This site is the archived OWASP Foundation Wiki and is no longer accepting Account Requests.
To view the new OWASP Foundation website, please visit https://owasp.org
Difference between revisions of "Conduct search engine discovery/reconnaissance for information leakage (OTG-INFO-001)"
m (moved Testing: Search engine discovery/reconnaissance (OWASP-IG-002) to Testing: Conduct search engine discovery/reconnaissance for information leakage (OTG-INFO-001): Align with common numbering effort and clarify purpose of test case) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template:OWASP Testing Guide v4}} | {{Template:OWASP Testing Guide v4}} | ||
| − | == | + | == Summary == |
There are direct and indirect elements to Search engine discovery and reconnaissance. Direct methods relate to searching the Google Index and remove the associated web content from the Google Cache. Indirect methods relate to gleaning sensitive design and configuration information by searching forums, newsgroups and tendering websites. | There are direct and indirect elements to Search engine discovery and reconnaissance. Direct methods relate to searching the Google Index and remove the associated web content from the Google Cache. Indirect methods relate to gleaning sensitive design and configuration information by searching forums, newsgroups and tendering websites. | ||
| − | |||
Once the GoogleBot has completed crawling, it commences indexing the web page based on tags and associated attributes, such as <TITLE>, in order to return the relevant search results. [1] | Once the GoogleBot has completed crawling, it commences indexing the web page based on tags and associated attributes, such as <TITLE>, in order to return the relevant search results. [1] | ||
| Line 11: | Line 10: | ||
Therefore, it must be removed from the Google Cache. | Therefore, it must be removed from the Google Cache. | ||
| − | == Black Box Testing== | + | == Test Objectives == |
| + | |||
| + | To understand what sensitive design and configuration information is exposed of the application/system/organisation both directly (on the organisation's website) or indirectly (on a third party website) | ||
| + | |||
| + | == How to Test == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Black Box Testing === | ||
Using the advanced "site:" search operator, it is possible to restrict Search Results to a specific domain [2]. | Using the advanced "site:" search operator, it is possible to restrict Search Results to a specific domain [2]. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 23: | ||
The Google SOAP Search API supports the doGetCachedPage and the associated doGetCachedPageResponse SOAP Messages [3] to assist with retrieving cached pages. An implementation of this is under development by the [[::Category:OWASP_Google_Hacking_Project |OWASP "Google Hacking" Project]]. | The Google SOAP Search API supports the doGetCachedPage and the associated doGetCachedPageResponse SOAP Messages [3] to assist with retrieving cached pages. An implementation of this is under development by the [[::Category:OWASP_Google_Hacking_Project |OWASP "Google Hacking" Project]]. | ||
| − | == Example == | + | ==== Example ==== |
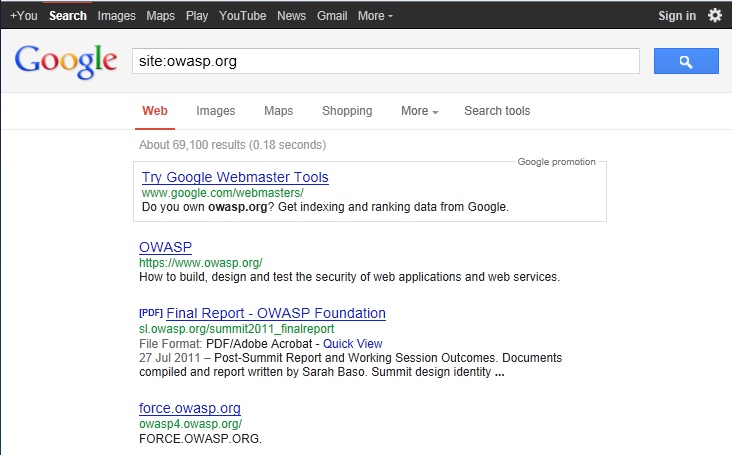
To find the web content of owasp.org indexed by Google Cache the following Google Search Query is issued: | To find the web content of owasp.org indexed by Google Cache the following Google Search Query is issued: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 31: | Line 36: | ||
[[Image:Google_cache_Operator_Search_Results_Example_20121219.jpg]] | [[Image:Google_cache_Operator_Search_Results_Example_20121219.jpg]] | ||
| + | === Gray Box testing and example === | ||
| + | Grey Box testing is the same as Black Box testing above. | ||
| + | == Tools == | ||
| + | [1] FoundStone SiteDigger - http://www.mcafee.com/uk/downloads/free-tools/sitedigger.aspx <br> | ||
| + | [2] Google Hacker - http://yehg.net/lab/pr0js/files.php/googlehacker.zip<br> | ||
| + | [3] Stach & Liu's Google Hacking Diggity Project - http://www.stachliu.com/resources/tools/google-hacking-diggity-project/ <br> | ||
| − | == | + | == Vulnerability References == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
'''Web'''<br> | '''Web'''<br> | ||
[1] "Google Basics: Learn how Google Discovers, Crawls, and Serves Web Pages" - http://www.google.com/support/webmasters/bin/answer.py?answer=70897 <br> | [1] "Google Basics: Learn how Google Discovers, Crawls, and Serves Web Pages" - http://www.google.com/support/webmasters/bin/answer.py?answer=70897 <br> | ||
[2] "Operators and More Search Help" - http://support.google.com/websearch/bin/answer.py?hl=en&answer=136861 <br> | [2] "Operators and More Search Help" - http://support.google.com/websearch/bin/answer.py?hl=en&answer=136861 <br> | ||
| − | + | == Remediation == | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 11:52, 21 July 2013
This article is part of the new OWASP Testing Guide v4.
