes a line that roughly translates to "random guessing." The ultimate measure of a security tool is how much better it can do than this line. The diagram below shows how we will evaluate security tools against the Benchmark. Benchmark ValidityThe Benchmark tests are not exactly like real applications. The tests are derived from coding patterns observed in real applications, but many of them are considerably simpler than real applications. Other tests may have coding patterns that don't occur frequently in real code. It's best to imagine the Benchmark as a continuum of tests from very simple all the way up to pretty difficult. Remember, we are trying to test the capabilities of the tools and make them explicit, so that *users* can make informed decisions about what tools to use, how to use them, and what results to expect. This is exactly aligned with the OWASP mission to make application security visible. Benchmark Scoring and Reporting ResultsWe encourage both vendors, open source tools, and end users to verify their application security tools against the Benchmark. We encourage everyone to contribute their results to the project. In order to ensure that the results are fair and useful, we ask that you follow a few simple rules when publishing results. We won't recognize any results that aren't easily reproducible.
Code RepoThe code for this project is hosted at the OWASP Git repository. Along with the code comes a Maven pom.xml file so you can download all the dependencies and build the entire project with ease using Maven. Using the pom, it should be easy to verify all the code compiles correctly. To download and build everything, if you already have git and maven installed, all you have to do is: $ git clone https://github.com/OWASP/benchmark $ cd benchmark $ mvn compile LicensingThe OWASP Benchmark is free to use under the GNU General Public License v2.0. Mailing ListProject LeadersProject References
Related Projects |
Quick DownloadAll test code and project files can be downloaded from OWASP GitHub. News and Events
Classifications
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Version 1.0 of the Benchmark was published on April 15, 2015 and had 20,983 test cases. On May 23, 2015, version 1.1 of the Benchmark was released. The 1.1 release improves on the previous version by making sure that there are both true positives and false positives in every vulnerability area. The test case areas and quantities for the 1.1 release are:
| Vulnerability Area | Number of Tests | CWE Number |
|---|---|---|
| Command Injection | 2708 | 78 |
| Weak Cryptography | 1440 | 327 |
| Weak Hashing | 1421 | 328 |
| LDAP Injection | 736 | 90 |
| Path Traversal | 2630 | 22 |
| Secure Cookie Flag | 416 | 614 |
| SQL Injection | 3529 | 89 |
| Trust Boundary Violation | 725 | 501 |
| Weak Randomness | 3640 | 330 |
| XPATH Injection | 347 | 643 |
| XSS (Cross-Site Scripting) | 3449 | 79 |
| Total Test Cases | 21,041 |
To download a spreadsheet that lists every test case, the vulnerability category, the CWE number, and the expected result (true finding/false positive), click here.
Every test case is:
- a servlet or JSP (currently they are all servlets, but we plan to add JSPs soon)
- either a true vulnerability or a false positive for a single issue
The benchmark is intended to help determine how well analysis tools correctly analyze a broad array of application and framework behavior, including:
- HTTP request and response problems
- Simple and complex data flow
- Simple and complex control flow
- Popular frameworks
- Inversion of control
- Reflection
- Class loading
- Annotations
- Popular UI technologies (particularly JavaScript frameworks)
Not all of these are yet tested by the Benchmark but future enhancements intend to provide more coverage of these issues.
Additional future enhancements could cover:
- All vulnerability types in the OWASP Top 10
- Does the tool find flaws in libraries?
- Does the tool find flaws spanning custom code and libraries?
- Does tool handle web services? REST, XML, GWT, etc…
- Does tool work with different app servers? Java platforms?
