This site is the archived OWASP Foundation Wiki and is no longer accepting Account Requests.
To view the new OWASP Foundation website, please visit https://owasp.org
Codereview-Authorization
Introduction
Authorisation is key in multiuser environments where user data should be segregated. different clients/users should not see other clients data (Horizontal authorisation). Authorisation can also be used to restrict functionality to a subset of users. "super users" would have extra admin functionality a "regular user" would not have access to (Vertical authorisation).
Authorisation is a very bespoke area in application development. It can be implemented via a lookup table in a users session which is loaded upon sucessful authentication. It coule be a realtime interrogation of a backend LDAP or database system upon each request.
Good Example
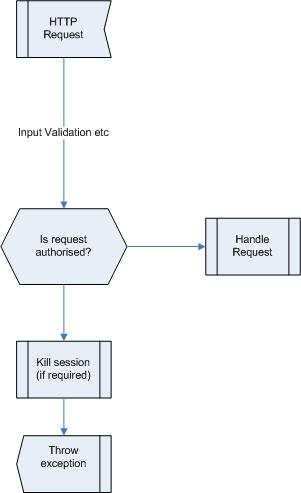
Check authorisation upon every user request.
String action = request.getParameter("action")
if (action == "doStuff"){
boolean permit = session.authTable.isAuthorised(action); // check table if authoirsed to do action
}
if (permit){
doStuff();
}else{
throw new (InvalidRequestException("Unauthorised request"); // inform user of no authorisation
session.invalidate(); // Kill session
}
Authorisation being performed upon all requests from external entities
Bad Example
Building the GUI based on the users authorisation. "If he cant see the control we wont be able to use it"
- Common enough error. If a user has the URL the functionality can still be called. This is due to no authorisation check being perfromed upon every HTTP request.
Related Vulnerabilities
Operating system injection can be used to totally ignore authorisation constraints.
SQL injection can be used to circumvent authorisation
The root of all evil
Insecure class files, folders in deployment may be used to attack an application outside the actual application itself.