Back to the OWASP Testing Guide v4 ToC: https://www.owasp.org/index.php/OWASP_Testing_Guide_v4_Table_of_Contents Back to the OWASP Testing Guide Project: https://www.owasp.org/index.php/OWASP_Testing_Project
Summary
There are direct and indirect elements to Search engine discovery and reconnaissance. Direct methods relate to searching the Google Index and remove the associated web content from the Google Cache. Indirect methods relate to gleaning sensitive design and configuration information by searching forums, newsgroups and tendering websites.
Once the GoogleBot has completed crawling, it commences indexing the web page based on tags and associated attributes, such as <TITLE>, in order to return the relevant search results. [1]
If the robots.txt file is not updated during the lifetime of the web site, then it is possible for web content not intended to be included in Google's Search Results to be returned.
Therefore, it must be removed from the Google Cache.
Test Objectives
To understand what sensitive design and configuration information is exposed of the application/system/organisation both directly (on the organisation's website) or indirectly (on a third party website)
How to Test
Black Box Testing
Using the advanced "site:" search operator, it is possible to restrict Search Results to a specific domain [2].
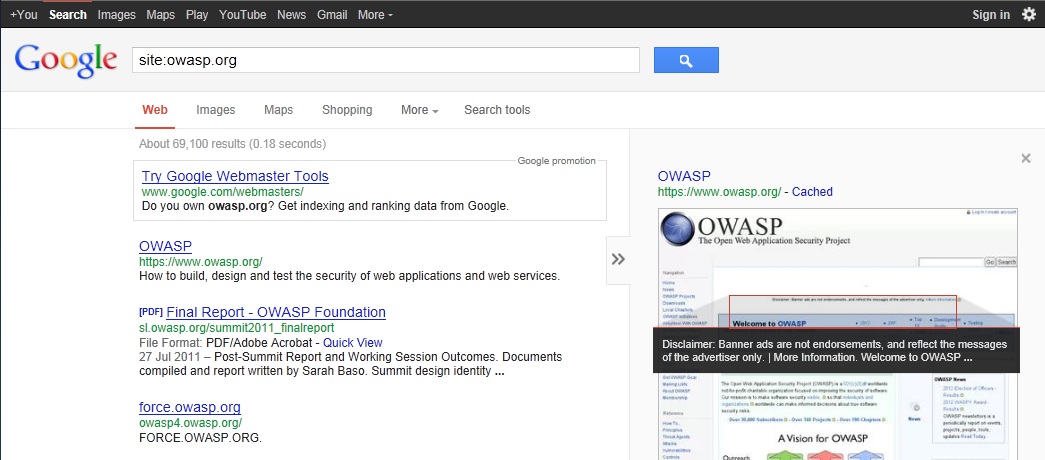
Google provides the Advanced "cache:" search operator [2], but this is the equivalent to clicking the "Cached" next to each Google Search Result. Hence, the use of the Advanced "site:" Search Operator and then clicking "Cached" is preferred.
The Google SOAP Search API supports the doGetCachedPage and the associated doGetCachedPageResponse SOAP Messages [3] to assist with retrieving cached pages. An implementation of this is under development by the OWASP "Google Hacking" Project.
Example
To find the web content of owasp.org indexed by Google Cache the following Google Search Query is issued:
site:owasp.org
To display the index.html of owasp.org as cached by Google the following Google Search Query is issued:
cache:owasp.org
Gray Box testing and example
Grey Box testing is the same as Black Box testing above.
Tools
[1] FoundStone SiteDigger - http://www.mcafee.com/uk/downloads/free-tools/sitedigger.aspx
[2] Google Hacker - http://yehg.net/lab/pr0js/files.php/googlehacker.zip
[3] Stach & Liu's Google Hacking Diggity Project - http://www.stachliu.com/resources/tools/google-hacking-diggity-project/
Vulnerability References
Web
[1] "Google Basics: Learn how Google Discovers, Crawls, and Serves Web Pages" - http://www.google.com/support/webmasters/bin/answer.py?answer=70897
[2] "Operators and More Search Help" - http://support.google.com/websearch/bin/answer.py?hl=en&answer=136861