Example Test Case
Each test case is a simple Java EE servlet. BenchmarkTest00001 in version 1.0 of the Benchmark was an LDAP Injection test with the following metadata in the accompanying BenchmarkTest00001.xml file:
<test-metadata> <category>ldapi</category> <test-number>00001</test-number> <vulnerability>true</vulnerability> <cwe>90</cwe> </test-metadata>
BenchmarkTest00001.java in the OWASP Benchmark 1.0 simply reads in all the cookie values, looks for a cookie named "foo", and uses the value of this cookie when performing an LDAP query. Here's the code for BenchmarkTest00001.java:
package org.owasp.benchmark.testcode;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet("/BenchmarkTest00001")
public class BenchmarkTest00001 extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
@Override
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// some code
javax.servlet.http.Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
String param = null;
boolean foundit = false;
if (cookies != null) {
for (javax.servlet.http.Cookie cookie : cookies) {
if (cookie.getName().equals("foo")) {
param = cookie.getValue();
foundit = true;
}
}
if (!foundit) {
// no cookie found in collection
param = "";
}
} else {
// no cookies
param = "";
}
try {
javax.naming.directory.DirContext dc = org.owasp.benchmark.helpers.Utils.getDirContext();
Object[] filterArgs = {"a","b"};
dc.search("name", param, filterArgs, new javax.naming.directory.SearchControls());
} catch (javax.naming.NamingException e) {
throw new ServletException(e);
}
}
}
At this time, our vulnerability detection tool results aren't ready for publication. The Benchmark can generate results for the following tools:
Free Static Analysis Tools:
- PMD (which really has no security rules)
- Findbugs
- FindBugs with the FindSecurityBugs plugin
- SonarQube
Commercial Static Analysis Tools:
- Coverity Code Advisor (On-Demand and stand-alone versions)
- HP Fortify (On-Demand and stand-alone versions)
- IBM AppScan Source
- Parasoft Jtest
- Veracode SAST
The free tools come bundled with the Benchmark so you can run them yourselves. If you have a license for any commercial SAST tool, you can also run them against the Benchmark. Just put your results files in the /results folder of the project, and then run the BenchmarkScore script for your platform (.sh / .bat) and it will generate a scorecard in the /scorecard directory for all the tools you have results for that are currently supported.
If you would like to contribute to this project by running a tool against the Benchmark and sending us the tool's results file, please contact the project lead.
The project has automated test harnesses for these vulnerability detection tools, so we can repeatably run the tools against each version of the Benchmark and automatically produce scorecards in our desired format.
We want to test as many tools as possible against the Benchmark. If you are:
- A tool vendor and want to participate in the project
- Someone who wants to help score a free tool agains the project
- Someone who has a license to a commercial tool and the terms of the license allow you to publish tool results, and you want to participate
please let me know!
What is in the Benchmark?
The Benchmark is a Java Maven project. Its primary component is thousands of test cases (e.g., BenchmarkTest00001.java) , each of which is a single Java servlet that contains a single vulnerability (either a true positive or false positive). The vulnerabilities span about a dozen different types currently and are expected to expand significantly in the future.
An expectedresults.csv is published with each version of the Benchmark (e.g., expectedresults-1.1.csv) and it specifically lists the expected results for each test case. Here’s what the first two rows in this file looks like for version 1.1 of the Benchmark:
# test name category real vulnerability CWE Benchmark version: 1.1 2015-05-22 BenchmarkTest00001 crypto TRUE 327
This simply means that the first test case is a crypto test case (use of weak cryptographic algorithms), this is a real vulnerability (as opposed to a false positive), and this issue maps to CWE 327. It also indicates this expected results file is for Benchmark version 1.1 (produced May 22, 2015). There is a row in this file for each of the tens of thousands of test cases in the Benchmark. Each time a new version of the Benchmark is published, a new corresponding results file is generated and each test case can be completely different from one version to the next.
The Benchmark also comes with a bunch of different utilities, commands, and prepackaged open source security analysis tools, all of which can be executed through Maven goals, including:
- Open source vulnerability detection tools to be run against the Benchmark
- A scorecard generator, which computes a scorecard for each of the tools you have results files for.
What Can You Do With the Benchmark?
- Compile all the software in the Benchmark project (e.g., mvn compile)
- Run a vulnerability detection tool against the Benchmark test cases to generate a results file for that tool.
- These prepackaged open source tools have Maven goals for running these tools on the Benchmark. The following open source tools are currently supported:
- PMD
- FindBugs
- FindBugs with the FindSecurityBugs extension for FindBugs
- SonaryQube (support coming soon)
- These prepackaged open source tools have Maven goals for running these tools on the Benchmark. The following open source tools are currently supported:
- Generate scorecards for each of the tools you have results files for. In addition to supporting the open source tools listed above, scorecards for the following commercial tools can also be generated:
- Coverity Code Advisor
- HP Fortify
- IBM AppScan Source
- Parasoft Jtest
- Veracode SAST
The OWASP Benchmark project team can quickly generate new scorecard generators for other static analysis tools. We just don’t have access to any other licenses at this time in order to run them against the Benchmark. If you have a license, and can send us a tool generated results file, please send it to us, and we’ll generate a scorecard generator for it so that tool is now formally supported by the project.
The following people have contributed to this project and their contributions are much appreciated!
- Juan Gama - Development of initial release and continued support
- Ken Prole - Assistance with automated scorecard development using CodeDx
- Nick Sanidas - Development of initial release
We are looking for volunteers. Please contact Dave Wichers if you are interested in contributing new test cases, tool results run against the benchmark, or anything else.